
نمونه سوالات آزمون CCNA Routing & Switching 200-120
Topic 4, IP Routing Technologies
QUESTION NO: 181
Which command shows your active Telnet connections?
A. show cdp neigbors
B. show session
C. show users
D. show vty logins
Answer: B
Explanation:
The “show users” shows telnet/ssh connections to your router while “show sessions” shows telnet/ssh connections from your router (to other devices). The question asks about “your active Telnet connections”, meaning connections from your router so the answer should be A.
QUESTION NO: 182
Which type of EIGRP route entry describes a feasible successor?
A. a backup route, stored in the routing table
B. a primary route, stored in the routing table
C. a backup route, stored in the topology table
D. a primary route, stored in the topology table
Answer: C
Explanation:
EIGRP uses the Neighbor Table to list adjacent routers. The Topology Table list all the learned routers to destination whilst the Routing Table contains the best route to a destination, which is known as the Successor. The Feasible Successor is a backup route to a destination which is kept in the Topology Table.
QUESTION NO: 183
The network administrator cannot connect to Switch1 over a Telnet session, although the hosts attached to Switch1 can ping the interface Fa0/0 of the router.
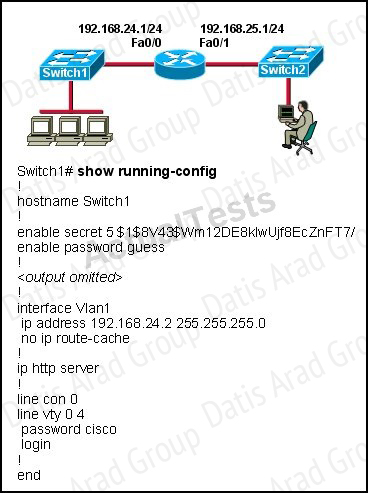
Given the information in the graphic and assuming that the router and Switch2 are configured properly, which of the following commands should be issued on Switch1 to correct this problem?
A. Switch1(config)# line con0
Switch1(config-line)# password cisco
Switch1(config-line)#login
B. Switch1(config)# interface fa0/1
Switch1(config-if)# ip address 192.168.24.3 255.255.255.0
C. Switch1(config)# ip default-gateway 192.168.24.1
D. Switch1(config)# interface fa0/1
Switch1(config-if)# duplex full
Switch1(config-if)# speed 100
E. Switch1(config)# interface fa0/1
Switch1(config-if)# switchport mode trunk
Answer: C
Explanation:
Since we know hosts can reach the router through the switch, we know that connectivity, duplex. Speed, etc. are good. However, for the switch itself to reach networks outside the local one, the ip default-gateway command must be used.
QUESTION NO: 184
Refer to the exhibit.

Which of these statements correctly describes the state of the switch once the boot process has been completed?
A. As FastEthernet0/12 will be the last to come up, it will be blocked by STP.
B. Remote access management of this switch will not be possible without configuration change.
C. More VLANs will need to be created for this switch.
D. The switch will need a different IOS code in order to support VLANs and STP.
Answer: B
Explanation:
Notice the line, which says “Interface VLAN1, changed state to administratively down”. This shows that VLAN1 is shut down. Hence remote management of this switch is not possible unless VLAN1 is brought back up. Since VLAN1 is the only interface shown in the output, you have to assume that no other VLAN interface has been configured with an IP Address.
QUESTION NO: 185
Two routers named Atlanta and Brevard are connected via their serial interfaces as illustrated, but they are unable to communicate. The Atlanta router is known to have the correct configuration.
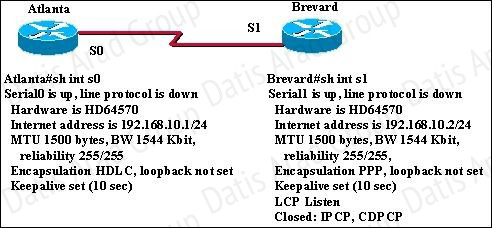
Given the partial configurations, identify the fault on the Brevard router that is causing the lack of connectivity.
A. incompatible IP address
B. insufficient bandwidth
C. incorrect subnet mask
D. incompatible encapsulation
E. link reliability too low
F. IPCP closed
Answer: D
Explanation:
Because Interface Serial 0 of Atlanta Router has 192.168.10.1 And Interface Serial 1 of Router Brevard has 192.168.11.2. These are from different network.
