نمونه سوالات آزمون CCNA Routing & Switching 200-120
Topic 3, IP addressing (IPv4 / IPv6)
QUESTION NO: 101
What is the alternative notation for the IPv6 address
B514:82C3:0000:0000:0029:EC7A:0000:EC72?
A. B514 : 82C3 : 0029 : EC7A : EC72
B. B514 : 82C3 :: 0029 : EC7A : EC72
C. B514 : 82C3 : 0029 :: EC7A : 0000 : EC72
D. B514 : 82C3 :: 0029 : EC7A : 0 : EC72
Answer: D
Explanation:
There are two ways that an IPv6 address can be additionally compressed: compressing leading zeros and substituting a group of consecutive zeros with a single double colon (::). Both of these can be used in any number of combinations to notate the same address. It is important to note that the double colon (::) can only be used once within a single IPv6 address notation. So, the extra 0’s can only be compressed once.
QUESTION NO: 102
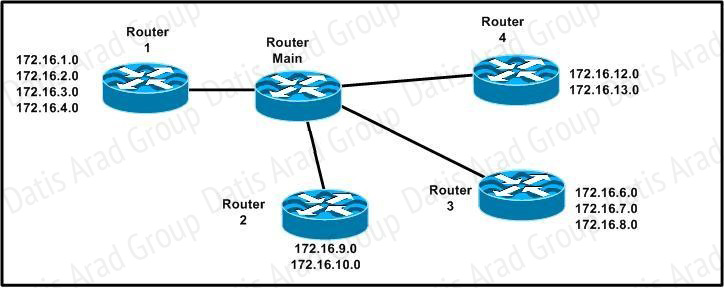
Refer to the exhibit.
All hosts have connectivity with one another. Which statements describe the addressing scheme that is in use in the network? (Choose three.)
A. The subnet mask in use is 255.255.255.192.
B. The subnet mask in use is 255.255.255.128.
C. The IP address 172.16.1.25 can be assigned to hosts in VLAN1
D. The IP address 172.16.1.205 can be assigned to hosts in VLAN1
E. The LAN interface of the router is configured with one IP address.
F. The LAN interface of the router is configured with multiple IP addresses.
Answer: B,C,F
Explanation:
The subnet mask in use is 255.255.255.128: This is subnet mask will support up to 126 hosts,
which is needed. The IP address 172.16.1.25 can be assigned to hosts in VLAN1: The usable host range in this subnet is 172.16.1.1-172.16.1.126.
The LAN interface of the router is configured with multiple IP addresses: The router will need 2 subinterfaces for the single physical interface, one with an IP address that belongs in each VLAN.
QUESTION NO: 103
Which two statements describe characteristics of IPv6 unicast addressing? (Choose two.)
A. Global addresses start with 2000::/3.
B. Link-local addresses start with FE00:/12.
C. Link-local addresses start with FF00::/10.
D. There is only one loopback address and it is ::1.
E. If a global address is assigned to an interface, then that is the only allowable address for the interface.
Answer: A,D
Explanation:
Below is the list of common kinds of IPv6 addresses:

QUESTION NO: 104
The network administrator has been asked to give reasons for moving from IPv4 to IPv6. What are two valid reasons for adopting IPv6 over IPv4? (Choose two.)
A. no broadcast
B. change of source address in the IPv6 header
C. change of destination address in the IPv6 header
D. Telnet access does not require a password
E. autoconfiguration
F. NAT
Answer: A,E
Explanation:
IPv6 does not use broadcasts, and autoconfiguration is a feature of IPV6 that allows for hosts to automatically obtain an IPv6 address.
QUESTION NO: 105
An administrator must assign static IP addresses to the servers in a network. For network 192.168.20.24/29, the router is assigned the first usable host address while the sales server is given the last usable host address. Which of the following should be entered into the IP properties
box for the sales server?
A. IP address: 192.168.20.14
Subnet Mask: 255.255.255.248
Default Gateway: 192.168.20.9
B. IP address: 192.168.20.254
Subnet Mask: 255.255.255.0
Default Gateway: 192.168.20.1
C. IP address: 192.168.20.30
Subnet Mask: 255.255.255.248
Default Gateway: 192.168.20.25
D. IP address: 192.168.20.30
Subnet Mask: 255.255.255.240
Default Gateway: 192.168.20.17
E. IP address: 192.168.20.30
Subnet Mask: 255.255.255.240
Default Gateway: 192.168.20.25
Answer: C
Explanation:
For the 192.168.20.24/29 network, the usable hosts are 192.168.24.25 (router) – 192.168.24.30 (used for the sales server).
QUESTION NO: 106
Which subnet mask would be appropriate for a network address range to be subnetted for up to eight LANs, with each LAN containing 5 to 26 hosts?
A. 0.0.0.240
B. 255.255.255.252
C. 255.255.255.0
D. 255.255.255.224
E. 255.255.255.240
Answer: D
Explanation:
For a class C network, a mask of 255.255.255.224 will allow for up to 8 networks with 32 IP
addresses each (30 usable).
