
نمونه سوالات آزمون CCNA Routing & Switching 200-120
Topic 2, LAN Switching Technologies
QUESTION NO: 41
Refer to the exhibit:
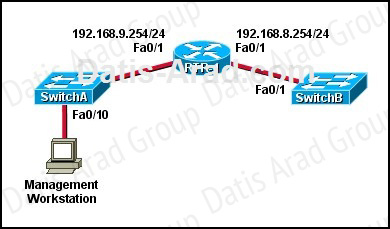
A technician has installed SwitchB and needs to configure it for remote access from the management workstation connected to SwitchA. Which set of commands is required to accomplish this task?
A. SwitchB(config)# interface FastEthernet 0/1
SwitchB(config-if)# ip address 192.168.8.252 255.255.255.0
SwitchB(config-if)# no shutdown
B. SwitchB(config)# interface vlan 1
SwitchB(config-if)# ip address 192.168.8.252 255.255.255.0
SwitchB(config-if)# ip default-gateway 192.168.8.254 255.255.255.0
SwitchB(config-if)# no shutdown
C. SwitchB(config)# ip default-gateway 192.168.8.254
SwitchB(config)# interface vlan 1
SwitchB(config-if)# ip address 192.168.8.252 255.255.255.0
SwitchB(config-if)# no shutdown
D. SwitchB(config)# ip default-network 192.168.8.254
SwitchB(config)# interface vlan 1
SwitchB(config-if)# ip address 192.168.8.252 255.255.255.0
SwitchB(config-if)# no shutdown
E. SwitchB(config)# ip route 192.168.8.254 255.255.255.0
SwitchB(config)# interface FastEthernet 0/1
SwitchB(config-if)# ip address 192.168.8.252 255.255.255.0
SwitchB(config-if)# no shutdown
Answer: C
Explanation:
To remote access to SwitchB, it must have a management IP address on a VLAN on that switch. Traditionally, we often use VLAN 1 as the management VLAN (but in fact it is not secure). In the exhibit, we can recognize that the Management Workstation is in a different subnet from the SwitchB. For intersubnetwork communication to occur, you must configure at least one default gateway. This default gateway is used to forward traffic originating from the switch only, not to forward traffic sent by devices connected to the switch.
QUESTION NO: 42
Which two states are the port states when RSTP has converged? (Choose two.)
A. discarding
B. listening
C. learning
D. forwarding
E. disabled
Answer: A,D
QUESTION NO: 43
Which two commands can be used to verify a trunk link configuration status on a given Cisco switch interface? (Choose two.)
A. show interface trunk
B. show interface interface
C. show ip interface brief
D. show interface vlan
E. show interface switchport
Answer: A,E
QUESTION NO: 44
Which command enables RSTP on a switch?
A. spanning-tree uplinkfast
B. spanning-tree mode rapid-pvst
C. spanning-tree backbonefast
D. spanning-tree mode mst
Answer: B
Explanation:
Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP) is an enhancement of the original STP 802.1D protocol.
The RSTP 802.1w protocol is an IEEE open implementation. Cisco has its own proprietary implementation of RSTP, that includes the benefits of its Per-VLAN spanning tree protocols, called Rapid-PVST+.
To activate the Rapid-PVST+ protocol: switch(config)#spanning-tree mode rapid-pvst
QUESTION NO: 45
Refer to the exhibit.
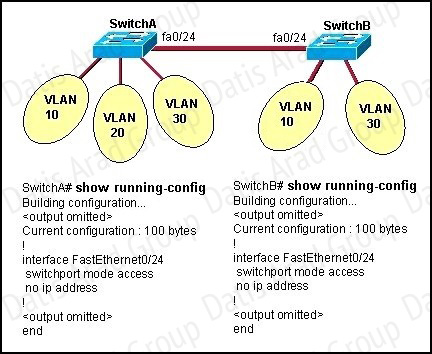
All switch ports are assigned to the correct VLANs, but none of the hosts connected to SwitchA can communicate with hosts in the same VLAN connected to SwitchB. Based on the output shown, what is the most likely problem?