QUESTION NO: 186
Users on the 172.17.22.0 network cannot reach the server located on the 172.31.5.0 network. The network administrator connected to router Coffee via the console port, issued the show ip route command, and was able to ping the server.
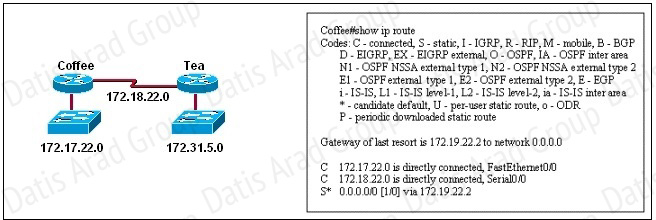
Based on the output of the show ip route command and the topology shown in the graphic, what is the cause of the failure?
A. The network has not fully converged.
B. IP routing is not enabled.
C. A static route is configured incorrectly.
D. The FastEthernet interface on Coffee is disabled.
E. The neighbor relationship table is not correctly updated.
F. The routing table on Coffee has not updated .
Answer: C
Explanation:
The default route or the static route was configured with incorrect next-hop ip address 172.19.22.2 The correct ip address will be 172.18.22.2 to reach server located on 172.31.5.0 network. Ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 172.18.22.2.
QUESTION NO: 187
A network administrator is trying to add a new router into an established OSPF network. The networks attached to the new router do not appear in the routing tables of the other OSPF routers. Given the information in the partial configuration shown below, what configuration error is causing this problem?
Router(config)# router ospf 1
Router(config-router)# network 10.0.0.0 255.0.0.0 area 0
A. The process id is configured improperly.
B. The OSPF area is configured improperly.
C. The network wildcard mask is configured improperly.
D. The network number is configured improperly.
E. The AS is configured improperly.
F. The network subnet mask is configured improperly.
Answer: C
Explanation:
When configuring OSPF, the mask used for the network statement is a wildcard mask similar to an access list. In this specific example, the correct syntax would have been “network 10.0.0.0 0.0.0.255 area 0.”
Topic 5, IP Services
QUESTION NO: 188
Which statement is correct regarding the operation of DHCP?
A. A DHCP client uses a ping to detect address conflicts.
B. A DHCP server uses a gratuitous ARP to detect DHCP clients.
C. A DHCP client uses a gratuitous ARP to detect a DHCP server.
D. If an address conflict is de0tected, the address is removed from the pool and an administrator must resolve the conflict.
E. If an address conflict is detected, the address is removed from the pool for an amount of time configurable by the administrator.
F. If an address conflict is detected, the address is removed from the pool and will not be reused until the server is rebooted.
Answer: D
Explanation:
An address conflict occurs when two hosts use the same IP address. During address assignment, DHCP checks for conflicts using ping and gratuitous ARP. If a conflict is detected, the address is removed from the pool. The address will not be assigned until the administrator resolves the conflict.
QUESTION NO: 189
Refer to the exhibit.
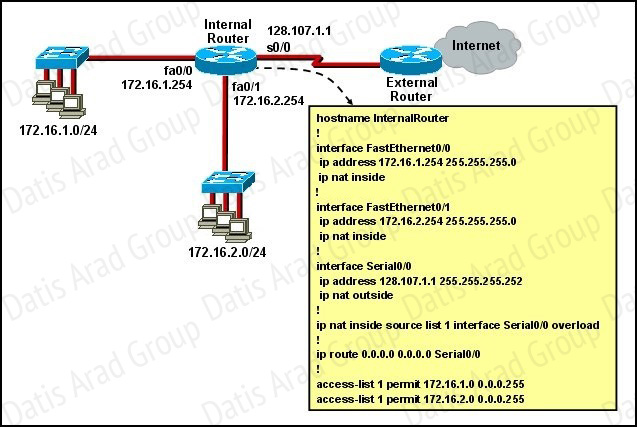
What statement is true of the configuration for this network?
A. The configuration that is shown provides inadequate outside address space for translation of the number of inside addresses that are supported.
B. Because of the addressing on interface FastEthernet0/1, the Serial0/0 interface address will not support the NAT configuration as shown.
C. The number 1 referred to in the ip nat inside source command references access-list number 1.
D. ExternalRouter must be configured with static routes to networks 172.16.1.0/24 and 172.16.2.0/24.
Answer: C
Explanation:
The “list 1 refers to the access-list number 1.