QUESTION NO: 107
How many bits are contained in each field of an IPv6 address?
A. 24
B. 4
C. 8
D. 16
Answer: D
Explanation:
An IPv6 address is represented as eight groups of four hexadecimal digits, each group representing 16 bits (two octets). The groups are separated by colons (:). An example of an IPv6 address is 2001:0db8:85a3:0000:0000:8a2e:0370:7334.
QUESTION NO: 108
What are three approaches that are used when migrating from an IPv4 addressing scheme to an IPv6 scheme. (Choose three.)
A. enable dual-stack routing
B. configure IPv6 directly
C. configure IPv4 tunnels between IPv6 islands
D. use proxying and translation to translate IPv6 packets into IPv4 packets
E. statically map IPv4 addresses to IPv6 addresses
F. use DHCPv6 to map IPv4 addresses to IPv6 addresses
Answer: A,C,D
Explanation:
Several methods are used terms of migration including tunneling, translators, and dual stack. Tunnels are used to carry one protocol inside another, while translators simply translate IPv6 packets into IPv4 packets. Dual stack uses a combination of both native IPv4 and IPv6. With dual stack, devices are able to run IPv4 and IPv6 together and if IPv6 communication is possible that is the preferred protocol. Hosts can simultaneously reach IPv4 and IPv6 content.
QUESTION NO: 109
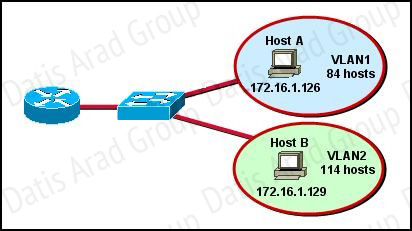
Refer to the exhibit.
In this VLSM addressing scheme, what summary address would be sent from router A?
A. 172.16.0.0 /16
B. 172.16.0.0 /20
C. 172.16.0.0 /24
D. 172.32.0.0 /16
E. 172.32.0.0 /17
F. 172.64.0.0 /16
Answer: A
QUESTION NO: 110
How is an EUI-64 format interface ID created from a 48-bit MAC address?
A. by appending 0xFF to the MAC address
B. by prefixing the MAC address with 0xFFEE
C. by prefixing the MAC address with 0xFF and appending 0xFF to it
D. by inserting 0xFFFE between the upper three bytes and the lower three bytes of the MAC address
E. by prefixing the MAC address with 0xF and inserting 0xF after each of its first three bytes
Answer: D
Explanation:
The modified EUI-64 format interface identifier is derived from the 48-bit link-layer (MAC) address by inserting the hexadecimal number FFFE between the upper three bytes (OUI field) and the lower three bytes (serial number) of the link layer address.
QUESTION NO: 111
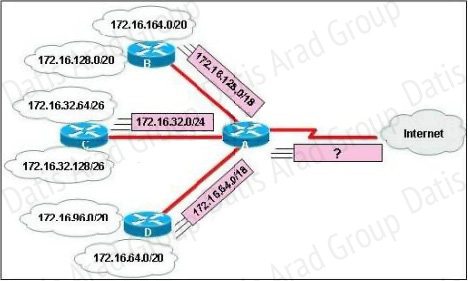
Refer to the exhibit:
What is the most efficient summarization that R1 can use to advertise its networks to R2?
A. 172.1.0.0/22
B. 172.1.0.0/21
C. 172.1.4.0/22
D. 172.1.4.0/24
172.1.5.0/24
172.1.6.0/24
172.1.7.0/24
E. 172.1.4.0/25
172.1.4.128/25
172.1.5.0/24
172.1.6.0/24
172.1.7.0/24
Answer: C
Explanation:
The 172.1.4.0/22 subnet encompasses all routes from the IP range 172.1.4.0 – 172.1.7.255.
QUESTION NO: 112
Which option is a valid IPv6 address?
A. 2001:0000:130F::099a::12a
B. 2002:7654:A1AD:61:81AF:CCC1
C. FEC0:ABCD:WXYZ:0067::2A4
D. 2004:1:25A4:886F::1
Answer: D
Explanation:
An IPv6 address is represented as eight groups of four hexadecimal digits, each group representing 16 bits (two octets). The groups are separated by colons (:). An example of an IPv6 address is 2001:0db8:85a3:0000:0000:8a2e:0370:7334. The leading 0’s in a group can be collapsed using ::, but this can only be done once in an IP address.
QUESTION NO: 113
Which three are characteristics of an IPv6 anycast address? (Choose three.)
