نمونه سوالات آزمون
Troubleshooting and Maintaining Cisco Networks -exam 300-135
تاریخ به روز رسانی: 2015 , Oct 02
تعداد سوالات: 59
ورژن: 4.0
منبع: Actual Test
QUESTION NO: 1
Refer to exhibit:
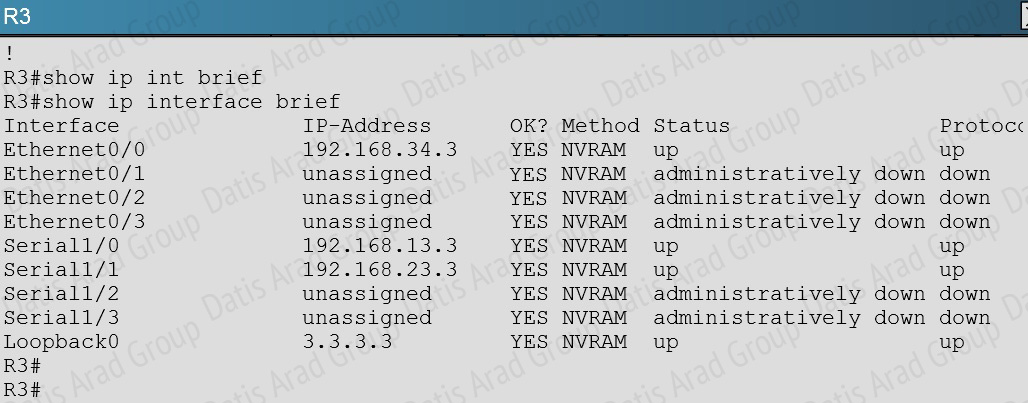
A network administrator is troubleshooting an EIGRP connection between RouterA, IP address 10.1.2.1, and RouterB, IP address 10.1.2.2. Given the debug output on RouterA, which two statements are true? (Choose two.)
A. To support DHCP clients on a single physical network segment where multiple logical IP networks are used.
B. To allow for the sending of network traffic to a group of endpointsdestination hosts.
C. To support remote DHCP clients located on the far side of DHCP and BOOTP relay agents.
D. To provide fault tolerance.
Answer: D,F
Explanation:
QUESTION NO: 2
When troubleshooting an EIGRP connectivity problem, you notice that two connected EIGRP routers are not becoming EIGRP neighbors. A ping between the two routers was successful. What is the next thing that should be checked?
A. Verify that the EIGRP hello and hold timers match exactly.
B. Verify that EIGRP broadcast packets are not being dropped between the two routers with the show ip EIGRP peer command.
C. Verify that EIGRP broadcast packets are not being dropped between the two routers with the show ip EIGRP traffic command.
D. Verify that EIGRP is enabled for the appropriate networks on the local and neighboring router.
Answer: D
Explanation:
QUESTION NO: 3
Refer to the exhibit.
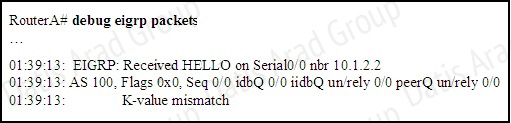
How would you confirm on R1 that load balancing is actually occurring on the default-network (0.0.0.0)?
A. Use ping and the show ip route command to confirm the timers for each default network resets to 0.
B. Load balancing does not occur over default networks; the second route will only be used for failover.
C. Use an extended ping along with repeated show ip route commands to confirm the gateway of last resort address toggles back and forth.
D. Use the traceroute command to an address that is not explicitly in the routing table.
Answer: D
Explanation:
QUESTION NO: 4
Which IPsec mode will encrypt a GRE tunnel to provide multiprotocol support and reduced overhead?
A. 3DES
B. multipoint GRE
C. tunnel
D. transport
Answer: D
Explanation:
QUESTION NO: 5
Which three features are benefits of using GRE tunnels in conjunction with IPsec for building siteto- site VPNs? (Choose three.)
A. allows dynamic routing over the tunnel
B. supports multi-protocol (non-IP) traffic over the tunnel
C. reduces IPsec headers overhead since tunnel mode is used
D. simplifies the ACL used in the crypto map
E. uses Virtual Tunnel Interface (VTI) to simplify the IPsec VPN configuration
Answer: A,B,D
Explanation:
QUESTION NO: 6
Which statement is true about an IPsec/GRE tunnel?
A. The GRE tunnel source and destination addresses are specified within the IPsec transform set.
B. An IPsec/GRE tunnel must use IPsec tunnel mode.
C. GRE encapsulation occurs before the IPsec encryption process.
D. Crypto map ACL is not needed to match which traffic will be protected.
Answer: C
Explanation:
QUESTION NO: 7
A customer network engineer has made configuration changes that have resulted in some loss of connectivity. You have been called in to evaluate a switch network and suggest resolutions to the problems.
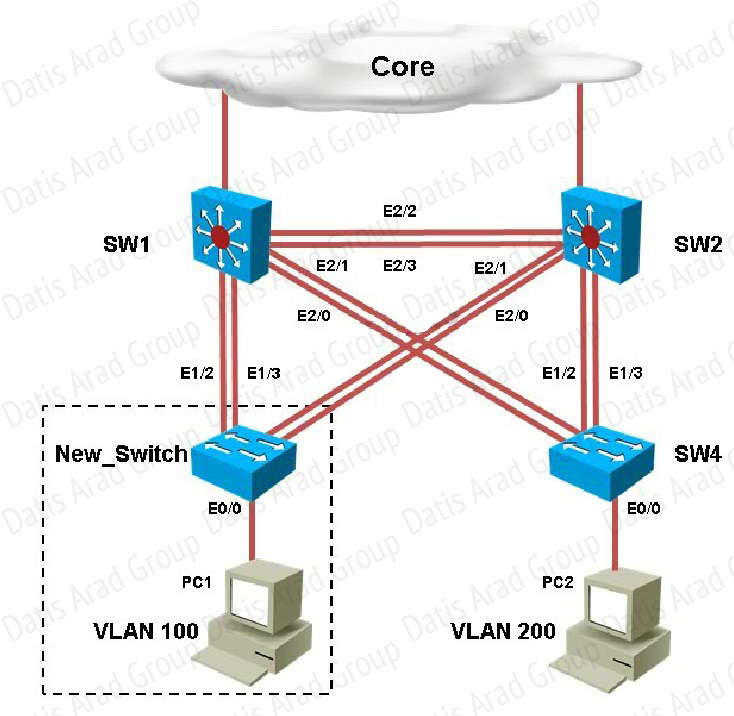
PC2 in VLAN 200 is unable to ping the gateway address 172.16.200.1; identify the issue.