A. The access link needs to be configured in multiple VLANs.
B. The link between the switches is configured in the wrong VLAN.
C. The link between the switches needs to be configured as a trunk.
D. VTP is not configured to carry VLAN information between the switches.
E. Switch IP addresses must be configured in order for traffic to be forwarded between the switches.
Answer: C
Explanation:
In order to pass traffic from VLANs on different switches, the connections between the switches must be configured as trunk ports.
QUESTION NO: 46
Refer to the exhibit.
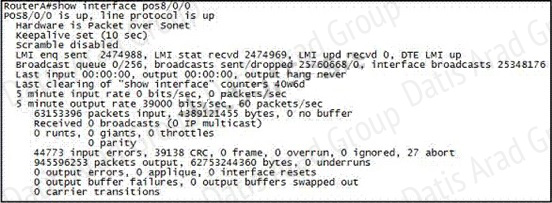
Which WAN protocol is being used?
A. ATM
B. HDLC
C. Frame Relay
D. PPP
Answer: C
Explanation:
This question is to examine the show int command. According to the information provided in the exhibit, we can know that the data link protocol used in this network is the Frame Relay protocol.
“LMI enq sent…”
QUESTION NO: 47
Refer to the exhibit.
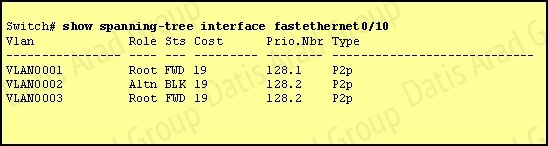
Given the output shown from this Cisco Catalyst 2950, what is the reason that interface FastEthernet 0/10 is not the root port for VLAN 2?
A. This switch has more than one interface connected to the root network segment in VLAN 2.
B. This switch is running RSTP while the elected designated switch is running 802.1d Spanning Tree.
C. This switch interface has a higher path cost to the root bridge than another in the topology.
D. This switch has a lower bridge ID for VLAN 2 than the elected designated switch.
Answer: C
Explanation:
Since the port is in the blocked status, we must assume that there is a shorter path to the root bridge elsewhere.
QUESTION NO: 48
Why will a switch never learn a broadcast address?
A. Broadcasts only use network layer addressing.
B. A broadcast frame is never forwarded by a switch.
C. A broadcast address will never be the source address of a frame.
D. Broadcast addresses use an incorrect format for the switching table.
E. Broadcast frames are never sent to switches.
Answer: C
Explanation:
Switches dynamically learn MAC addresses based on the source MAC addresses that it sees, and since a broadcast is never the source, it will never learn the broadcast address.
QUESTION NO: 49
Refer to the exhibit.
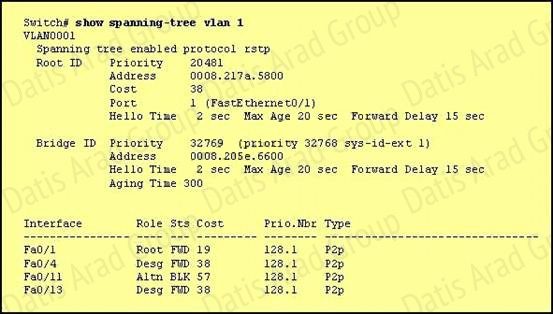
Why has this switch not been elected the root bridge for VLAN1?
A. It has more than one interface that is connected to the root network segment.
B. It is running RSTP while the elected root bridge is running 802.1d spanning tree.
C. It has a higher MAC address than the elected root bridge.
D. It has a higher bridge ID than the elected root bridge.
Answer: D
Explanation:
The root bridge is determined by the lowest bridge ID, and this switch has a bridge ID priority of 32768, which is higher than the roots priority of 20481.
