
نمونه سوالات آزمون CCNA Routing & Switching 200-120
Topic 4, IP Routing Technologies
QUESTION NO: 161
Refer to the exhibit:
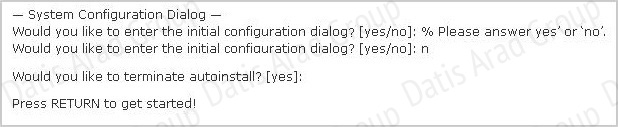
A network administrator configures a new router and enters the copy startup-config running-config command on the router. The network administrator powers down the router and sets it up at a remote location. When the router starts, it enters the system configuration dialog as shown. What is the cause of the problem?
A. The network administrator failed to save the configuration.
B. The configuration register is set to 0x2100.
C. The boot system flash command is missing from the configuration.
D. The configuration register is set to 0x2102.
E. The router is configured with the boot system startup command.
Answer: A
Explanation:
The “System Configuration Dialog” appears only when no startup configuration file is found. The network administrator has made a mistake because the command “copy startup-config runningconfig” will copy the startup config (which is empty) over the running config (which is configured by the administrator). So everything configured was deleted.
Note: We can tell the router to ignore the start-up configuration on the next reload by setting the register to 0×2142. This will make the “System Configuration Dialog” appear at the next reload.
QUESTION NO: 162
What is the default administrative distance of OSPF?
A. 90
B. 100
C. 110
D. 120
Answer: C
Explanation:
Administrative distance is the feature that routers use in order to select the best path when there are two or more different routes to the same destination from two different routing protocols. Administrative distance defines the reliability of a routing protocol. Each routing protocol is prioritized in order of most to least reliable (believable) with the help of an administrative distance value.
QUESTION NO: 163
Which characteristics are representative of a link-state routing protocol? (Choose three.)
A. provides common view of entire topology
B. exchanges routing tables with neighbors
C. calculates shortest path
D. utilizes event-triggered updates
E. utilizes frequent periodic updates
Answer: A,C,D
Explanation:
Each of routers running link-state routing protocol learns paths to all the destinations in its “area”
so we can say although it is a bit unclear.
Link-state routing protocols generate routing updates only (not the whole routing table) when a change occurs in the network topology so Link-state routing protocol like OSPF uses Dijkstra algorithm to calculate the shortest path.
Unlike Distance vector routing protocol (which utilizes frequent periodic updates), link-state routing protocol utilizes event-triggered updates (only sends update when a change occurs)
QUESTION NO: 164
Refer to the exhibit.
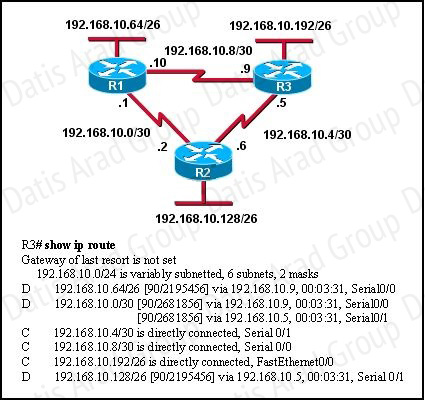
Based on the exhibited routing table, how will packets from a host within the 192.168.10.192/26 LAN be forwarded to 192.168.10.1?
A. The router will forward packets from R3 to R2 to R1.
B. The router will forward packets from R3 to R1 to R2.
C. The router will forward packets from R3 to R2 to R1 AND from R3 to R1.
D. The router will forward packets from R3 to R1.
Answer: C
Explanation:
From the routing table we learn that network 192.168.10.0/30 is learned via 2 equal-cost paths (192.168.10.9 &192.168.10.5) -> traffic to this network will be load-balancing.
QUESTION NO: 165
Refer to the exhibit.
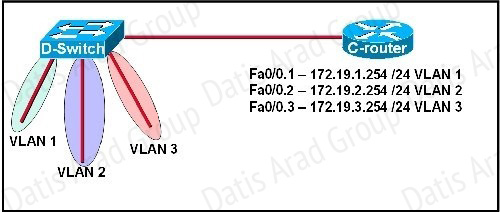
C-router is to be used as a "router-on-a-stick" to route between the VLANs. All the interfaces have been properly configured and IP routing is operational. The hosts in the VLANs have been configured with the appropriate default gateway. What is true about this configuration?