A. VTP domain name mismatch on SW4
B. VLAN 200 not configured on SW1
C. VLAN 200 not configured on SW2
D. VLAN 200 not configured on SW4
Answer: C
Explanation:
By looking at the configuration for SW2, we see that it is missing VLAN 200, and the “switchport access vlan 200” command is missing under interface eth 0/0:
QUESTION NO: 8
A customer network engineer has made configuration changes that have resulted in some loss of connectivity. You have been called in to evaluate a switch network and suggest resolutions to the problems.
 Which of statement is true regarding STP issue identified with switches in the given topology?
Which of statement is true regarding STP issue identified with switches in the given topology?
A. Loopguard configured on the New_Switch places the ports in loop inconsistent state
B. Rootguard configured on SW1 places the ports in root inconsistent state
C. Bpduguard configured on the New_Switch places the access ports in error-disable
D. Rootguard configured on SW2 places the ports in root inconsistent state
Answer: A
Explanation:
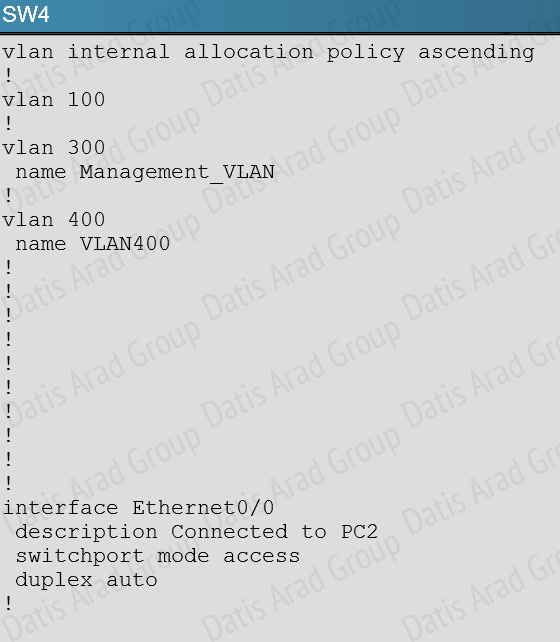
On the new switch, we see that loopguard has been configured with the “spanning-tree guard loop” command.
The loop guard feature makes additional checks. If BPDUs are not received on a non-designated port, and loop guard is enabled, that port is moved into the STP loop-inconsistent blocking state, instead of the listening / learning / forwarding state. Without the loop guard feature, the port assumes the designated port role. The port moves to the STP forwarding state and creates a loop.
QUESTION NO: 9
A customer network engineer has made configuration changes that have resulted in some loss of connectivity. You have been called in to evaluate a switch network and suggest resolutions to the problems.
 You have configured PVST+ load balancing between SW1 and the New_Switch in such a way that both the links E2/2 and E2/3 are utilized for traffic flow, which component of the configuration is preventing PVST+ load balancing between SW1 and SW2 links
You have configured PVST+ load balancing between SW1 and the New_Switch in such a way that both the links E2/2 and E2/3 are utilized for traffic flow, which component of the configuration is preventing PVST+ load balancing between SW1 and SW2 links
A. Port priority configuration on SW1
B. Port priority configuration on the New_Switch
C. Path cost configuration on SW1
D. Path cost configuration on the New_Switch
Answer: D
Explanation:
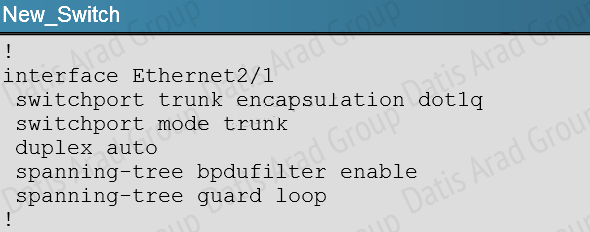
Here is the configuration found on the New_Switch:
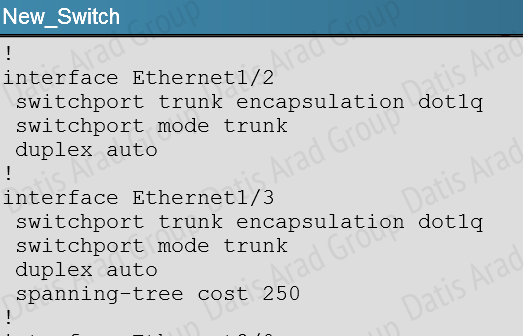 This causes the port cost for link eth 1/3 to increase the path cost to 250 for all VLANs, making that link less preferred so that only eth 1/2 will be used.
This causes the port cost for link eth 1/3 to increase the path cost to 250 for all VLANs, making that link less preferred so that only eth 1/2 will be used.
QUESTION NO: 10
A customer network engineer has made configuration changes that have resulted in some loss of connectivity. You have been called in to evaluate a switch network and suggest resolutions to the problems.
 Refer to the topology.