A. one-to-many communication model
B. one-to-nearest communication model
C. any-to-many communication model
D. a unique IPv6 address for each device in the group
E. the same address for multiple devices in the group
F. delivery of packets to the group interface that is closest to the sending device
Answer: B,E,F
Explanation:
A new address type made specifically for IPv6 is called the Anycast Address. These IPv6 addresses are global addresses, these addresses can be assigned to more than one interface unlike an IPv6 unicast address. Anycast is designed to send a packet to the nearest interface that is apart of that anycast group. The sender creates a packet and forwards the packet to the anycast address as the destination address which goes to the nearest router. The nearest router or interface is found by using the metric of a routing protocol currently running on the network. However in a LAN setting the nearest interface is found depending on the order the neighbors were learned. The anycast packet in a LAN setting forwards the packet to the neighbor it learned about first.
QUESTION NO: 114
A national retail chain needs to design an IP addressing scheme to support a nationwide network.
The company needs a minimum of 300 sub-networks and a maximum of 50 host addresses per
subnet. Working with only one Class B address, which of the following subnet masks will support
an appropriate addressing scheme? (Choose two.)
A. 255.255.255.0
B. 255.255.255.128
C. 255.255.252.0
D. 255.255.255.224
E. 255.255.255.192
F. 255.255.248.0
Answer: B,E
Explanation:
Subnetting is used to break the network into smaller more efficient subnets to prevent excessive rates of Ethernet packet collision in a large network. Such subnets can be arranged hierarchically, with the organization's network address space (see also Autonomous System) partitioned into a tree-like structure. Routers are used to manage traffic and constitute borders between subnets. A routing prefix is the sequence of leading bits of an IP address that precede the portion of the address used as host identifier. In IPv4 networks, the routing prefix is often expressed as a "subnet mask", which is a bit mask covering the number of bits used in the prefix. An IPv4 subnet mask is frequently expressed in quad-dotted decimal representation, e.g., 255.255.255.0 is the subnet mask for the 192.168.1.0 network with a 24-bit routing prefix (192.168.1.0/24).
QUESTION NO: 115
Refer to the exhibit.
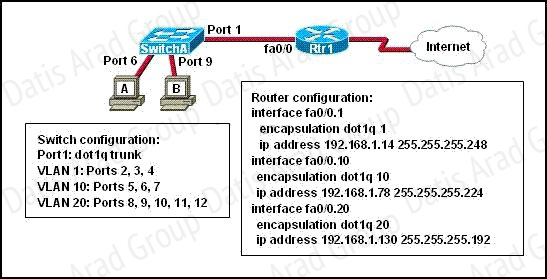
A network administrator is adding two new hosts to SwitchA. Which three values could be used for the configuration of these hosts? (Choose three.)
A. host A IP address: 192.168.1.79
B. host A IP address: 192.168.1.64
C. host A default gateway: 192.168.1.78
D. host B IP address: 192.168.1.128
E. host B default gateway: 192.168.1.129
F. host B IP address: 192.168.1.190
Answer: A,C,F
Explanation:
QUESTION NO: 116
Which IPv6 address is the all-router multicast group?
A. FF02::1
B. FF02::2
C. FF02::3
D. FF02::4
Answer: B
Explanation:
QUESTION NO: 117
Refer to the exhibit.
Which address range efficiently summarizes the routing table of the addresses for router Main?
A. 172.16.0.0./21
B. 172.16.0.0./20
C. 172.16.0.0./16
D. 172.16.0.0/18
Answer: B
Explanation:
The 172.16.0.0./20 network is the best option as it includes all networks from 172.16.0.0 – 172.16.16.0 and does it more efficiently than the /16 and /18 subnets. The /21 subnet will not include all the other subnets in this one single summarized address.
QUESTION NO: 118
Which IPv6 address is valid?
A. 2001:0db8:0000:130F:0000:0000:08GC:140B
B. 2001:0db8:0:130H::87C:140B
C. 2031::130F::9C0:876A:130B
D. 2031:0:130F::9C0:876A:130B
Answer: D
Explanation:
An IPv6 address is represented as eight groups of four hexadecimal digits, each group representing 16 bits (two octets). The groups are separated by colons (:). An example of an IPv6 address is 2001:0db8:85a3:0000:0000:8a2e:0370:7334. The leading 0’s in a group can be collapsed using ::, but this can only be done once in an IP address.
QUESTION NO: 119
Which command can you use to manually assign a static IPv6 address to a router interface?
A. ipv6 autoconfig 2001:db8:2222:7272::72/64
B. ipv6 address 2001:db8:2222:7272::72/64
C. ipv6 address PREFIX_1 ::1/64
D. ipv6 autoconfig
Answer: B
Explanation:
To assign an IPv6 address to an interface, use the “ipv6 address” command and specify the IP address you wish to use.
QUESTION NO: 120
Which of these represents an IPv6 link-local address?
A. FE80::380e:611a:e14f:3d69
B. FE81::280f:512b:e14f:3d69
C. FEFE:0345:5f1b::e14d:3d69
D. FE08::280e:611:a:f14f:3d69
Answer: A
Explanation:
In the Internet Protocol Version 6 (IPv6), the address block fe80::/10 has been reserved for linklocal unicast addressing. The actual link local addresses are assigned with the prefix fe80::/64. They may be assigned by automatic (stateless) or stateful (e.g. manual) mechanisms.