A. These commands need to be added to the configuration:
C-router(config)# router eigrp 123
C-router(config-router)# network 172.19.0.0
B. These commands need to be added to the configuration:
C-router(config)# router ospf 1
C-router(config-router)# network 172.19.0.0 0.0.3.255 area 0
C. These commands need to be added to the configuration:
C-router(config)# router rip
C-router(config-router)# network 172.19.0.0
D. No further routing configuration is required.
Answer: D
Explanation:
Since all the same router (C-router) is the default gateway for all three VLANs, all traffic destined to a different VLA will be sent to the C-router. The C-router will have knowledge of all three networks since they will appear as directly connected in the routing table. Since the C-router already knows how to get to all three networks, no routing protocols need to be configured.
QUESTION NO: 166
Refer to the exhibit.

Why is flash memory erased prior to upgrading the IOS image from the TFTP server?
A. The router cannot verify that the Cisco IOS image currently in flash is valid.
B. Flash memory on Cisco routers can contain only a single IOS image.
C. Erasing current flash content is requested during the copy dialog.
D. In order for the router to use the new image as the default, it must be the only IOS image in flash.
Answer: C
Explanation:
During the copy process, the router asked “Erasing flash before copying? [confirm]” and the administrator confirmed (by pressing Enter) so the flash was deleted. Note: In this case, the flash has enough space to copy a new IOS without deleting the current one. The current IOS is deleted just because the administrator wants to do so. If the flash does not have enough space you will see an error message like this:
%Error copying tftp://192.168.2.167/ c1600-k8sy-mz.l23-16a.bin (Not enough space on device)
QUESTION NO: 167
Which command would you configure globally on a Cisco router that would allow you to view directly connected Cisco devices?
A. enable cdp
B. cdp enable
C. cdp run
D. run cdp
Answer: C
Explanation:
CDP is enabled on Cisco routers by default. If you prefer not to use the CDP capability, disable it with the no cdp run command. In order to reenable CDP, use the cdp run command in global configuration mode. The “cdp enable” command is an interface command, not global.
QUESTION NO: 168
Refer to the exhibit.
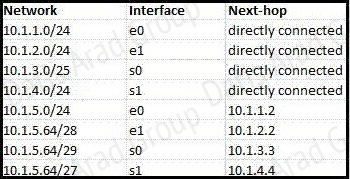
According to the routing table, where will the router send a packet destined for 10.1.5.65?
A. 10.1.1.2
B. 10.1.2.2
C. 10.1.3.3
D. 10.1.4.4
Answer: C
Explanation:
The destination IP address 10.1.5.65 belongs to 10.1.5.64/28, 10.1.5.64/29 & 10.1.5.64/27 subnets but the “longest prefix match” algorithm will choose the most specific subnet mask -> the prefix “/29 will be chosen to route the packet. Therefore the next-hop should be 10.1.3.3.
QUESTION NO: 169
Refer to the exhibit.
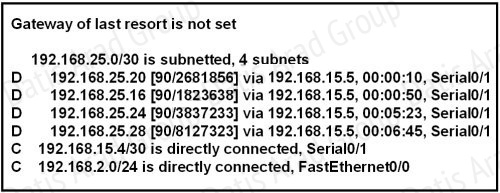
Which address and mask combination represents a summary of the routes learned by EIGRP?
A. 192.168.25.0 255.255.255.240
B. 192.168.25.0 255.255.255.252
C. 192.168.25.16 255.255.255.240
D. 192.168.25.16 255.255.255.252
E. 192.168.25.28 255.255.255.240
F. 192.168.25.28 255.255.255.252
Answer: C
Explanation:
The binary version of 20 is 10100.
The binary version of 16 is 10000.
The binary version of 24 is 11000.
The binary version of 28 is 11100.
The subnet mask is /28. The mask is 255.255.255.240.
Note:
From the output above, EIGRP learned 4 routes and we need to find out the summary of them:
+ 192.168.25.16
+ 192.168.25.20
+ 192.168.25.24
+ 192.168.25.28
The increment should be 28 – 16 = 12 but 12 is not an exponentiation of 2 so we must choose 16 (24). Therefore the subnet mask is /28 (=1111 1111.1111 1111.1111 1111.11110000) = 255.255.255.240
So the best answer should be 192.168.25.16 255.255.255.240
QUESTION NO: 170
Refer to the exhibit.
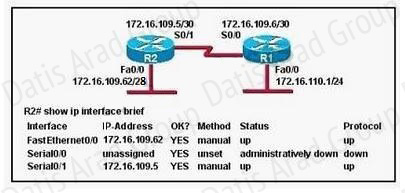
Assuming that the entire network topology is shown, what is the operational status of the interfaces of R2 as indicated by the command output shown?