QUESTION NO: 50
Which two link protocols are used to carry multiple VLANs over a single link? (Choose two.)
A. VTP
B. 802.1q
C. IGP
D. ISL
E. 802.3u
Answer: B,D
Explanation:
Cisco switches can use two different encapsulation types for trunks, the industry standard 802.1q or the Cisco proprietary ISL. Generally, most network engineers prefer to use 802.1q since it is standards based and will interoperate with other vendors.
QUESTION NO: 51
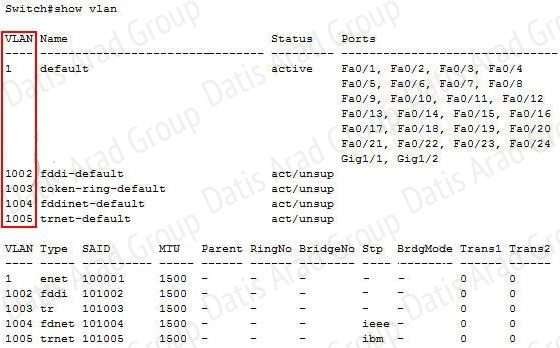
Assuming the default switch configuration, which VLAN range can be added, modified, and removed on a Cisco switch?Assuming the default switch configuration, which VLAN range can be added, modified, and removed on a Cisco switch?
A. 1 through 1001
B. 2 through 1001
C. 1 through 1002
D. 2 through 1005
Answer: B
Explanation:
VLAN 1 is the default VLAN on Cisco switch. It always exists and can not be added, modified or removed.
VLANs 1002-1005 are default VLANs for FDDI & Token Ring and they can’t be deleted or used for Ethernet.
QUESTION NO: 52
Which statement about VLAN operation on Cisco Catalyst switches is true?
A. When a packet is received from an 802.1Q trunk, the VLAN ID can be determined from the source MAC address and the MAC address table.
B. Unknown unicast frames are retransmitted only to the ports that belong to the same VLAN.
C. Broadcast and multicast frames are retransmitted to ports that are configured on different VLAN.
D. Ports between switches should be configured in access mode so that VLANs can span across the ports.
Answer: B
Explanation:
Each VLAN resides in its own broadcast domain, so incoming frames with unknown destinations are only transmitted to ports that reside in the same VLAN as the incoming frame.
QUESTION NO: 53
Refer to the topology shown in the exhibit.
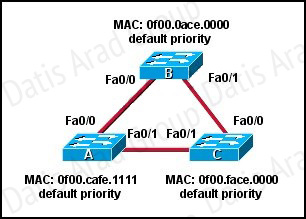
Which ports will be STP designated ports if all the links are operating at the same bandwidth? (Choose three.)
A. Switch A - Fa0/0
B. Switch A - Fa0/1
C. Switch B - Fa0/0
D. Switch B - Fa0/1
E. Switch C - Fa0/0
F. Switch C - Fa0/1
Answer: B,C,D
Explanation:
This question is to check the spanning tree election problem.
1. First, select the root bridge, which can be accomplished by comparing the bridge ID, the smallest will be selected. Bridge-id= bridge priority + MAC address. The three switches in the figure all have the default priority, so we should compare the MAC address, it is easy to find that SwitchB is the root bridge.
2. Select the root port on the non-root bridge, which can be completed through comparing root path cost. The smallest will be selected as the root port.
3. Next, select the Designated Port. First, compare the path cost, if the costs happen to be the same, then compare the BID, still the smallest will be selected. Each link has a DP. Based on the exhibit above, we can find DP on each link. The DP on the link between SwitchA and SwitchC is SwitchA'Fa0/1, because it has the smallest MAC address.
QUESTION NO: 54
Refer to the exhibit.