QUESTION NO: 190
Which statement describes the process of dynamically assigning IP addresses by the DHCP server?
A. Addresses are allocated after a negotiation between the server and the host to determine the length of the agreement.
B. Addresses are permanently assigned so that the hosts uses the same address at all times.
C. Addresses are assigned for a fixed period of time, at the end of the period, a new request for an address must be made.
D. Addresses are leased to hosts, which periodically contact the DHCP server to renew the lease.
Answer: D
QUESTION NO: 191
What are two benefits of using NAT? (Choose two.)
A. NAT facilitates end-to-end communication when IPsec is enabled.
B. NAT eliminates the need to re-address all hosts that require external access.
C. NAT conserves addresses through host MAC-level multiplexing.
D. Dynamic NAT facilitates connections from the outside of the network.
E. NAT accelerates the routing process because no modifications are made on the packets.
F. NAT protects network security because private networks are not advertised.
Answer: B,F
Explanation:
By not revealing the internal Ip addresses, NAT adds some security to the inside network -> F is correct.
NAT has to modify the source IP addresses in the packets -> E is not correct.
Connection from the outside of the network through a “NAT” network is more difficult than a more network because IP addresses of inside hosts are hidden -> C is not correct.
In order for IPsec to work with NAT we need to allow additional protocols, including Internet Key Exchange (IKE), Encapsulating Security Payload (ESP) and Authentication Header (AH) -> more complex -> A is not correct.
By allocating specific public IP addresses to inside hosts, NAT eliminates the need to re-address the inside hosts -> B is correct.
NAT does conserve addresses but not through host MAC-level multiplexing. It conserves addresses by allowing many private IP addresses to use the same public IP address to go to the Internet -> C is not correct.
QUESTION NO: 192
On which options are standard access lists based?
A. destination address and wildcard mask
B. destination address and subnet mask
C. source address and subnet mask
D. source address and wildcard mask
Answer: D
Explanation:
Standard ACL’s only examine the source IP address/mask to determine if a match is made.
Extended ACL’s examine the source and destination address, as well as port information.
QUESTION NO: 193
A network engineer wants to allow a temporary entry for a remote user with a specific username and password so that the user can access the entire network over the Internet. Which ACL can be used?
A. standard
B. extended
C. dynamic
D. reflexive
Answer: C
Explanation:
We can use a dynamic access list to authenticate a remote user with a specific username and password. The authentication process is done by the router or a central access server such as a TACACS+ or RADIUS server. The configuration of dynamic ACL can be read here:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/tech/tk583/tk822/technologies_tech_note09186a0080094524.shtml
QUESTION NO: 194
How does a DHCP server dynamically assign IP addresses to hosts?
A. Addresses are permanently assigned so that the host uses the same address at all times.
B. Addresses are assigned for a fixed period of time. At the end of the period, a new request for an address must be made, and another address is then assigned.
C. Addresses are leased to hosts. A host will usually keep the same address by periodically contacting the DHCP server to renew the lease.
D. Addresses are allocated after a negotiation between the server and the host to determine the length of the agreement.
Answer: C
Explanation:
DHCP works in a client/server mode and operates like any other client/server relationship. When a PC connects to a DHCP server, the server assigns or leases an IP address to that PC. The PC connects to the network with that leased IP address until the lease expires. The host must contact the DHCP server periodically to extend the lease. This lease mechanism ensures that hosts that move or power off do not hold onto addresses that they do not need. The DHCP server returns these addresses to the address pool and reallocates them as necessary.
QUESTION NO: 195
Refer to the exhibit.

Which rule does the DHCP server use when there is an IP address conflict?
A. The address is removed from the pool until the conflict is resolved.
B. The address remains in the pool until the conflict is resolved.
C. Only the IP detected by Gratuitous ARP is removed from the pool.
D. Only the IP detected by Ping is removed from the pool.
E. The IP will be shown, even after the conflict is resolved.
Answer: A
Explanation:
An address conflict occurs when two hosts use the same IP address. During address assignment, DHCP checks for conflicts using ping and gratuitous ARP. If a conflict is detected, the address is removed from the pool. The address will not be assigned until the administrator resolves the conflict.
QUESTION NO: 196
Refer to the exhibit.