A. One interface has a problem.
B. Two interfaces have problems.
C. The interfaces are functioning correctly.
D. The operational status of the interfaces cannot be determined from the output shown.
Answer: C
Explanation:
The output shown shows normal operational status of the router’s interfaces. Serial0/0 is down because it has been disabled using the “shutdown” command.
QUESTION NO: 171
Which two locations can be configured as a source for the IOS image in the boot system
command? (Choose two.)
A. RAM
B. NVRAM
C. flash memory
D. HTTP server
E. TFTP server
F. Telnet server
Answer: C,E
Explanation:
The following locations can be configured as a source for the IOS image:
1. + Flash (the default location)
2. + TFTP server
3. + ROM (used if no other source is found)
4. (Please read the explanation of Question 4 for more information)
QUESTION NO: 172
Refer to the exhibit.
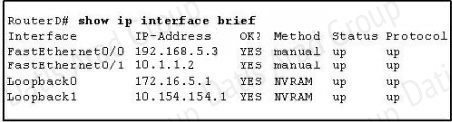
Given the output for this command, if the router ID has not been manually set, what router ID will OSPF use for this router?
A. 10.1.1.2
B. 10.154.154.1
C. 172.16.5.1
D. 192.168.5.3
Answer: C
Explanation:
The highest IP address of all loopback interfaces will be chosen -> Loopback 0 will be chosen as the router ID.
QUESTION NO: 173
Refer to the exhibit.
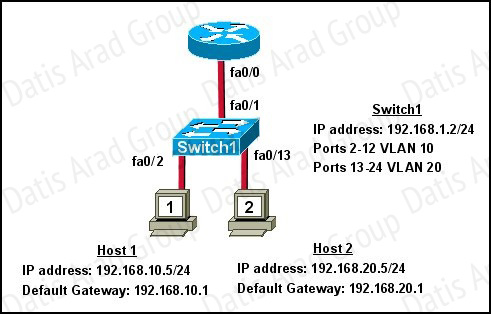
What commands must be configured on the 2950 switch and the router to allow communication between host 1 and host 2? (Choose two.)
A. Router(config)# interface fastethernet 0/0
Router(config-if)# ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0
Router(config-if)# no shut down
B. Router(config)# interface fastethernet 0/0
Router(config-if)# no shut down
Router(config)# interface fastethernet 0/0.1
Router(config-subif)# encapsulation dot1q 10
Router(config-subif)# ip address 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.0
Router(config)# interface fastethernet 0/0.2
Router(config-subif)# encapsulation dot1q 20
Router(config-subif)# ip address 192.168.20.1 255.255.255.0
C. Router(config)# router eigrp 100
Router(config-router)# network 192.168.10.0
Router(config-router)# network 192.168.20.0
D. Switch1(config)# vlan database
Switch1(config-vlan)# vtp domain XYZ
Switch1(config-vlan)# vtp server
E. Switch1(config)# interface fastethernet 0/1
Switch1(config-if)# switchport mode trunk
F. Switch1(config)# interface vlan 1
Switch1(config-if)# ip default-gateway 192.168.1.1
Answer: B,E
Explanation:
The router will need to use subinterfaces, where each subinterface is assigned a VLAN and IP address for each VLAN. On the switch, the connection to the router need to be configured as a trunk using the switchport mode trunk command and it will need a default gateway for VLAN 1.
QUESTION NO: 174
Which two statements describe the process identifier that is used in the command to configure OSPF on a router? (Choose two.)
Router(config)# router ospf 1
A. All OSPF routers in an area must have the same process ID.
B. Only one process number can be used on the same router.
C. Different process identifiers can be used to run multiple OSPF processes
D. The process number can be any number from 1 to 65,535.
E. Hello packets are sent to each neighbor to determine the processor identifier.
Answer: C,D
Explanation:
Multiple OSPF processes can be configured on a router using multiple process ID’s. The valid process ID’s are shown below:
Edge-B(config)#router ospf ?
<1-65535> Process ID
QUESTION NO: 175
Refer to the exhibit.
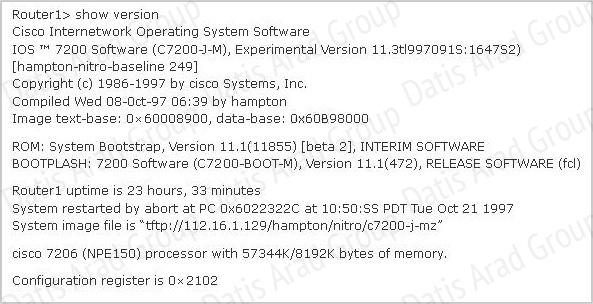
For what two reasons has the router loaded its IOS image from the location that is shown? (Choose two.)