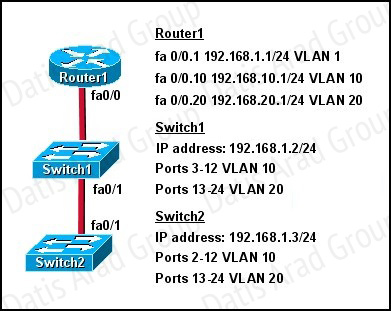
How should the FastEthernet0/1 ports on the 2950 model switches that are shown in the exhibit be configured to allow connectivity between all devices?
A. The ports only need to be connected by a crossover cable.
B. SwitchX(config)# interface fastethernet 0/1
SwitchX(config-if)# switchport mode trunk
C. SwitchX(config)# interface fastethernet 0/1
SwitchX(config-if)# switchport mode access
SwitchX(config-if)# switchport access vlan 1
D. SwitchX(config)# interface fastethernet 0/1
SwitchX(config-if)# switchport mode trunk
SwitchX(config-if)# switchport trunk vlan 1
SwitchX(config-if)# switchport trunk vlan 10
SwitchX(config-if)# switchport trunk vlan 20
Answer: B
Explanation:
In order for multiple VLANs to cross switches, the connection between the switches must be a trunk. The “switchport mode trunk” command is all that is needed, the individual VLANs should not be listed over that trunk interface.
QUESTION NO: 55
Refer to the exhibit.
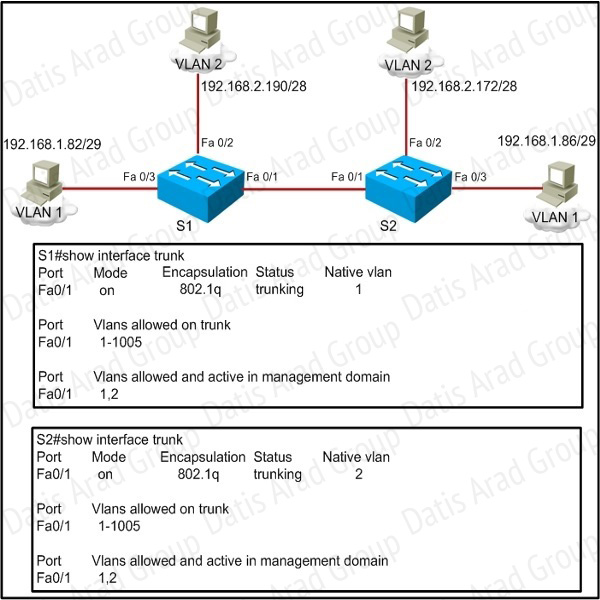
A frame on VLAN 1 on switch S1 is sent to switch S2 where the frame is received on VLAN 2. What causes this behavior?
A. trunk mode mismatches
B. allowing only VLAN 2 on the destination
C. native VLAN mismatches
D. VLANs that do not correspond to a unique IP subnet
Answer: C
Explanation:
Untagged frames are encapsulated with the native VLAN. In this case, the native VLANs are different so although S1 will tag it as VLAN 1 it will be received by S2.
QUESTION NO: 56
Which three statements about RSTP are true? (Choose three.)
A. RSTP significantly reduces topology reconverging time after a link failure.
B. RSTP expands the STP port roles by adding the alternate and backup roles.
C. RSTP port states are blocking, discarding, learning, or forwarding.
D. RSTP provides a faster transition to the forwarding state on point-to-point links than STP does.
E. RSTP also uses the STP proposal-agreement sequence.
F. RSTP uses the same timer-based process as STP on point-to-point links.
Answer: A,B,D
Explanation:
One big disadvantage of STP is the low convergence which is very important in switched network. To overcome this problem, in 2001, the IEEE with document 802.1w introduced an evolution of the Spanning Tree Protocol: Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP), which significantly reduces the convergence time after a topology change occurs in the network. While STP can take 30 to 50 seconds to transit from a blocking state to a forwarding state, RSTP is typically able to respond less than 10 seconds of a physical link failure.
RSTP works by adding an alternative port and a backup port compared to STP. These ports are allowed to immediately enter the forwarding state rather than passively wait for the network to converge.
