s
نمونه سوالات آزمون CCIE Routing and Switching 400-101
QUESTION NO: 91
Which protocol is the encapsulating protocol for mtrace packets?
A. ICMP
B. IGMP
C. PIM
D. GRE
Answer: B
Explanation:
“mtrace” is a diagnostic tool to trace the multicast path from a specified source to a destination for a multicast group. It runs over IGMP protocol. Mtrace uses any information available to it to determine a previous hop to forward the trace towards the source. Reference.
QUESTION NO: 92
Assume that the following MAC addresses are used for the bridge ID MAC address by four different switches in a network. Which switch will be elected as the spanning-tree root bridge?
A. SwitchA uses MAC 1000.AA-AA-AA-AA-AA-AA.
B. SwitchB uses MAC 2000.BB-BB-BB-BB-BB-BB.
C. SwitchC uses MAC 3000.CC-CC-CC-CC-CC-CC.
D. SwitchD uses MAC 4000.DD-DD-DD-DD-DD-DD.
Answer: A
Explanation:
The switch with the highest switch priority (the lowest numerical priority value) is elected as the root switch. If all switches are configured with the default priority (32768), the switch with the lowest MAC address in the VLAN becomes the root switch.
QUESTION NO: 93
What is the destination MAC address of a BPDU frame?
A. 01-80-C2-00-00-00
B. 01-00-5E-00-00-00
C. FF-FF-FF-FF-FF-FF
D. 01-80-C6-00-00-01
Answer: A
Explanation:
The root-bridge election process begins by having every switch in the domain believe it is the root and claiming it throughout the network by means of Bridge Protocol Data Units (BPDU). BPDUs are Layer 2 frames multicast to a well-known MAC address in case of IEEE STP (01-80-C2-00-00- 00) or vendor-assigned addresses, in other cases.
QUESTION NO: 4
Refer to the exhibit.
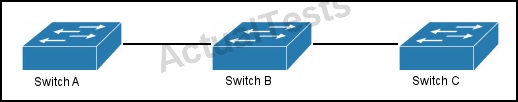
All switches are Cisco switches. Assume that Cisco Discovery Protocol is enabled only on switches A and C.
Which information is returned when you issue the command show cdp neighbors on switch C?
A. a limited amount of information about switch B
B. no neighbor details will be returned
C. neighbor details for switch B
D. neighbor details for switch A
E. neighbor details for switch C
Answer: B
Explanation:
CDP is used to discover information on directly connected neighbors only, so in this case SwitchC would only be able to obtain CDP information from SwitchB. However, since SwitchB is not running CDP then no neighbor information will be seen on SwitchC. Same goes for Switch A also in this topology.
QUESTION NO: 95
Which two features are supported when Cisco HDLC is implemented? (Choose two.)
A. error recovery
B. error detection
C. asynchronous links
D. multiple protocols
Answer: B,D
Explanation:
HDLC’s frame check sequence (FCS) is a 16-bit CRC-CCITT or a 32-bit CRC-32 computed over the Address, Control, and Information fields. It provides a means by which the receiver can detect errors that may have been induced during the transmission of the frame, such as lost bits, flipped bits, and extraneous bits.
Cisco’s HDLC contains a proprietary field that is used to support multiple protocols.
QUESTION NO: 96
Refer to the exhibit.
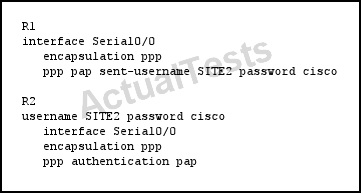 With these configurations for R1 and R2, which statement about PPP authentication is true?
With these configurations for R1 and R2, which statement about PPP authentication is true?
A. Authentication fails because R1 is missing a username and password.
B. R2 responds with the correct authentication credentials.
C. R2 requires authentication from R1.
D. R1 requires authentication from R2.
Answer: C
Explanation:
Tail Drop
Only R2 is configured with the “PPP authentication PAP” command so it requires authentication from R1, but R1 does not require authentication from R2.
QUESTION NO: 97
Refer to the exhibit.
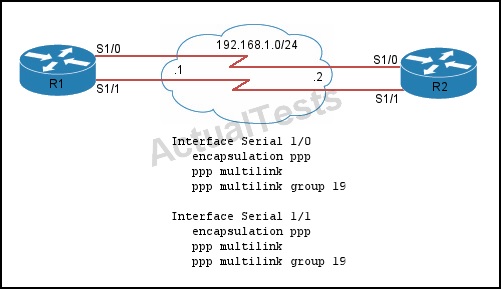 You must complete the configuration on R1 so that a maximum of three links can be used and fragmentation is supported.