A. Router1 has specific boot system commands that instruct it to load IOS from a TFTP server.
B. Router1 is acting as a TFTP server for other routers.
C. Router1 cannot locate a valid IOS image in flash memory.
D. Router1 defaulted to ROMMON mode and loaded the IOS image from a TFTP server.
E. Cisco routers will first attempt to load an image from TFTP for management purposes.
Answer: A,C
Explanation:
The loading sequence of CISCO IOS is as follows:
Booting up the router and locating the Cisco IOS
1. POST (power on self test)
2. Bootstrap code executed
3. Check Configuration Register value (NVRAM) which can be modified using the config-register command
0 = ROM Monitor mode
1 = ROM IOS
2 - 15 = startup-config in NVRAM
4. Startup-config filE. Check for boot system commands (NVRAM)
If boot system commands in startup-config
a. Run boot system commands in order they appear in startup-config to locate the IOS
b. [If boot system commands fail, use default fallback sequence to locate the IOS (Flash, TFTP, ROM)?]
If no boot system commands in startup-config use the default fallback sequence in locating the IOS:
a. Flash (sequential)
b. TFTP server (netboot)
c. ROM (partial IOS) or keep retrying TFTP depending upon router model
5. If IOS is loaded, but there is no startup-config file, the router will use the default fallback sequence for locating the IOS and then it will enter setup mode or the setup dialogue.
QUESTION NO: 176
Refer to the exhibit.
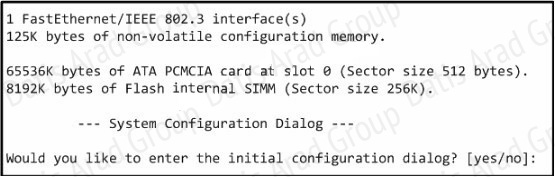
What can be determined about the router from the console output?
A. No configuration file was found in NVRAM.
B. No configuration file was found in flash.
C. No configuration file was found in the PCMCIA card.
D. Configuration file is normal and will load in 15 seconds.
Answer: A
Explanation:
When no startup configuration file is found in NVRAM, the System Configuration Dialog will appear to ask if we want to enter the initial configuration dialog or not.
QUESTION NO: 177
Which three elements must be used when you configure a router interface for VLAN trunking? (Choose three.)
A. one physical interface for each subinterface
B. one IP network or subnetwork for each subinterface
C. a management domain for each subinterface
D. subinterface encapsulation identifiers that match VLAN tags
E. one subinterface per VLAN
F. subinterface numbering that matches VLAN tags
Answer: B,D,E
QUESTION NO: 178
Which commands are required to properly configure a router to run OSPF and to add network 192.168.16.0/24 to OSPF area 0? (Choose two.)
A. Router(config)# router ospf 0
B. Router(config)# router ospf 1
C. Router(config)# router ospf area 0
D. Router(config-router)# network 192.168.16.0 0.0.0.255 0
E. Router(config-router)# network 192.168.16.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
F. Router(config-router)# network 192.168.16.0 255.255.255.0 area 0
Answer: B,E
Explanation:
In the router ospf command, the ranges from 1 to 65535 so o is an invalid number -> but To configure OSPF, we need a wildcard in the “network” statement, not a subnet mask. We also need to assgin an area to this process.
QUESTION NO: 179
A router receives information about network 192.168.10.0/24 from multiple sources. What will the router consider the most reliable information about the path to that network?
A. a directly connected interface with an address of 192.168.10.254/24
B. a static route to network 192.168.10.0/24
C. a RIP update for network 192.168.10.0/24
D. an OSPF update for network 192.168.0.0/16
E. a default route with a next hop address of 192.168.10.1
F. a static route to network 192.168.10.0/24 with a local serial interface configured as the next hop
Answer: A
Explanation:
When there is more than one way to reach a destination, it will choose the best one based on a couple of things. First, it will choose the route that has the longest match; meaning the most specific route. So, in this case the /24 routes will be chosen over the /16 routes. Next, from all the /24 routes it will choose the one with the lowest administrative distance. Directly connected routes have an AD of 1 so this will be the route chosen.
QUESTION NO: 180
What is the default maximum number of equal-cost paths that can be placed into the routing table of a Cisco OSPF router?
A. 2
B. 8
C. 16
D. unlimited
Answer: B
Explanation:
maximum-paths (OSPF)
To control the maximum number of parallel routes that Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) can support, use the maximum-paths command.