Refer to the topology.
SW1 Switch Management IP address is not pingable from SW4. What could be the issue?
A. Management VLAN not allowed in the trunk links between SW1 and SW4
B. Management VLAN not allowed in the trunk links between SW1 and SW2
C. Management VLAN not allowed in the trunk link between SW2 and SW4
D. Management VLAN ip address on SW4 is configured in wrong subnet
E. Management VLAN interface is shutdown on SW4
Answer: D
Explanation:
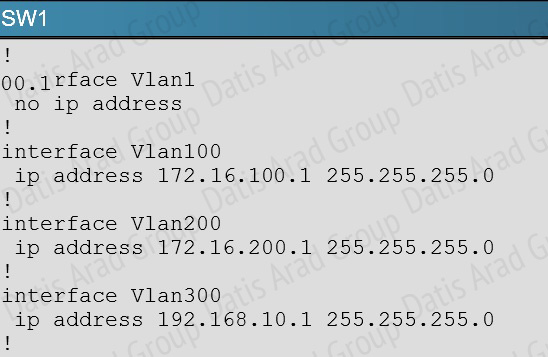
In the network, VLAN 300 is called the Management VLAN. Based on the configurations shown below, SW1 has VLAN 300 configured with the IP address of 192.168.10.1/24, while on SW4 VLAN 300 has an IP address of 192.168.100.4/24, which is not in the same subnet.
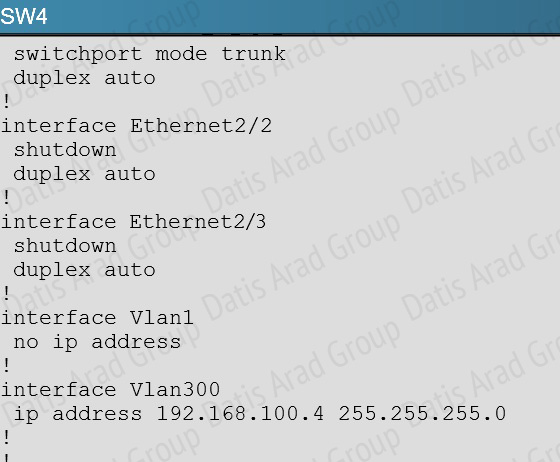
QUESTION NO: 11
You have been brought in to troubleshoot an EIGRP network. A network engineer has made configuration changes to the network rendering some locations unreachable. You are to locate the problem and suggest solution to resolve the issue.
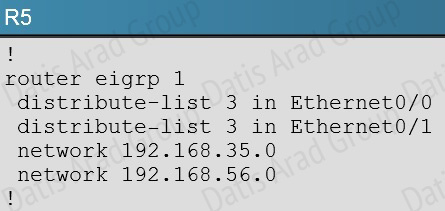
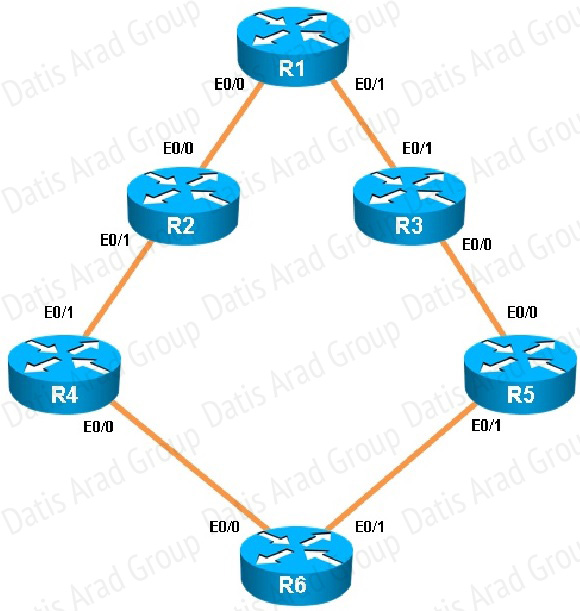 R5 has become partially isolated from the remainder of the network. R5 can reach devices on directly connected networks but nothing else. What is causing the problem?
R5 has become partially isolated from the remainder of the network. R5 can reach devices on directly connected networks but nothing else. What is causing the problem?
A. An outbound distribute list in R3
B. Inbound distribute lists in R5
C. An outbound distribute list in R6
D. Incorrect EIGRP routing process ID in R5
Answer: B
Explanation:
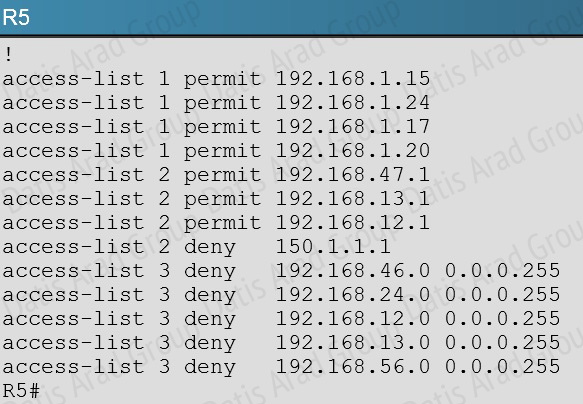
Here we see that distribute list 3 has been applied to EIGRP on router R%, but access-list 3 contains only deny statements so this will effectively block all routing advertisements from its two EIGRP neighbors, thus isolating R5 from the rest of the EIGRP network:
QUESTION NO: 12 Scenario
You have been brought in to troubleshoot an EIGRP network. You have resolved the initial issue between routers R2 and R4, but another issue remains. You are to locate the problem and suggest solution to resolve the issue.
The customer has disabled access to the show running-config command.

The network segment between R2 and R4 has become disconnected from the remainder of the network. How should this issue be resolved?
