نمونه سوالات آزمون CCNA Routing & Switching 200-120
Topic 1, Operation of IP Data Networks
QUESTION NO: 21
Host 1 is trying to communicate with Host 2. The e0 interface on Router C is down.
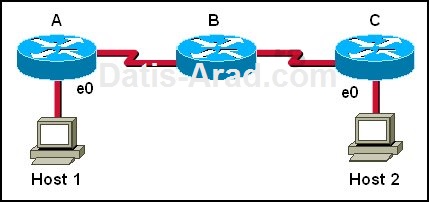
Which of the following are true? (Choose two.)
A. Router C will use ICMP to inform Host 1 that Host 2 cannot be reached.
B. Router C will use ICMP to inform Router B that Host 2 cannot be reached.
C. Router C will use ICMP to inform Host 1, Router A, and Router B that Host 2 cannot be reached.
D. Router C will send a Destination Unreachable message type.
E. Router C will send a Router Selection message type.
F. Router C will send a Source Quench message type.
Answer: A,D
Explanation:
Host 1 is trying to communicate with Host 2. The e0 interface on Router C is down. Router C will
send ICMP packets to inform Host 1 that Host 2 cannot be reached.
QUESTION NO: 22
What is the difference between a CSU/DSU and a modem?
A. A CSU/DSU converts analog signals from a router to a leased line; a modem converts analog
signals from a router to a leased line.
B. A CSU/DSU converts analog signals from a router to a phone line; a modem converts digital signals from a router to a leased line.
C. A CSU/DSU converts digital signals from a router to a phone line; a modem converts analog
signals from a router to a phone line.
D. A CSU/DSU converts digital signals from a router to a leased line; a modem converts digital
signals from a router to a phone line.
Answer: D
Explanation:
CSU/DSU is used to convert digital signals from a router to a network circuit such as a T1, while a modem is used to convert digital signals over a regular POTS line.
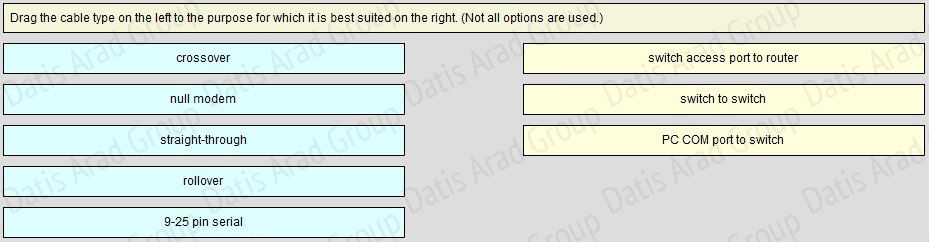
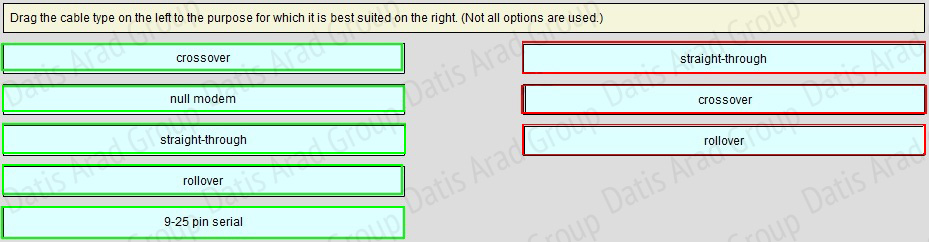
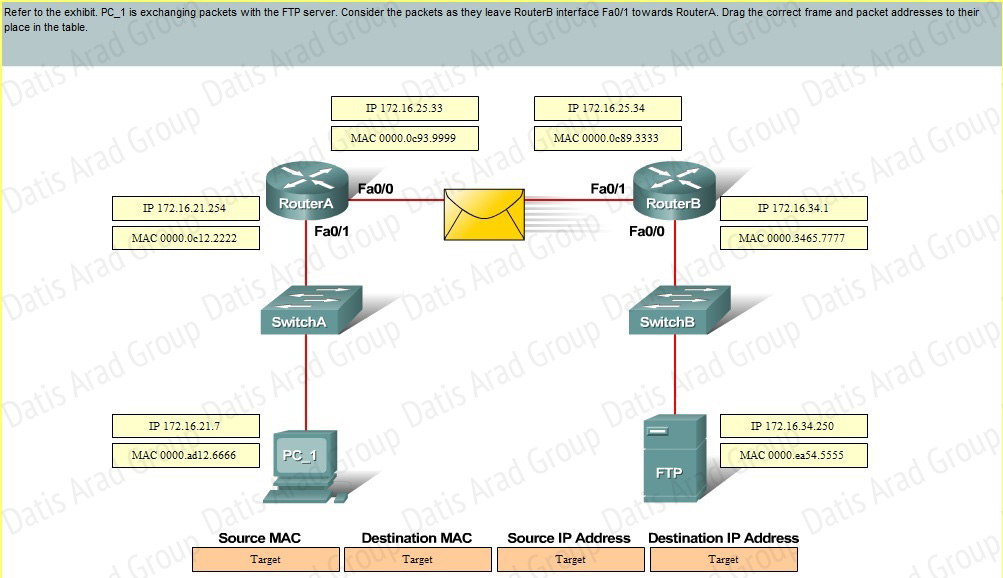
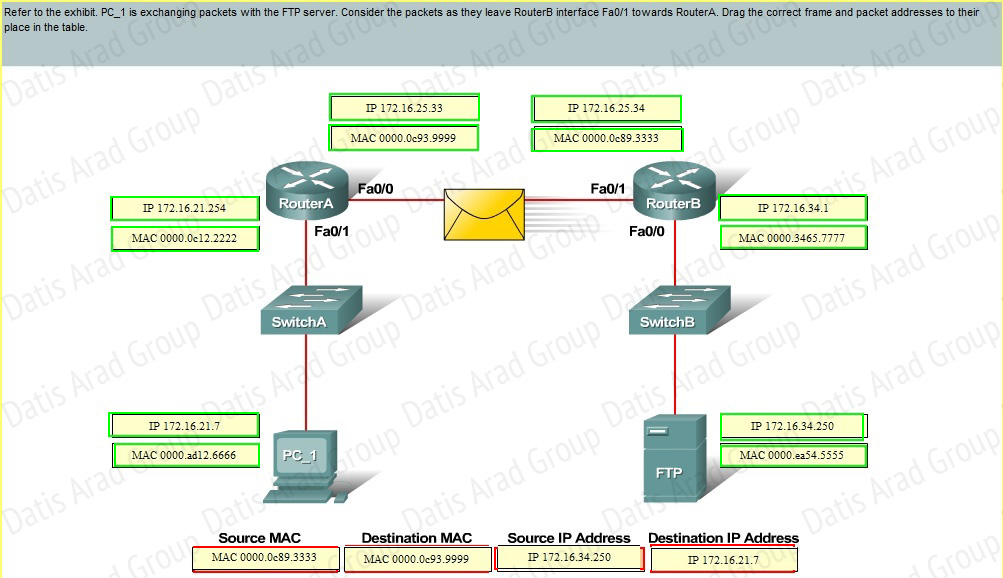
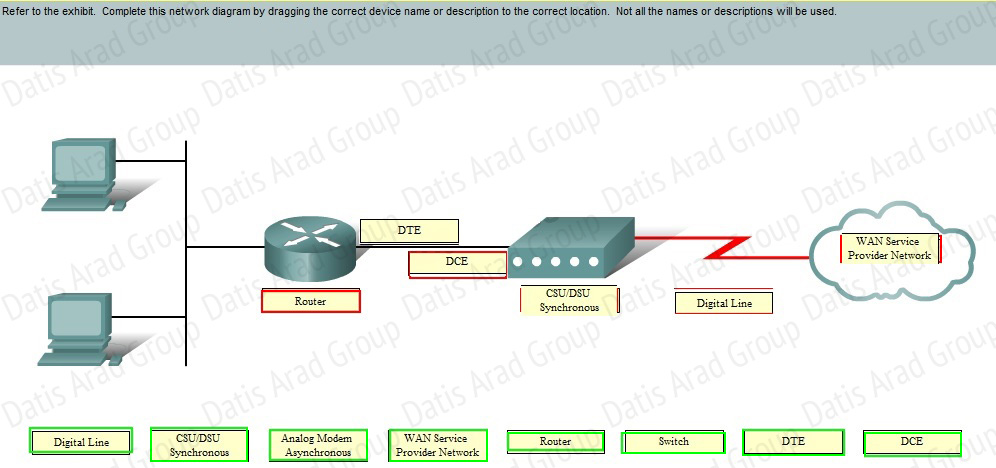
