
نمونه سوالات آزمون CCNA Routing & Switching 200-120
Topic 8, WAN Technologies
QUESTION NO: 261
Which PPP subprotocol negotiates authentication options?
A. NCP
B. ISDN
C. SLIP
D. LCP
E. DLCI
Answer: D
Explanation:
The PPP Link Control Protocol (LCP) is documented in RFC 1661. LPC negotiates link and PPP parameters to dynamically configure the data link layer of a PPP connection. Common LCP options include the PPP MRU, the authentication protocol, compression of PPP header fields, callback, and multilink options.
QUESTION NO: 262
What are two characteristics of Frame Relay point-to-point subinterfaces? (Choose two.)
A. They create split-horizon issues.
B. They require a unique subnet within a routing domain.
C. They emulate leased lines.
D. They are ideal for full-mesh topologies.
E. They require the use of NBMA options when using OSPF.
Answer: B,C
Explanation:
Subinterfaces are used for point to point frame relay connections, emulating virtual point to point leased lines. Each subinterface requires a unique IP address/subnet. Remember, you can not assign multiple interfaces in a router that belong to the same IP subnet.
QUESTION NO: 263
What command is used to verify the DLCI destination address in a Frame Relay static configuration?
A. show frame-relay pvc
B. show frame-relay lmi
C. show frame-relay map
D. show frame relay end-to-end
Answer: C
QUESTION NO: 264
What is the purpose of Inverse ARP?
A. to map a known IP address to a MAC address
B. to map a known DLCI to a MAC address
C. to map a known MAC address to an IP address
D. to map a known DLCI to an IP address
E. to map a known IP address to a SPID
F. to map a known SPID to a MAC address
Answer: D
Explanation:
Dynamic address mapping relies on the Frame Relay Inverse Address Resolution Protocol (Inverse ARP), defined by RFC 1293, to resolve a next hop network protocol (IP) address to a local DLCI value. The Frame Relay router sends out Inverse ARP requests on its Frame Relay PVC to discover the protocol address of the remote device connected to the Frame Relay network. The responses to the Inverse ARP requests are used to populate an address-to-DLCI mapping table on the Frame Relay router or access server. The router builds and maintains this address-to- DLCI mapping table, which contains all resolved Inverse ARP requests, including both dynamic and static mapping entries.
Topic 9, Mix Questions Set
QUESTION NO: 265
What is a valid HSRP virtual MAC address?
A. 0000.5E00.01A3
B. 0007.B400.AE01
C. 0000.0C07.AC15
D. 0007.5E00.B301
Answer: C
Explanation:
With HSRP, two or more devices support a virtual router with a fictitious MAC address and unique IP address. There are two version of HSRP.
+ With HSRP version 1, the virtual router’s MAC address is 0000.0c07.ACxx , in which xx is the HSRP group.
+ With HSRP version 2, the virtual MAC address if 0000.0C9F.Fxxx, in which xxx is the HSRP group.
Note: Another case is HSRP for IPv6, in which the MAC address range from 0005.73A0.0000 through 0005.73A0.0FFF.
QUESTION NO: 266
In GLBP, which router will respond to client ARP requests?
A. The active virtual gateway will reply with one of four possible virtual MAC addresses.
B. All GLBP member routers will reply in round-robin fashion.
C. The active virtual gateway will reply with its own hardware MAC address.
D. The GLBP member routers will reply with one of four possible burned in hardware addresses.
Answer: A
Explanation:
One disadvantage of HSRP and VRRP is that only one router is in use, other routers must wait for the primary to fail because they can be used. However, Gateway Load Balancing Protocol (GLBP) can use of up to four routers simultaneously. In GLBP, there is still only one virtual IP address but each router has a different virtual MAC address. First a GLBP group must elect an Active Virtual Gateway (AVG). The AVG is responsible for replying ARP requests from hosts/clients. It replies with different virtual MAC addresses that correspond to different routers (known as Active Virtual Forwarders – AVFs) so that clients can send traffic to different routers in that GLBP group (load sharing).
QUESTION NO: 267
Which statement describes VRRP object tracking?