You must complete the configuration on R1 so that a maximum of three links can be used and fragmentation is supported.
Which additional configuration accomplishes this task?
A. interface Multilink19
ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0
ppp multilink
ppp multilink group 19
ppp multilink links minimum 1
ppp multilink links maximum 3
ppp multilink interleave
B. interface Multilink19
ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0
ppp multilink
ppp multilink group 19
ppp multilink links maximum 3
ppp multilink fragment delay 20
C. interface Multilink19
ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0
ppp multilink
ppp multilink group 19
ppp multilink links maximum 3
ppp multilink fragment delay 20
ppp multilink interleave
D. interface Multilink19
ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.252
ppp multilink
ppp multilink group 19
ppp multilink links maximum 3
ppp multilink interleave
Answer: A
Explanation:
The “ppp multilink interleave” command is needed to enable link fragmentation and Interleaving (LFI). The Cisco IOS Link Fragmentation and Interleaving (LFI) feature uses Multilink PPP (MLP). MLP provides a method of splitting, recombining, and sequencing datagrams across multiple logical data links. MLP allows packets to be fragmented and the fragments to be sent at the same time over multiple point-to-point links to the same remote address.
ppp multilink links maximum
To limit the maximum number of links that Multilink PPP (MLP) can dial for dynamic allocation, use the ppp multilink links maximum command in interface configuration mode.
QUESTION NO: 98
Refer to the exhibit.
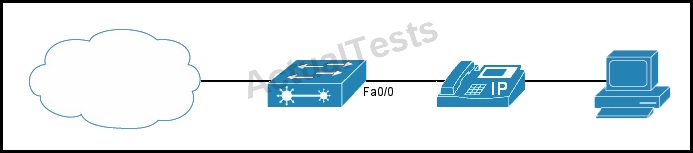 Which statement about configuring the switch to manage traffic is true?
Which statement about configuring the switch to manage traffic is true?
A. The switchport priority extend cos command on interface FastEthernet0/0 prevents traffic to
and from the PC from taking advantage of the high-priority data queue that is assigned to the IP phone.
B. The switchport priority extend cos command on interface FastEthernet0/0 enables traffic to and from the PC to use the high priority data queue that is assigned to the IP phone.
C. When the switch is configured to trust the CoS label of incoming traffic, the trusted boundary feature is disabled automatically.
D. The mls qos cos override command on interface FastEthernet0/0 configures the port to trust the CoS label of traffic to and from the PC.
Answer: A
Explanation:
In some situations, you can prevent a PC connected to the Cisco IP Phone from taking advantage of a high-priority data queue. You can use the switchport priority extend cos interface configuration command to configure the telephone through the switch CLI to override the priority of the traffic received from the PC.
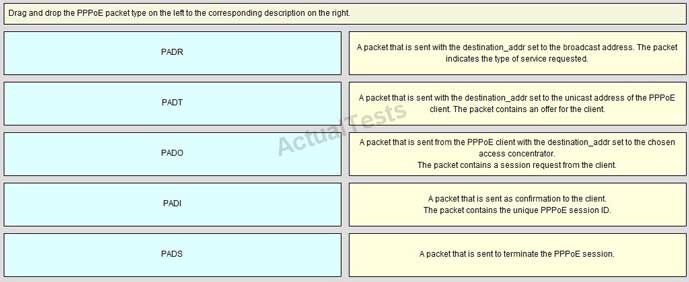
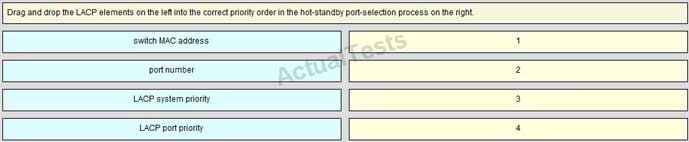
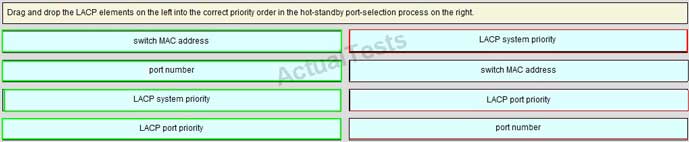
QUESTION NO: 99 Drag & Drop
Answer:
QUESTION NO: 100
What is the destination multicast MAC address for BPDUs on the native VLAN, for a switch that is running 802.1D?