QUESTION NO: 23 Drag and Drop
Answer:
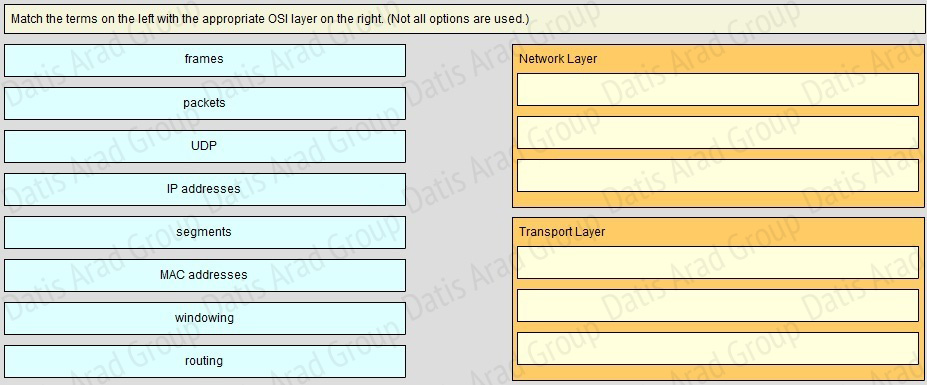
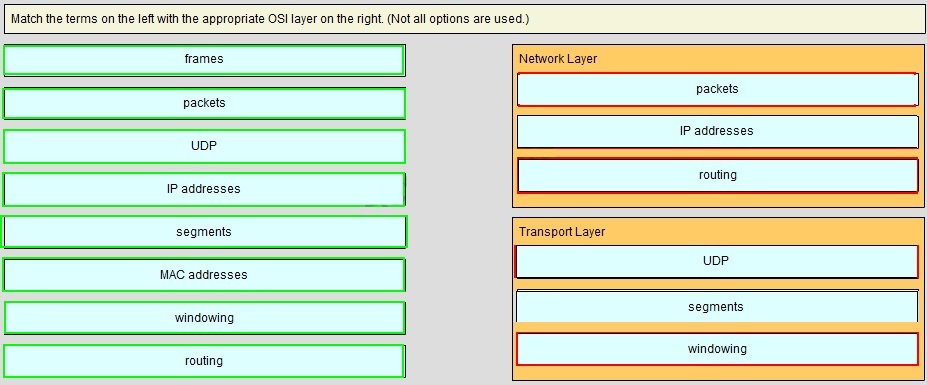
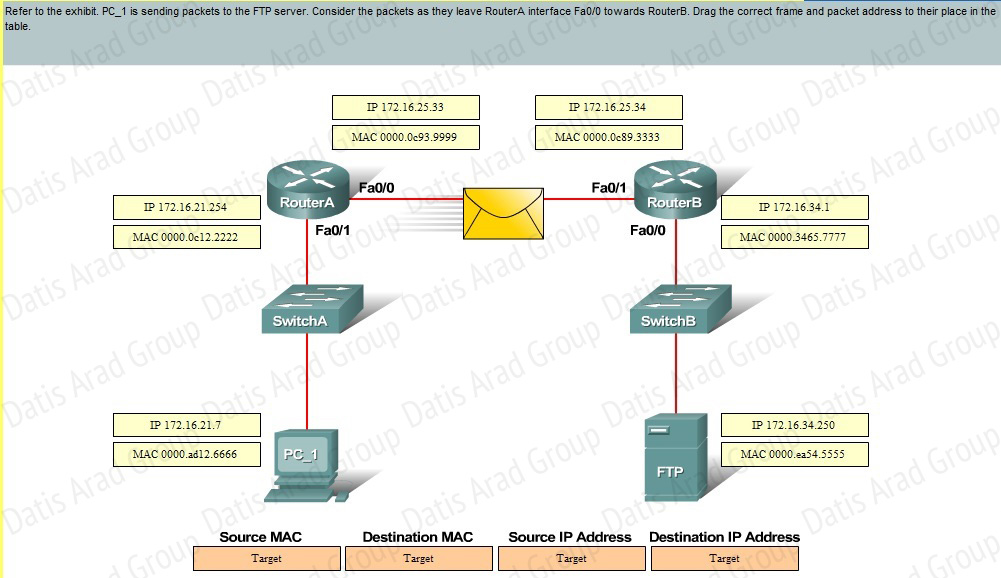
QUESTION NO: 24 Drog and Drop
Answer:
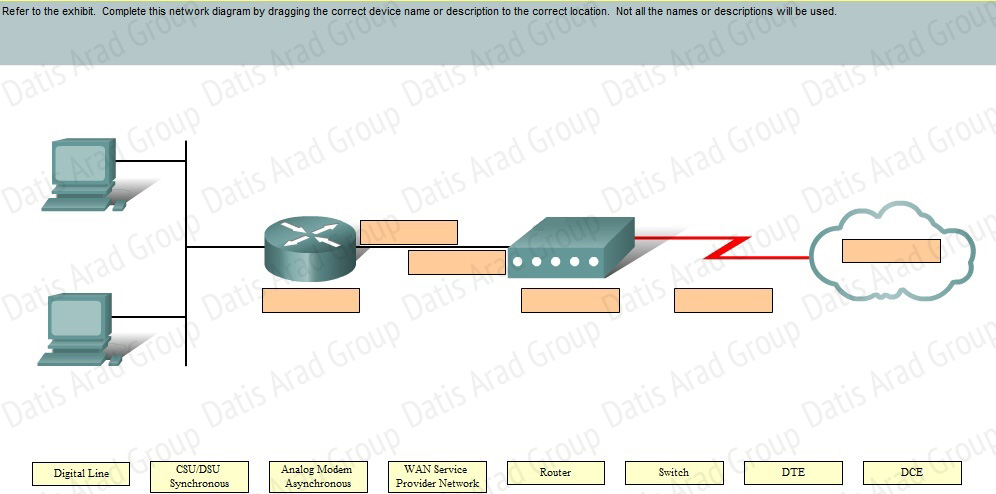
QUESTION NO: 25 Drag and Drop
Answer:
QUESTION NO: 26
Answer:
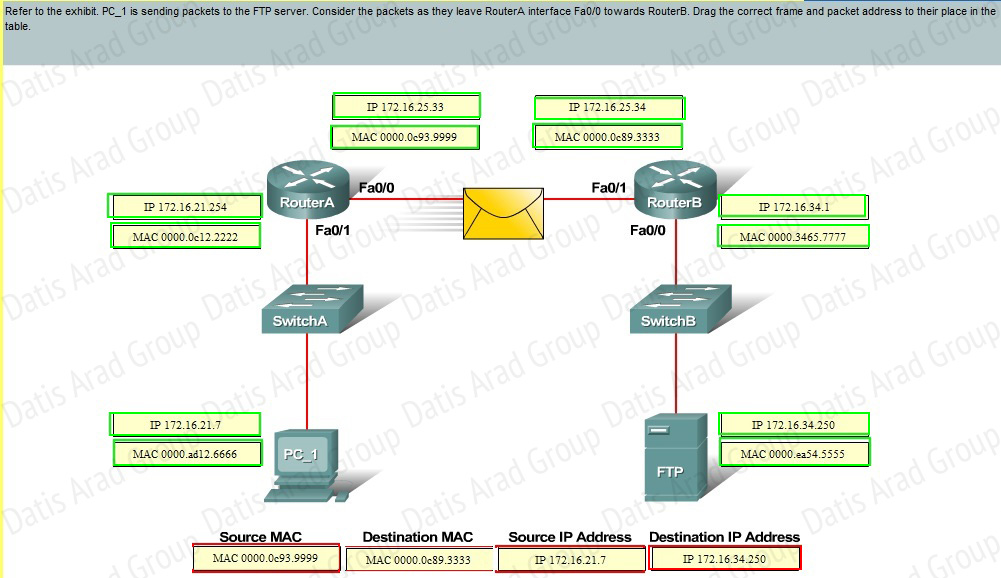
QUESTION NO: 27 Drag and Drop
Answer:
Topic 2, LAN Switching Technologies
QUESTION NO: 28
Refer to the exhibit.

Switch port FastEthernet 0/24 on ALSwitch1 will be used to create an IEEE 802.1Q-compliant trunk to another switch. Based on the output shown, what is the reason the trunk does not form, even though the proper cabling has been attached?
A. VLANs have not been created yet.
B. An IP address must be configured for the port.
C. The port is currently configured for access mode.
D. The correct encapsulation type has not been configured.