A. Change the autonomous system number in the remainder of the network to be consistent with R2 and R4.
B. Move the 192.168.24.0 network to the EIGRP 1 routing process in R2 and R4.
C. Enable the R2 and R4 router interfaces connected to the 192.168.24.0 network.
D. Remove the distribute-list command from the EIGRP 200 routing process in R2.
E. Remove the distribute-list command from the EIGRP 100 routing process in R2.
Answer: B
Explanation:
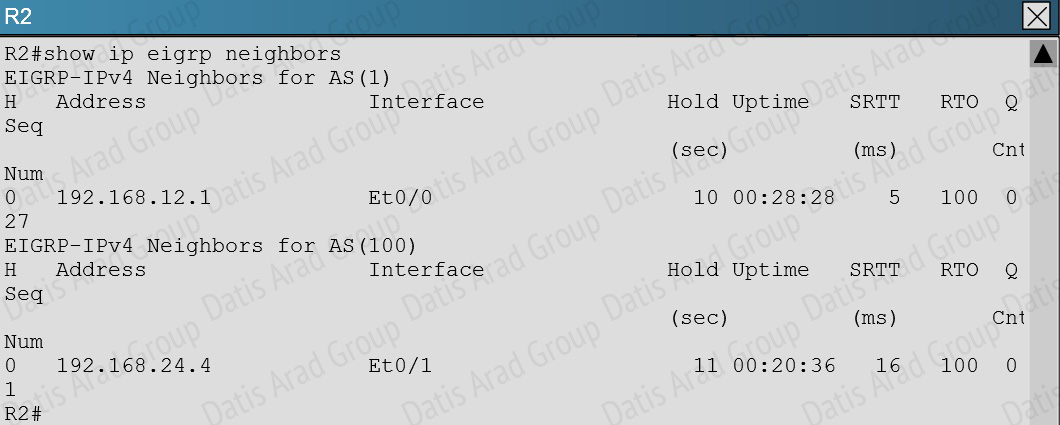
When issuing the “show ip eigrp neighbor” command (which is about the only command that it lets you do in this question) you will see that all other routers are configured for EIGRP AS 1. However, the 192.16824.0 network between R2 and R4 is incorrectly configured for EIGRP AS 100:
QUESTION NO: 13 Scenario
You have been asked by your customer to help resolve issues in their routed network. Their network engineer has deployed HSRP. On closer inspection HSRP doesn't appear to be operating properly and it appears there are other network problems as well. You are to provide solutions to all the network problems.
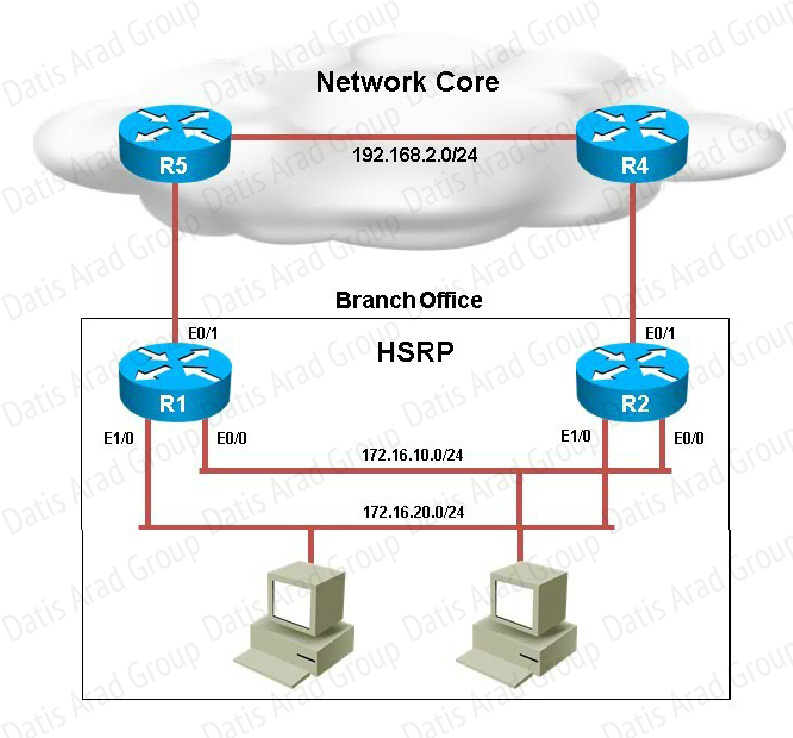 You have received notification from network monitoring system that link between R1 and R5 is down and you noticed that the active router for HSRP group 1 has not failed over to the standby router for group 1. You are required to troubleshoot and identify the issue.
You have received notification from network monitoring system that link between R1 and R5 is down and you noticed that the active router for HSRP group 1 has not failed over to the standby router for group 1. You are required to troubleshoot and identify the issue.
A. There is an HSRP group track command misconfiguration
B. There is an HSRP group priority misconfiguration
C. There is an HSRP authentication misconfiguration
D. There is an HSRP group number mismatch
E. This is not an HSRP issue; this is routing issue.
Answer: A
Explanation:
When looking at the HSRP configuration of R1, we see that tracking has been enabled, but that it is not tracking the link to R5, only the link to R2:
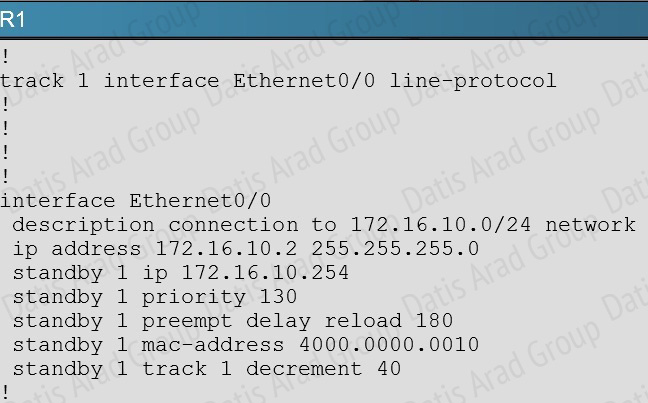
R1 should be tracking the Eth 0/1 link, not 0/0 to achieve the desired affect.