A. 0185. C400. 0000
B. 0100.0CCC.CCCC
C. 0100.0CCC.CCCD
D. 0180.C200.0000
Answer: D
Explanation:
If the native vlan is 1:A STP BPDU for VLAN 1 will be sent untagged to MAC 0180.c200.0000 (this is the common spanning tree)A PVST+ BPDU for VLAN 1 will be sent untagged to MAC 0100.0ccc.cccdA PVST+ BPDU for all other vlans will be sent with a 802.1Q tag to MAC 0100.0ccc.cccd (with a PVID = to the VLAN)If the native vlan is not 1:A STP BPDU for VLAN 1 will be sent untagged (on the native vlan) to MAC 0180.c200.0000 (this is the common spanning tree)A PVST+ BPDU for VLAN1 will be sent with a 802.1Q tag to MAC 0100.0ccc.cccd (with a PVID=1)A PVST+ BPDU for the native vlan will be sent untagged to MAC 0100.0ccc.cccd (with a PVID=native vlan)A PVST+ BPDU for all other vlans will be sent with a 802.1Q tag to MAC 0100.0ccc.cccd (with a PVID = to the VLAN)
QUESTION NO: 101
Refer to the exhibit.
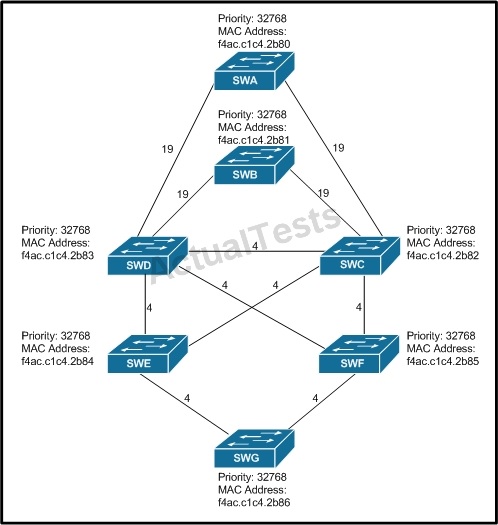
All switches have default bridge priorities, and originate BPDUs with MAC addresses as indicated. The numbers shown are STP link metrics.
After STP converges, you discover that traffic from switch SWG toward switch SWD takes a less optimal path. What can you do to optimize the STP tree in this switched network?
A. Change the priority of switch SWA to a lower value than the default value.
B. Change the priority of switch SWB to a higher value than the default value.
C. Change the priority of switch SWG to a higher value than the default value.
D. Change the priority of switch SWD to a lower value than the default value.
Answer: D
Explanation:
In this topology, we see that all port paths and priorities are the same, so the lowest MAC address will be used to determine the best STP path. From SWG, SWE will be chosen as the next switch in the path because it has a lower MAC address than SWF. From SWE, traffic will go to SWC because it has a lower MAC address, and then to SWD, instead of going from SWE directly to SWD. If we lower the priority of SWD (lower means better with STP) then traffic will be sent directly to SWD.
QUESTION NO: 102
Which three statements are true about VSS? (Choose three.)
A. VSS separates the control planes of the active and the standby chassis.
B. Configuration changes can be made on both active and standby chassis.
C. When the VSS active chassis recovers after a failure, it initiates a switchover and takes on the active role again.
D. VSS unifies the control planes of the active and the standby chassis.
E. HSRP configuration is not required to run VSS.
F. The VSS standby chassis monitors the VSS active chassis using the VSL.
Answer: D,E,F
Explanation:
VSS operates on a unified control plane with a distributed forwarding architecture in which the active supervisor (or switch) is responsible for actively participating with the rest of the network and for managing and maintaining control plane information.
VSS actually removes the need for a next-hop redundancy protocol like HSRP or VRRP. These first-hop redundancy protocols are usually heavily tied to a fast-converging routing protocol like EIGRP, and still require that each device maintain it’s own control plane. The standby chassis monitors the active chassis using the VSL. If it detects failure, the standby chassis initiates a switchover and takes on the active role. When the failed chassis recovers, it takes on the standby role.
QUESTION NO: 103
Which flag in a configuration BPDU instructs all switches to shorten their bridge table aging process from the default 300 seconds to the current forward delay value?