E. The “no shutdown” command has not been entered for the port.
Answer: C
Explanation:
According to the output shown the switchport (layer 2 Switching) is enabled and the port is in access mode. To make a trunk link the port should configured as a trunk port, not an access port, by using the following command: (Config-if)#switchport mode trunk
QUESTION NO: 29
Which port state is introduced by Rapid-PVST?
A. learning
B. listening
C. discarding
D. forwarding
Answer: C
Explanation:
PVST+ is based on IEEE802.1D Spanning Tree Protocol (STP). But PVST+ has only 3 port states (discarding, learning and forwarding) while STP has 5 port states (blocking, listening, learning, forwarding and disabled). So discarding is a new port state in PVST+.
QUESTION NO: 30
VLAN 3 is not yet configured on your switch. What happens if you set the switchport access vlan 3 command in interface configuration mode?
A. The command is rejected.
B. The port turns amber.
C. The command is accepted and the respective VLAN is added to vlan.dat.
D. The command is accepted and you must configure the VLAN manually.
Answer: C
Explanation:
The “switchport access vlan 3” will put that interface as belonging to VLAN 3 while also updated the VLAN database automatically to include VLAN 3.
QUESTION NO: 31
What value is primarily used to determine which port becomes the root port on each nonroot switch in a spanning-tree topology?
A. path cost
B. lowest port MAC address
C. VTP revision number
D. highest port priority number
E. port priority number and MAC address
Answer: A
Explanation:
The path cost to the root bridge is the most important value to determine which port will become the root port on each non-root switch. In particular, the port with lowest cost to the root bridge will become root port (on non-root switch).
QUESTION NO: 32
In a switched environment, what does the IEEE 802.1Q standard describe?