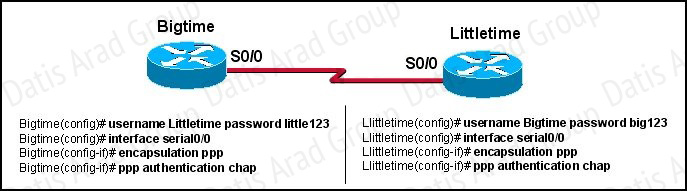 The Bigtime router is unable to authenticate to the Littletime router. What is the cause of the problem?
The Bigtime router is unable to authenticate to the Littletime router. What is the cause of the problem?
A. The usernames are incorrectly configured on the two routers.
B. The passwords do not match on the two routers.
C. CHAP authentication cannot be used on a serial interface.
D. The routers cannot be connected from interface S0/0 to interface S0/0.
E. With CHAP authentication, one router must authenticate to another router. The routers cannotbe configured to authenticate to each other.
Answer: B
Explanation:
With CHAP authentication, the configured passwords must be identical on each router. Here, it is configured as little123 on one side and big123 on the other.
QUESTION NO: 197
Which two tasks does the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol perform? (Choose two.)
A. Set the IP gateway to be used by the network.
B. Perform host discovery used DHCPDISCOVER message.
C. Configure IP address parameters from DHCP server to a host.
D. Provide an easy management of layer 3 devices.
E. Monitor IP performance using the DHCP server.
F. Assign and renew IP address from the default pool.
Answer: C,F
Explanation:
The Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) is a network protocol used to configure devices that are connected to a network (known as hosts) so they can communicate on that network using the Internet Protocol (IP). It involves clients and a server operating in a client-server model. DHCP servers assigns IP addresses from a pool of addresses and also assigns other parameters such as DNS and default gateways to hosts.
QUESTION NO: 198
When a DHCP server is configured, which two IP addresses should never be assignable to hosts? (Choose two.)
A. network or subnetwork IP address
B. broadcast address on the network
C. IP address leased to the LAN
D. IP address used by the interfaces
E. manually assigned address to the clients
F. designated IP address to the DHCP server
Answer: A,B
Explanation:
Network or subnetwork IP address (for example 11.0.0.0/8 or 13.1.0.0/16) and broadcast address (for example 23.2.1.255/24) should never be assignable to hosts. When try to assign these addresses to hosts, you will receive an error message saying that they can’t be assignable.
QUESTION NO: 199
Which two statements about static NAT translations are true? (Choose two.)
A. They allow connections to be initiated from the outside.
B. They require no inside or outside interface markings because addresses are statically defined.
C. They are always present in the NAT table.
D. They can be configured with access lists, to allow two or more connections to be initiated from the outside.
Answer: A,C
Explanation:
Static NAT is to map a single outside IP address to a single inside IP address. This is typically done to allow incoming connections from the outside (Internet) to the inside. Since these are static, they are always present in the NAT table even if they are not actively in use.
Topic 6, Network Device Security
QUESTION NO: 200
A network administrator needs to configure port security on a switch. Which two statements are true? (Choose two.)
A. The network administrator can apply port security to dynamic access ports.
B. The network administrator can apply port security to EtherChannels.
C. When dynamic MAC address learning is enabled on an interface, the switch can learn new addresses, up to the maximum defined.
D. The sticky learning feature allows the addition of dynamically learned addresses to the running configuration.
E. The network administrator can configure static secure or sticky secure MAC addresses in the voice VLAN.
Answer: C,D
Explanation:
Follow these guidelines when configuring port security:
+ Port security can only be configured on static access ports, trunk ports, or 802.1Q tunnel ports.
+ A secure port cannot be a dynamic access port.
+ A secure port cannot be a destination port for Switched Port Analyzer (SPAN).
+ A secure port cannot belong to a Fast EtherChannel or Gigabit EtherChannel port group.
+ You cannot configure static secure or sticky secure MAC addresses on a voice VLAN.
+ When you enable port security on an interface that is also configured with a voice VLAN, you must set the maximum allowed secure addresses on the port to at least two.
+ If any type of port security is enabled on the access VLAN, dynamic port security is automatically enabled on the voice VLAN.
+ When a voice VLAN is configured on a secure port that is also configured as a sticky secure port, all addresses seen on the voice VLAN are learned as dynamic secure addresses, and all addresses seen on the access VLAN (to which the port belongs) are learned as sticky secure addresses.
+ The switch does not support port security aging of sticky secure MAC addresses.
+ The protect and restrict options cannot be simultaneously enabled on an interface.