QUESTION NO: 14
You have been asked by your customer to help resolve issues in their routed network. Their network engineer has deployed HSRP. On closer inspection HSRP doesn't appear to be operating properly and it appears there are other network problems as well. You are to provide solutions to all the network problems.
 The following debug messages are noticed for HSRP group 2. But still neither R1 nor R2 has identified one of them as standby router. Identify the reason causing the issue.
The following debug messages are noticed for HSRP group 2. But still neither R1 nor R2 has identified one of them as standby router. Identify the reason causing the issue.
Note: only show commands can be used to troubleshoot the ticket.
R1#
'Mar 26 11:17:39.234: HSRP: Et1/0 Grp 2 Hello out 172.16.20.2 Active pri 100 vIP 172.16.20.254
'Mar 26 11:17:40.034: HSRP: EtO/0 Grp 1 Hello out 172.16.10.2 Active prj 130 vIP 172.16.10.254
R1#
'Mar 26 11:17:40.364: HSRP: EtO/0 Grp 1 Hello in 172.16.10.1 Standby pri 100 vIP 172.16.10.254
R1#
'Mar 26 11:17:41.969: HSRP: Et1/0 Grp 2 Hello out 172.16.20.2 Active pri 100 vIP 172.16.20.254
172.16.20.254
'Mar 26 11:17:53.338: HSRP: EtO/0 Grp 1 Hello out 172.16.10.2 Active pri130vlP
172.16.10.254
'Mar 26 11:17:53.633: HSRP: EtO/0 Grp 1 Hello in 172.16.10.1 Standby pri 100 vIP
172.16.10.254
A. HSRP group priority misconfiguration
B. There is an HSRP authentication misconfiguration
C. There is an HSRP group number mismatch
D. This is not an HSRP issue: this is DHCP issue.
E. The ACL applied to interface is blocking HSRP hello packet exchange
Answer: E
Explanation:
On R1 we see that access list 102 has been applied to the Ethernet 1/0 interface:
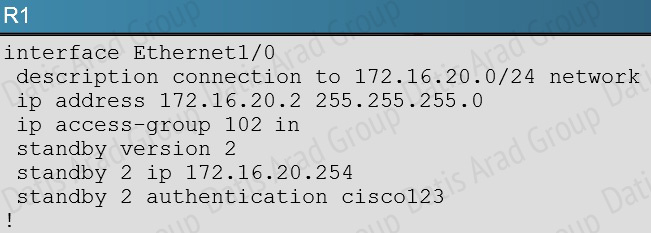
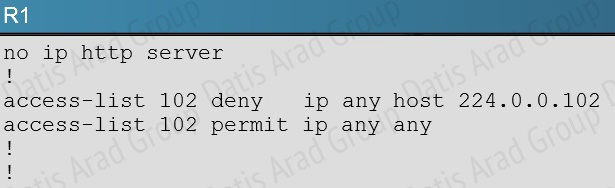
This access list is blocking all traffic to the 224.0.0.102 IP address, which is the multicast address used by HSRP.
QUESTION NO: 15
You have been asked by your customer to help resolve issues in their routed network. Their network engineer has deployed HSRP. On closer inspection HSRP doesn't appear to be operating properly and it appears there are other network problems as well. You are to provide solutions to all the network problems.
Examine the configuration on R4. The routing table shows no entries for 172.16.10.0/24 and 172.16.20.0/24. Identify which of the following is the issue preventing route entries being installed on R4 routing table?
A. HSRP issue between R4 and R2
B. This is an OSPF issue between R4 and R2
C. This is a DHCP issue between R4 and R2
D. The distribute-list configured on R4 is blocking route entries
E. The ACL configured on R4 is blocking inbound traffic on the interface connected to R2
Answer: D
Explanation:
If we look at the configuration on R4 we see that there is a distribute list applied to OSPF, which blocks the 172.16.20.0/24 and 172.16.10.0/24 networks.
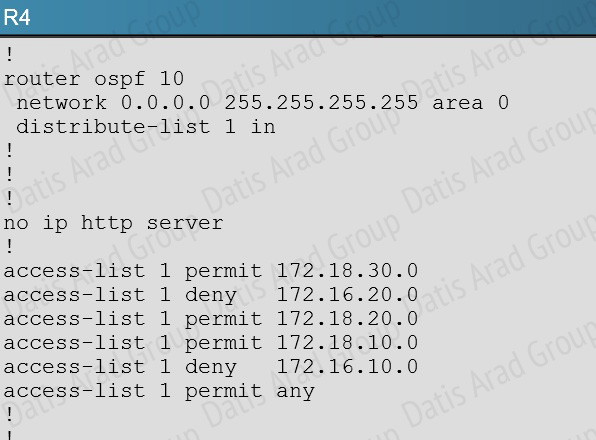
QUESTION NO: 16
You have been asked by your customer to help resolve issues in their routed network. Their network engineer has deployed HSRP. On closer inspection HSRP doesn't appear to be operating properly and it appears there are other network problems as well. You are to provide solutions to all the network problems.
Examine the configuration on R5. Router R5 do not see any route entries learned from R4; what could be the issue?