A. the operation of VTP
B. a method of VLAN trunking
C. an approach to wireless LAN communication
D. the process for root bridge selection
E. VLAN pruning
Answer: B
Explanation:
A broadcast domain must sometimes exist on more than one switch in the network. To accomplish this, one switch must send frames to another switch and indicate which VLAN a particular frame belongs to. On Cisco switches, a trunk link is created to accomplish this VLAN identification. ISL and IEEE 802.1Q are different methods of putting a VLAN identifier in a Layer 2 frame. The IEEE 802.1Q protocol interconnects VLANs between multiple switches, routers, and servers. With 802.1Q, a network administrator can define a VLAN topology to span multiple physical devices.
Cisco switches support IEEE 802.1Q for FastEthernet and Gigabit Ethernet interfaces. An 802.1Q trunk link provides VLAN identification by adding a 4-byte tag to an Ethernet Frame as it leaves a trunk port.
QUESTION NO: 33
Refer to the exhibit.
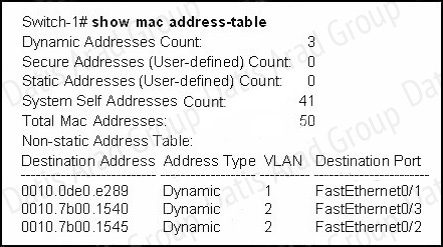
Switch-1 needs to send data to a host with a MAC address of 00b0.d056.efa4. What will Switch-1 do with this data?
A. Switch-1 will drop the data because it does not have an entry for that MAC address.
B. Switch-1 will flood the data out all of its ports except the port from which the data originated.
C. Switch-1 will send an ARP request out all its ports except the port from which the data originated.
D. Switch-1 will forward the data to its default gateway.
Answer: B
Explanation:
This question tests the operating principles of the Layer 2 switch. Check the MAC address table of Switch1 and find that the MAC address of the host does not exist in the table. Switch1 will flood the data out all of its ports except the port from which the data originated to determine which port the host is located in.
Switches work as follows:
In output there is no MAC address of give host so switch floods to all ports except the source port.
QUESTION NO: 34
What is the function of the command switchport trunk native vlan 999 on a Cisco Catalyst switch?
A. It creates a VLAN 999 interface.
B. It designates VLAN 999 for untagged traffic.
C. It blocks VLAN 999 traffic from passing on the trunk.
D. It designates VLAN 999 as the default for all unknown tagged traffic.
Answer: B
Explanation:
Configuring the Native VLAN for Untagged Traffic A trunk port configured with 802.1Q tagging can receive both tagged and untagged traffic. By default, the switch forwards untagged traffic in the native VLAN configured for the port. The native VLAN is VLAN 1 by default.
QUESTION NO: 35
Which two protocols are used by bridges and/or switches to prevent loops in a layer 2 network?
(Choose two.)
A. 802.1d
B. VTP
C. 802.1q
D. STP
E. SAP
Answer: A,D
Explanation:
This question is to examine the STP protocol.
STP (802.1d) is used to prevent Layer 2 loops.
802.1q is a Frame Relay protocol which belongs to VLAN.
SAP is a concept of the OSI model.
QUESTION NO: 36
Which switch would STP choose to become the root bridge in the selection process?
A. 32768: 11-22-33-44-55-66
B. 32768: 22-33-44-55-66-77
C. 32769: 11-22-33-44-55-65
D. 32769: 22-33-44-55-66-78
Answer: A
Explanation:
The root bridge of the spanning tree is the bridge with the smallest (lowest) bridge ID. Each bridge has a configurable priority number and a MAC Address; the bridge ID contains both numbers combined together - Bridge priority + MAC (32768.0200.0000.1111). The Bridge priority default is 32768 and can only be configured in multiples of 4096(Spanning tree uses the 12 bits extended system ID). To compare two bridge IDs, the priority is compared first, as if looking at a real number anything less than 32768...will become the target of being the root. If two bridges have equal priority then the MAC addresses are compared; for example, if switches A (MAC=0200.0000.1111) and B (MAC=0200.0000.2222) both have a priority of 32768 then switch A will be selected as the root bridge.
In this case, 32768: 11-22-33-44-55-66 would be the bridge because it has a lower priority and MAC address.