A. It monitors traffic flow and link utilization.
B. It ensures the best VRRP router is the virtual router master for the group.
C. It causes traffic to dynamically move to higher bandwidth links.
D. It thwarts man-in-the-middle attacks.
Answer: B
Explanation:
Object tracking is the process of tracking the state of a configured object and uses that state to determine the priority of the VRRP router in a VRRP group.
QUESTION NO: 268
What are three benefits of GLBP? (Choose three.)
A. GLBP supports up to eight virtual forwarders per GLBP group.
B. GLBP supports clear text and MD5 password authentication between GLBP group members.
C. GLBP is an open source standardized protocol that can be used with multiple vendors.
D. GLBP supports up to 1024 virtual routers.
E. GLBP can load share traffic across a maximum of four routers.
F. GLBP elects two AVGs and two standby AVGs for redundancy.
Answer: B,D,E
QUESTION NO: 269
Which three statements about HSRP operation are true? (Choose three.)
A. The virtual IP address and virtual MA+K44C address are active on the HSRP Master router.
B. The HSRP default timers are a 3 second hello interval and a 10 second dead interval.
C. HSRP supports only clear-text authentication.
D. The HSRP virtual IP address must be on a different subnet than the routers' interfaces on the same LAN.
E. The HSRP virtual IP address must be the same as one of the router's interface addresses on the LAN.
F. HSRP supports up to 255 groups per interface, enabling an administrative form of load balancing.
Answer: A,B,F
Explanation:
The virtual MAC address of HSRP version 1 is 0000.0C07.ACxx, where xx is the HSRP group number in hexadecimal based on the respective interface. For example, HSRP group 10 uses the HSRP virtual MAC address of 0000.0C07.AC0A. HSRP version 2 uses a virtual MAC address of 0000.0C9F.FXXX (XXX: HSRP group in hexadecimal)
QUESTION NO: 270
Which three statements about Syslog utilization are true? (Choose three.)
A. Utilizing Syslog improves network performance.
B. The Syslog server automatically notifies the network administrator of network problems.
C. A Syslog server provides the storage space necessary to store log files without using router disk space.
D. There are more Syslog messages available within Cisco IOS than there are comparable SNMP trap messages.
E. Enabling Syslog on a router automatically enables NTP for accurate time stamping.
F. A Syslog server helps in aggregation of logs and alerts.
Answer: C,D,F
QUESTION NO: 271
A network administrator enters the following command on a router: logging trap 3. What are three message types that will be sent to the Syslog server? (Choose three.)
A. informational
B. emergency
C. warning
D. critical
E. debug
F. error
Answer: B,D,F
QUESTION NO: 272
What is the default Syslog facility level?
A. local4
B. local5
C. local6
D. local7
Answer: D
QUESTION NO: 273
What command instructs the device to timestamp Syslog debug messages in milliseconds?
A. service timestamps log datetime localtime
B. service timestamps debug datetime msec
C. service timestamps debug datetime localtime
D. service timestamps log datetime msec
Answer: B
Explanation:
The “service timestamps debug” command configures the system to apply a time stamp to debugging messages. The time-stamp format for datetime is MMM DD HH:MM:SS, where MMM is the month, DD is the date, HH is the hour (in 24-hour notation), MM is the minute, and SS is the second. With the additional keyword msec, the system includes milliseconds in the time stamp, in the format HH:DD:MM:SS.mmm, where .mmm is milliseconds
QUESTION NO: 274
Refer to the exhibit.
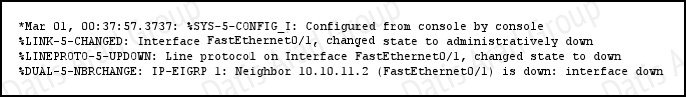
What is the cause of the Syslog output messages?
A. The EIGRP neighbor on Fa0/1 went down due to a failed link.
B. The EIGRP neighbor connected to Fa0/1 is participating in a different EIGRP process, causing the adjacency to go down.