A. HSRP issue between R5 and R4
B. There is an OSPF issue between R5and R4
C. There is a DHCP issue between R5 and R4
D. The distribute-list configured on R5 is blocking route entries
E. The ACL configured on R5 is blocking traffic for the subnets advertised from R4.
Answer: B
Explanation:
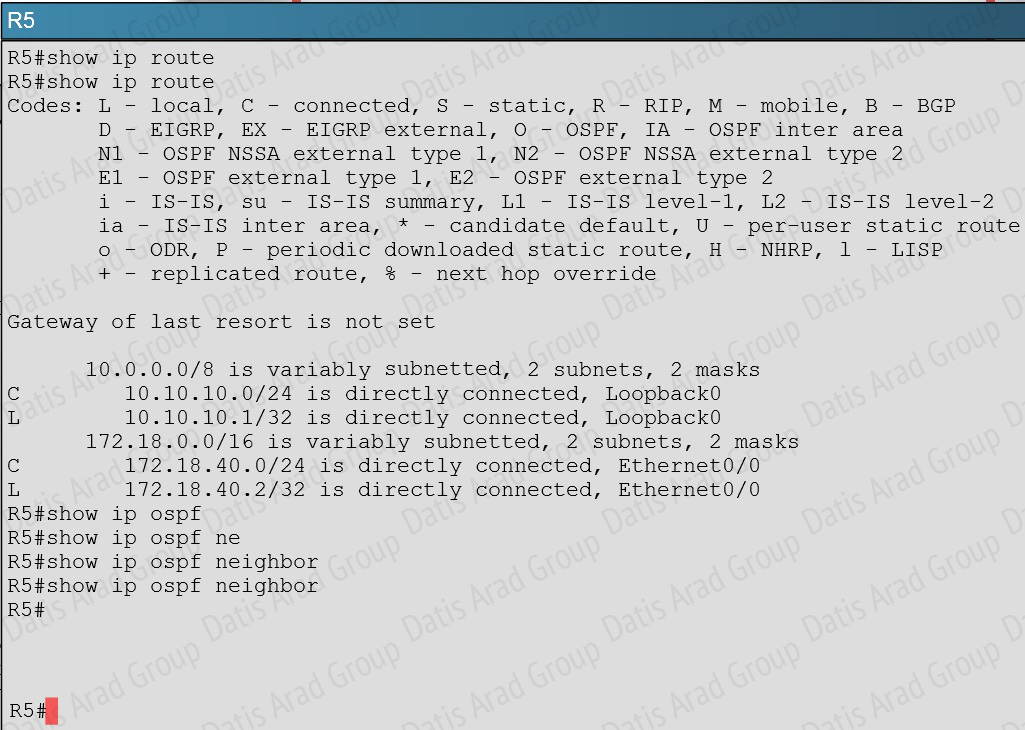
If we issue the “show ip route” and “show ip ospf neighbor” commands on R5, we see that there are no learned OSPF routes and he has no OSPF neighbors.
QUESTION NO: 17
A customer network engineer has edited their OSPF network configuration and now your customer is experiencing network issues. They have contacted you to resolve the issues and return the network to full functionality.
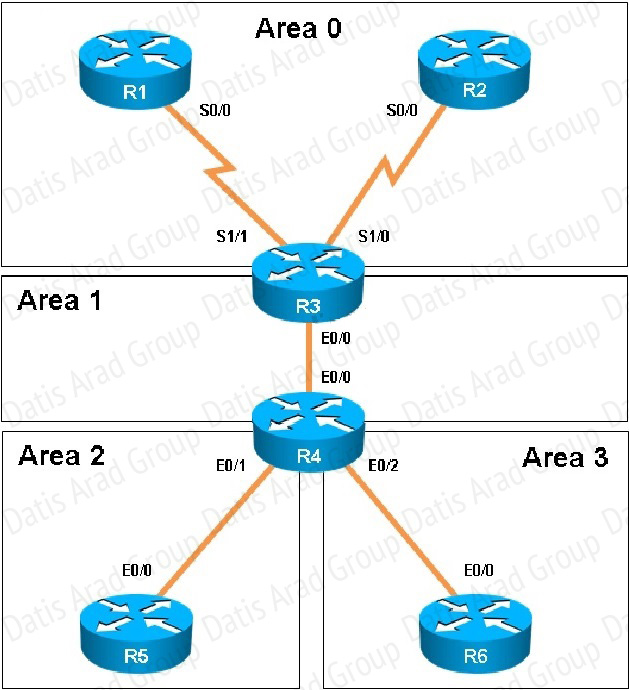
The OSPF neighbour relationship has been lost between R1 and R3. What is causing this problem?