A. topology change bit
B. topology change acknowledgment bit
C. priority bit
D. max-age bit
Answer: A
Explanation:
The Root Bridge continues to set the Topology Change flag (TCN bit) in all Configuration BPDUs that it sends out for a total of Forward Delay + Max Age seconds (default = 35 (20+15) seconds). This flag instructs all bridges to shorten their MAC address table (Bridge table) aging process from the default value of 300 seconds to the current Forward Delay value of the bridge (default=15 seconds).
The TCA flag is set by the upstream bridge to tell the downstream bridges to stop sending TCN BPDUs. The TC flag is set in configuration BPDU by the Root Bridge to shorten the bridge table age-out period from default 300 seconds to Forward Delay seconds.
QUESTION NO: 104
Refer to the exhibit.
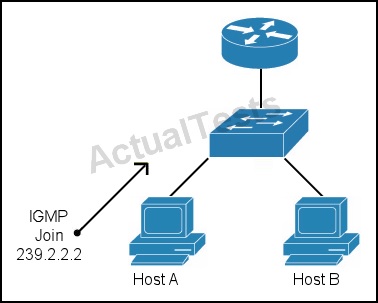 Which technology can be used on the switch to enable host A to receive multicast packets for 239.2.2.2 but prevent host B from receiving them?
Which technology can be used on the switch to enable host A to receive multicast packets for 239.2.2.2 but prevent host B from receiving them?
A. IGMP filtering
B. MLD snooping
C. IGMP snooping
D. MLD filtering
Answer: C
Explanation:
IGMP snooping is the process of listening to Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP) network traffic. The feature allows a network switch to listen in on the IGMP conversation between hosts and routers. By listening to these conversations the switch maintains a map of which links need which IP multicast streams. Multicasts may be filtered from the links which do not need them and thus controls which ports receive specific multicast traffic.
QUESTION NO: 105
Which option describes the purpose of the PPP endpoint discriminator?
A. It identifies the maximum payload packet.
B. It notifies the peer that it prefers 12-bit sequence numbers.
C. It identifies the system attached to the link.
D. It determines whether a loopback is on the link.
Answer: C
Explanation:
In situations in which many clients use the same username to initiate an MP connection, or when interoperating with non-Cisco routers, you need to control the order in which the bundle name is created. It is necessary to configure the access server to create a bundle name based on the endpoint discriminator first, the username second, or both. The endpoint discriminator identifies the system transmitting the packet and advises the network access server (NAS) that the peer on this link could be the same as the peer on another existing link. Because every client has a unique endpoint discriminator, only multiple links from the same client are bundled into a single unique MP connection. For example, consider when two PC clients initiate a multilink connection to an access server using the same username. If the multilink bundle name is established based on the endpoint discriminator first, then on the username or on both, the NAS can accurately bundle the links from each client using the endpoint discriminator as a bundle name. This bundle name is unique to the peer system transmitting the packet.
QUESTION NO: 106
Which three statements about SPAN traffic monitoring are true? (Choose three.)
A. Traffic from a non-source VLAN is discarded when it arrives on a source VLAN.
B. Multiple sessions can send traffic to an individual destination port.
C. It supports up to 32 SPAN ports per switch.
D. The destination port acts as a normal switchport.
E. It supports up to 64 SPAN ports per switch.
F. Only one session can send traffic to an individual destination port.
Answer: A,E,F
Explanation:
You can create up to a total of 64 SPAN and ERSPAN sessions to define sources and destinations on the local device.You can also create a SPAN session to monitor multiple VLAN sources and choose only VLANs of interest to transmit on multiple destination ports. For example, you can configure SPAN on a trunk port and monitor traffic from different VLANs on different destination ports.
You can configure a particular destination port in only one SPAN session.
Traffic from a non-source VLAN is discarded when it arrives on a source VLAN
QUESTION NO: 107
Which option describes how a VTPv3 device responds when it detects a VTPv2 device on a trunk port?
A. It sends VTPv3 packets only.
B. It sends VTPv2 packets only.
C. It sends VTPv3 and VTPv2 packets.
D. It sends a special packet that contains VTPv3 and VTPv2 packet information.
Answer: C
Explanation:
When a VTP version 3 device on a trunk port receives messages from a VTP version 2 device, the VTP version 3 device sends a scaled-down version of the VLAN database on that particular trunk in a VTP version 2 format. A VTP version 3 device does not send out VTP version 2-formatted packets on a trunk port unless it first receives VTP version 2 packets on that trunk. If the VTP version 3 device does not receive VTP version 2 packets for an interval of time on the trunk port, the VTP version 3 device stops transmitting VTP version 2 packets on that trunk port. Even when a VTP version 3 device detects a VTP version 2 device on a trunk port, the VTP version 3 device continues to send VTP version 3 packets in addition to VTP version 3 device 2 packets, to allow two kinds of neighbors to coexist on the trunk. VTP version 3 sends VTP version 3 and VTP version 2 updates on VTP version 2-detected trunks.