RSTP bridge port roles:
* Root port– A forwarding port that is the closest to the root bridge in terms of path cost
* Designated port– A forwarding port for every LAN segment
* Alternate port– A best alternate path to the root bridge. This path is different than using the root port. The alternative port moves to the forwarding state if there is a failure on the designated port for the segment.
* Backup port– A backup/redundant path to a segment where another bridge port already connects. The backup port applies only when a single switch has two links to the same segment (collision domain). To have two links to the same collision domain, the switch must be attached to a hub.
* Disabled port– Not strictly part of STP, a network administrator can manually disable a port.
QUESTION NO: 57
At which layer of the OSI model is RSTP used to prevent loops?
A. physical
B. data link
C. network
D. transport
Answer: B
Explanation:
RSTP and STP operate on switches and are based on the exchange of Bridge Protocol Data Units
(BPDUs) between switches. One of the most important fields in BPDUs is the Bridge Priority in
which the MAC address is used to elect the Root Bridge.
RSTP operates at Layer 2 – Data Link layer.
QUESTION NO: 58
What does a Layer 2 switch use to decide where to forward a received frame?
A. source MAC address
B. source IP address
C. source switch port
D. destination IP address
E. destination port address
F. destination MAC address
Answer: F
Explanation:
When a frame is received, the switch looks at the destination hardware address and finds the interface if it is in its MAC address table. If the address is unknown, the frame is broadcast on all interfaces except the one it was received on.
QUESTION NO: 59
Refer to the exhibit.
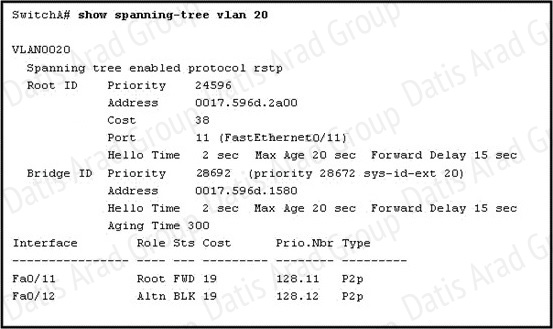
Which statement is true?
A. The Fa0/11 role confirms that SwitchA is the root bridge for VLAN 20.
B. VLAN 20 is running the Per VLAN Spanning Tree Protocol.
C. The MAC address of the root bridge is 0017.596d.1580.
D. SwitchA is not the root bridge, because not all of the interface roles are designated.
Answer: D
Explanation:
Only non-root bridge can have root port. Fa0/11 is the root port so we can confirm this switch is not the root bridge.
From the output we learn this switch is running Rapid STP, not PVST.
0017.596d.1580 is the MAC address of this switch, not of the root bridge. The MAC address of the root bridge is 0017.596d.2a00.
All of the interface roles of the root bridge are designated. SwitchA has one Root port and 1 Alternative port so it is not the root bridge.
QUESTION NO: 60
Which two benefits are provided by creating VLANs? (Choose two.)
A. added security
B. dedicated bandwidth
C. provides segmentation
D. allows switches to route traffic between subinterfaces
E. contains collisions
Answer: A,C
Explanation:
A VLAN is a switched network that is logically segmented on an organizational basis, by functions, project teams, or applications rather than on a physical or geographical basis.
Security:
VLANs also improve security by isolating groups. High-security users can be grouped into a VLAN, possible on the same physical segment, and no users outside that VLAN can communicate with them.
LAN Segmentation:
VLANs allow logical network topologies to overlay the physical switched infrastructure such that any arbitrary collection of LAN ports can be combined into an autonomous user group or community of interest. The technology logically segments the network into separate Layer 2 broadcast domains whereby packets are switched between ports designated to be within the same VLAN. By containing traffic originating on a particular LAN only to other LANs in the same VLAN, switched virtual networks avoid wasting bandwidth.