A. The serial interface in R1 should be taken out of the shutdown state.
B. A neighbor statement needs to be configured in R1 and R3 pointing at each other.
C. The R1 network type should be changed to point-to-multipoint non-broadcast.
D. The hello, dead and wait timers on R1 need to be reconfigured to match the values on R3.
Answer: C
Explanation:
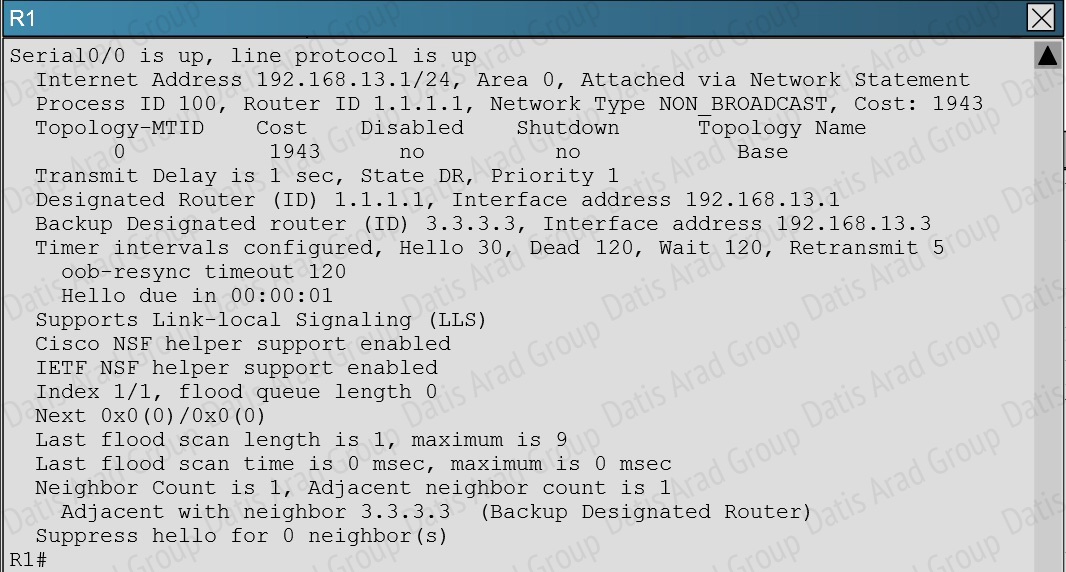
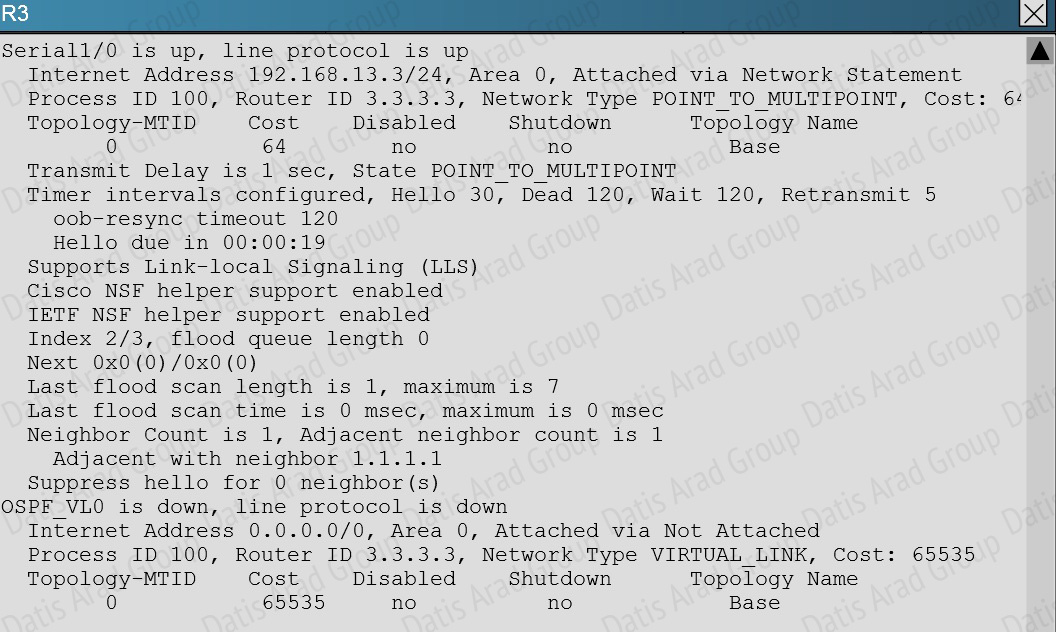
In order for two OSPF routers to become neighbors, they must have matching network types across the links. In this case, we see that R1 has been configured as non-broadcast and R3 is using point to point non-broadcast.
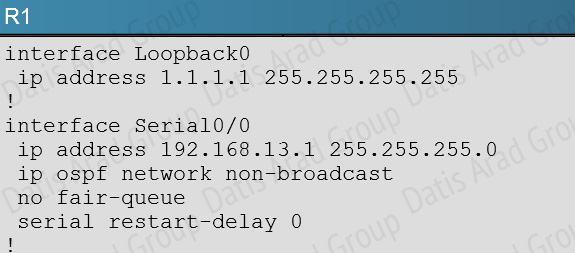
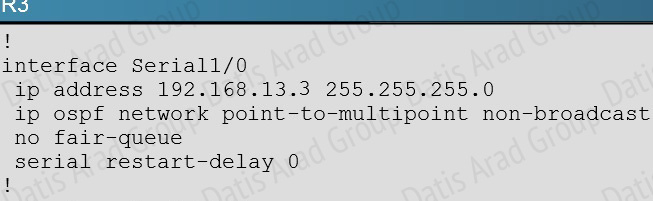
This can be seen by issuing the “show running-config” command on each router, or the “show ip ospf interface” command:
QUESTION NO: 18
A customer network engineer has edited their OSPF network configuration and now your customer is experiencing network issues. They have contacted you to resolve the issues and return the network to full functionality.

Connectivity from R3 to R4, R5 and R6 has been lost. How should connectivity be reestablished?
A. Configure R4 with a virtual link to 192.168.13.2
B. Change the R3 and R4 hello-interval and retransmit-interface timers to zero so the link won't go down.
C. Add an OSPF network statement for 4.4.4.4 0.0.0.0 area 1 in R3
D. Add an OSPF network statement for 192.168.34.3 0.0.0.255 area 2 in R3
E. Add an OSPF network statement for 192.168.34.0 0.0.0.255 area 1 in R3
Answer: E
Explanation:
Based on the network diagram, we know that a virtual link will need to be configured to logically connect area 2 to the back area 0. However, this is not the problem as we can see that R3 has been correctly configured to do this. It is, however, missing the network statement for the link to R4.
Here, we see that the link to R4 is using the 192.168.34.0 network, but that this network has not been added to OSPF
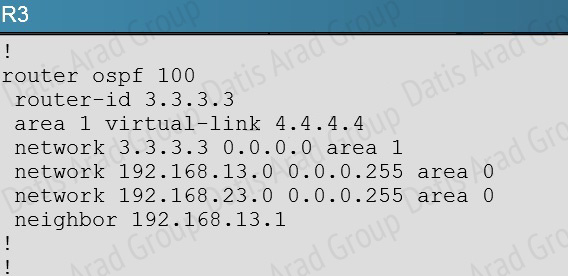
Based on the network diagram, this link should be added to Area 1, not Area 2.