QUESTION NO: 108
Which three statements about bridge assurance are true? (Choose three.)
A. Bridge assurance must be enabled on both ends of a link.
B. Bridge assurance can be enabled on one end of a link or on both ends.
C. Bridge assurance is enabled on STP point-to-point links only.
D. Bridge assurance is enabled on STP multipoint links only.
E. If a bridge assurance port fails to receive a BPDU after a timeout, the port is put into a blocking state.
F. If a bridge assurance port fails to receive a BPDU after a timeout, the port is put into an error disabled state.
Answer: A,C,E
Explanation:
Bridge Assurance is enabled by default and can only be disabled globally. Also, Bridge Assurance can be enabled only on spanning tree network ports that are point-to-point links. Finally, both ends of the link must have Bridge Assurance enabled.
With Bridge Assurance enabled, BPDUs are sent out on all operational network ports, including alternate and backup ports, for each hello time period. If the port does not receive a BPDU for a specified period, the port moves into the blocking state and is not used in the root port calculation. Once that port receives a BPDU, it resumes the normal spanning tree transitions.
QUESTION NO: 109
What is the hop limit for an MLD message?
A. 1
B. 2
C. 15
D. 255
Answer: A
Explanation:
MLD uses the Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) to carry its messages. All MLD messages are link-local with a hop limit of 1, and they all have the alert option set. The alert option implies an implementation of the hop-by-hop option header.
QUESTION NO: 110
Refer to the exhibit.
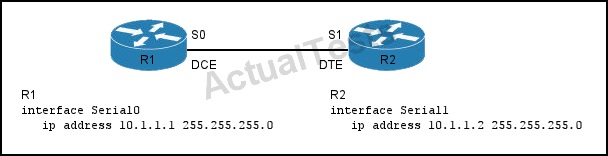
Which action must you take to enable the WAN link to function properly?
A. Enter a clock rate on the DCE interface.
B. Enter a clock rate on the DTE interface.
C. Enter a compression algorithm on both interfaces.
D. Configure both interfaces for HDLC encapsulation.
Answer: A
Explanation:
When connecting a serial cable to the serial interface of the router, clocking is provided by an external device, such as a CSU/DSU device. A CSU/DSU (Channel Service Unit/Data Service Unit) is a digital-interface device used to connect a router to a digital circuit. The router is the DTE (Data Terminal Equipment) and the external device is the DCE (Data Communications Equipment), where the DCE provides the clocking. However, in some cases we might connect two routers back-to-back using the routers’ serial interfaces (ExamplE. Inside the router labs). Each router is a DTE by default.
Since clocking is required to enable the interface, one of the two routers should function as DCE and should provide clocking. This can be done by using the "clock rate" command, from the interface configuration mode.
QUESTION NO: 111
Which two options are the two main phases of PPPoE? (Choose two.)
A. Active Discovery Phase
B. IKE Phase
C. Main Mode Phase
D. PPP Session Phase
E. Aggressive Mode Phase
F. Negotiation Phase
Answer: A,D
Explanation:
PPPoE is composed of two main phases:
Active Discovery Phase—In this phase, the PPPoE client locates a PPPoE server, called an access concentrator. During this phase, a Session ID is assigned and the PPPoE layer is established.
PPP Session Phase—In this phase, PPP options are negotiated and authentication is performed. Once the link setup is completed, PPPoE functions as a Layer 2 encapsulation method, allowing data to be transferred over the PPP link within PPPoE headers.
QUESTION NO: 112
Which three statements about EVCs are true? (Choose three.)
A. Spanning Tree must use MST mode on EVC ports.
B. PAGP is supported on EVC ports.
C. Spanning Tree must use RSTP mode on EVC ports.
D. LACP is supported on EVC ports.
E. Layer 2 multicast framing is supported.
F. Bridge domain routing is required.
Answer: A,B,D
Explanation:
EVC support requires the following:
–The spanning tree mode must be MST.
–The dot1ad global configuration mode command must be configured.