QUESTION NO: 37
A switch is configured with all ports assigned to VLAN 2 with full duplex FastEthernet to segment existing departmental traffic. What is the effect of adding switch ports to a new VLAN on the switch?
A. More collision domains will be created.
B. IP address utilization will be more efficient.
C. More bandwidth will be required than was needed previously.
D. An additional broadcast domain will be created.
Answer: D
Explanation:
Each VLAN creates its own broadcast domain. Since this is a full duplex switch, each port is a
separate collision domain.
QUESTION NO: 38
What are three benefits of implementing VLANs? (Choose three.)
A. A higher level of network security can be reached by separating sensitive data traffic from other network traffic.
B. A more efficient use of bandwidth can be achieved allowing many physical groups to use the same network infrastructure.
C. A more efficient use of bandwidth can be achieved allowing many logical networks to use the same network infrastructure.
D. Broadcast storms can be mitigated by increasing the number of broadcast domains, thus reducing their size.
E. Broadcast storms can be mitigated by decreasing the number of broadcast domains, thus increasing their size.
F. VLANs make it easier for IT staff to configure new logical groups, because the VLANs all belong to the same broadcast domain.
G. Port-based VLANs increase switch-port use efficiency, thanks to 802.1Q trunks.
Answer: A,C,D
Explanation:
VLAN is a network structure which allows users to communicate while in different locations by sharing one multicast domain and a single broadcast. They provide numerous networking benefits and have become popular in the market. For instance, it helps reduce administrative costs when users are geographically dispersed.
1. Inexpensive
The popularity of VLANs is due to the fact that changes, adds, and moves can be attained simply by making necessary configurations on the VLAN port. Time-consuming, re-addressing, and host reconfigurations is now a thing of the past, because network configuration can be made at ease when need arises.
2. Better management
A VLAN typically solve the scalability issues that exist in a large network by breaking the main domain into several VLAN groups or smaller broadcast configurations, thereby encourage better control of multicast traffic as well as broadcast domains.
3. Improves network security
High-security can be positioned in different VLAN groups to ensure that non-members cannot receive their broadcasts. On the other hand, a router is added and workgroups relocated into centralized locations.
4. Enhances performance
A more efficient use of bandwidth can be achieved allowing many logical networks to use the same network infrastructure.
5. Segment multiple networks
VLANs are typically used to achieve multiple purposes. They are popularly used to reduce broadcast traffic. Each VLAN creates a separate, smaller broadcast domain.
6. Better administration
VLANs facilitate grouping of multiple geographical stations. When VLAN users move to another physical location, the network does not have to be configured.
QUESTION NO: 39
Which IEEE standard protocol is initiated as a result of successful DTP completion in a switch over Fast Ethernet?
A. 802.3ad
B. 802.1w
C. 802.1D
D. 802.1Q
Answer: D
Explanation:
Dynamic Trunking Protocol (DTP) is a Cisco proprietary protocol for negotiating trunking on a link between two devices and for negotiating the type of trunking encapsulation (802.1Q) to be used.
QUESTION NO: 40
Which of the following are benefits of VLANs? (Choose three.)
A. They increase the size of collision domains.
B. They allow logical grouping of users by function.
C. They can enhance network security.
D. They increase the size of broadcast domains while decreasing the number of collision domains.
E. They increase the number of broadcast domains while decreasing the size of the broadcast domains.
F. They simplify switch administration.
Answer: B,C,E
Explanation:
When using VLAN the number and size of collision domains remain the same.
VLANs allow to group users by function, not by location or geography.
VLANs help minimize the incorrect configuration of VLANs so it enhances the security of the network.
VLAN increases the size of broadcast domains but does not decrease the number of collision domains.
VLANs increase the number of broadcast domains while decreasing the size of the broadcast domains which increase the utilization of the links. It is also a big advantage of VLAN.
VLANs are useful but they are more complex and need more administration.