C. A shut command was executed on interface Fa0/1, causing the EIGRP adjacency to go down.
D. Interface Fa0/1 has become error disabled, causing the EIGRP adjacency to go down.
Answer: C
QUESTION NO: 275
What are three components that comprise the SNMP framework? (Choose three.)
A. MIB
B. agent
C. set
D. AES
E. supervisor
F. manager
Answer: A,B,F
QUESTION NO: 276
Which spanning-tree protocol rides on top of another spanning-tree protocol?
A. MSTP
B. RSTP
C. PVST+
D. Mono Spanning Tree
Answer: A
QUESTION NO: 277
What SNMP message alerts the manager to a condition on the network?
A. response
B. get
C. trap
D. capture
Answer: C
Explanation:
An agent can send unsolicited traps to the manager. Traps are messages alerting the SNMP manager to a condition on the network. Traps can mean improper user authentication, restarts, link status (up or down), MAC address tracking, closing of a TCP connection, loss of connection to a neighbor, or other significant events.
QUESTION NO: 278
What authentication type is used by SNMPv2?
A. HMAC-MD5
B. HMAC-SHA
C. CBC-DES
D. community strings
Answer: D
QUESTION NO: 279
Which three statements about the features of SNMPv2 and SNMPv3 are true? (Choose three.)
A. SNMPv3 enhanced SNMPv2 security features.
B. SNMPv3 added the Inform protocol message to SNMP.
C. SNMPv2 added the Inform protocol message to SNMP.
D. SNMPv3 added the GetBulk protocol messages to SNMP.
E. SNMPv2 added the GetBulk protocol message to SNMP.
F. SNMPv2 added the GetNext protocol message to SNMP.
Answer: A,C,E
Explanation:
SNMPv1/v2 can neither authenticate the source of a management message nor provide encryption. Without authentication, it is possible for nonauthorized users to exercise SNMP network management functions. It is also possible for nonauthorized users to eavesdrop on management information as it passes from managed systems to the management system. Because of these deficiencies, many SNMPv1/v2 implementations are limited to simply a readonly capability, reducing their utility to that of a network monitor; no network control applications can be supported. To correct the security deficiencies of SNMPv1/v2, SNMPv3 was issued as a set of Proposed Standards in January 1998. -> A is correct.
The two additional messages are added in SNMP2 (compared to SNMPv1)
GetBulkRequest The GetBulkRequest message enables an SNMP manager to access large chunks of data. GetBulkRequest allows an agent to respond with as much information as will fit in the response PDU. Agents that cannot provide values for all variables in a list will send partial information. -> E is correct.
InformRequest The InformRequest message allows NMS stations to share trap information. (Traps are issued by SNMP agents when a device change occurs.) InformRequest messages are generally used between NMS stations, not between NMS stations and agents. -> C is correct.
Note: These two messages are carried over SNMPv3.
QUESTION NO: 280
What are three reasons to collect Netflow data on a company network? (Choose three.)
A. To identify applications causing congestion.
B. To authorize user network access.
C. To report and alert link up / down instances.
D. To diagnose slow network performance, bandwidth hogs, and bandwidth utilization.
E. To detect suboptimal routing in the network.
F. To confirm the appropriate amount of bandwidth that has been allocated to each Class of Service.
Answer: A,D,F
Explanation:
NetFlow facilitates solutions to many common problems encountered by IT professionals.
+ Analyze new applications and their network impact Identify new application network loads such as VoIP or remote site additions.
+ Reduction in peak WAN traffic Use NetFlow statistics to measure WAN traffic improvement from application-policy changes; understand who is utilizing the network and the network top talkers.
+ Troubleshooting and understanding network pain points Diagnose slow network performance, bandwidth hogs and bandwidth utilization quickly with command line interface or reporting tools. -> D is correct.
+ Detection of unauthorized WAN traffic Avoid costly upgrades by identifying the applications causing congestion. -> A is correct.
+ Security and anomaly detection NetFlow can be used for anomaly detection and worm diagnosis along with applications such as Cisco CS-Mars.
+ Validation of QoS parameters
Confirm that appropriate bandwidth has been allocated to each Class of Service (CoS) and that no CoS is over- or under-subscribed.-> F is correct.