QUESTION NO: 19
A customer network engineer has edited their OSPF network configuration and now your customer is experiencing network issues. They have contacted you to resolve the issues and return the network to full functionality.

After resolving the issues between R3 and R4. Area 2 is still experiencing routing issues. Based on the current router configurations, what needs to be resolved for routes to the networks behind R5 to be seen in the company intranet?
A. Configure R4 and R5 to use MD5 authentication on the Ethernet interfaces that connect to the common subnet.
B. Configure Area 1 in both R4 and R5 to use MD5 authentication.
C. Add ip ospf authentication-key 7 BEST to the R4 Ethernet interface that connects to R5 and ip ospf authentication-key 7 BEST to R5 Ethernet interface that connects to R4.
D. Add ip ospf authentication-key CISCO to R4 Ethernet 0/1 and add area 2 authentication to the R4 OSPF routing process.
Answer: D
Explanation:
Here, we see from the running configuration of R5 that OSPF authentication has been configured on the link to R4:
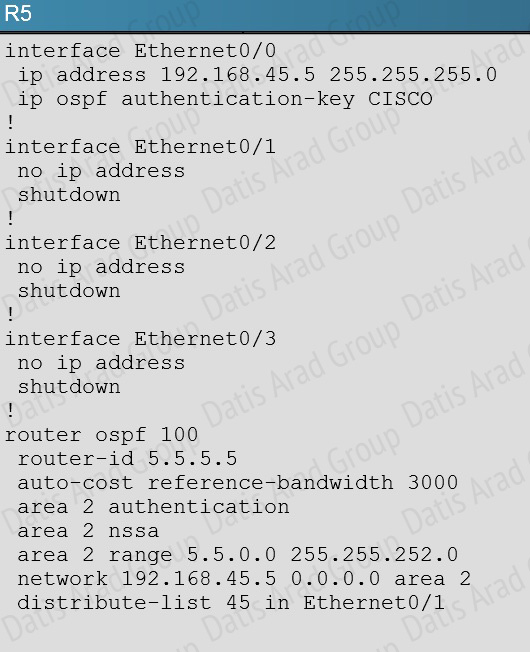
However, this has not been done on the link to R5 on R4:
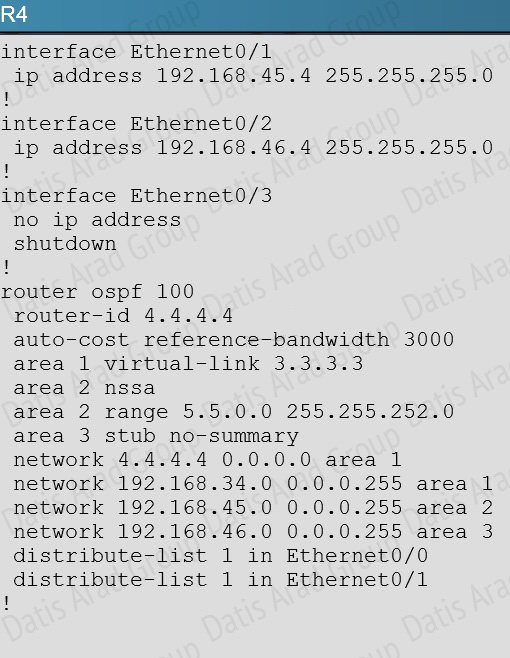
QUESTION NO: 20
A customer network engineer has edited their OSPF network configuration and now your customer is experiencing network issues. They have contacted you to resolve the issues and return the network to full functionality.
 The 6.6.0.0 subnets are not reachable from R4. how should the problem be resolved?
The 6.6.0.0 subnets are not reachable from R4. how should the problem be resolved?
A. Edit access-list 46 in R6 to permit all the 6.6.0.0 subnets
B. Apply access-list 46 in R6 to a different interface
C. Apply access-list 1 as a distribute-list out under router ospf 100 in R4
D. Remove distribute-list 64 out on R6
E. Remove distribute-list 1 in ethernet 0/1 in R4
F. Remove distribute-list 1 in ethernet 0/0 in R4
Answer: D
Explanation:
Here we see from the running configuration of R6 that distribute list 64 is being used in the outbound direction to all OSPF neighbors.
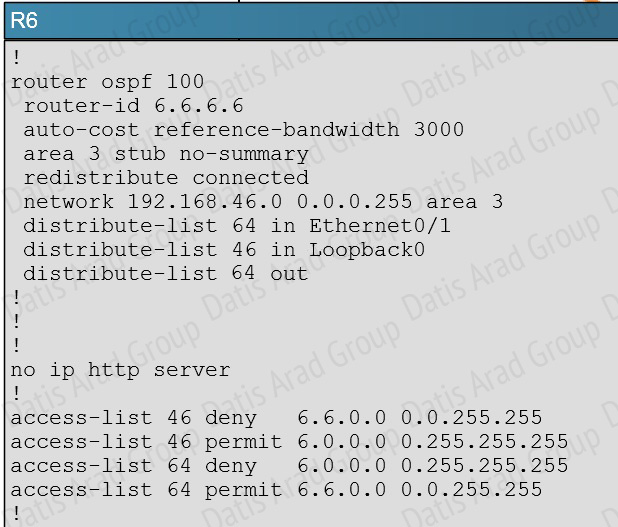
However, no packets will match the 6.6.0.0 in this access list because the first line blocks all 6.0.0.0 networks, and since the 6.6.0.0 networks will also match the first line of this ACL, these OSPF networks will not be advertised because they are first denied in the first line of the ACL.