These Layer 2 port-based features can run with EVC configured on a port:
–PAGP
–LACP
–UDLD
–LLDP
–CDP
–MSTP
QUESTION NO: 113 Drag & Drop
Answer:
QUESTION NO: 114
Which statement about Cisco Discovery Protocol is true?
A. The multicast address 0100.0cdd.dddd is used as the destination address for periodic advertisements.
B. An inactive VLAN that is configured on an access port passes periodic Cisco Discovery Protocol advertisements.
C. The multicast address 0100.0ccc.ccd is used as the destination address for periodic advertisements.
D. A VLAN must be active on an access port before periodic Cisco Discovery Protocol advertisements are passed.
Answer: D
Explanation:
All CDP packets include a VLAN ID. If you configure CDP on a Layer 2 access port, the CDP packets sent from that access port include the access port VLAN ID. If you configure CDP on a Layer 2 trunk port, the CDP packets sent from that trunk port include the lowest configured VLAN ID allowed on that trunk port.
CDP messages on the active physical interfaces (Ethernet NIC) to a well-known multicast address (0100.0CCC.CCCC.
QUESTION NO: 115
Which three TLVs does LLDP use to discover network devices? (Choose three.)
A. Management address
B. Port description
C. Network policy
D. System name
E. Location information
F. Power management
Answer: A,B,D
QUESTION NO: 116
Which command enables L2 QoS support in all VLANs (including the native VLAN)?
A. switchport priority extend cos
B. mls qos trust dscp
C. mls qos rewrite ip dscp
D. switchport trunk native vlan tag
Answer: D
Explanation:
You can enter the switchport trunk native vlan tag command to enable the tagging of native VLAN traffic on a per-port basis. When tagging is enabled, all the packets on the native VLAN are tagged and all incoming untagged data packets are dropped, but untagged control packets are accepted. When tagging is enabled, it will allow for L2 QoS support in all VLANs, including the native VLAN.
QUESTION NO: 117
Which three modes are valid for forming an EtherChannel between the ports of two switches? (Choose three.)
A. Active/active
B. Active/passive
C. Passive/passive
D. Auto/auto
E. Auto/desirable
F. Desirable/on
Answer: A,B,E
Explanation:
To configure an EtherChannel using LACP negotiation, each side must be set to either active or passive; only interfaces configured in active mode will attempt to negotiate an EtherChannel. Passive interfaces merely respond to LACP requests. PAgP behaves the same, but its two modes are refered to as desirable and auto.

QUESTION NO: 118
In which 802.1D port state are the root bridge, the root port, and the designated port(s) elected?
A. Listening
B. learning
C. forwarding
D. blocking
E. disabled
Answer: A
QUESTION NO: 119
In a network where a Layer 2 switch interconnects several routers, which feature restricts multicast packets for each IP multicast group to only those mulicast router ports that have downstream receivers joined to that group?
A. PIM snooping
B. IGMP snooping
C. IGMP filter
D. IGMP proxy
Answer: A
Explanation:
In networks where a Layer 2 switch interconnects several routers, such as an Internet exchange point (IXP), the switch floods IP multicast packets on all multicast router ports by default, even if there are no multicast receivers downstream. With PIM snooping enabled, the switch restricts multicast packets for each IP multicast group to only those multicast router ports that have downstream receivers joined to that group. When you enable PIM snooping, the switch learns which multicast router ports need to receive the multicast traffic within a specific VLAN by listening to the PIM hello messages, PIM join and prune messages, and bidirectional PIM designated forwarder-election messages.
QUESTION NO: 120
Which three statements about Cisco HDLC are true? (Choose three.)
A. HDLC serial encapsulation provides asynchronous framing and error detection.
B. Serial link keepalives are maintained by SLARP.
C. HDLC serial encapsulation provides synchronous framing without retransmission.
D. HDLC frame size can be reduced with MPPC compression.
E. The interface is brought down after five ignored keepalives.
F. The interface is brought down after three ignored keepalives.
Answer: B,C,F
Explanation:
Cisco High-Level Data Link Controller (HDLC) is the Cisco proprietary protocol for sending data over synchronous serial links using HDLC. Cisco HDLC also provides a simple control protocol called Serial Line Address Resolution Protocol (SLARP) to maintain serial link keepalives. For each encapsulation type, a certain number of keepalives ignored by a peer triggers the serial interface to transition to the down state. For HDLC encapsulation, three ignored keepalives causes the interface to be brought down.
By default, synchronous serial lines use the High-Level Data Link Control (HDLC) serial encapsulation method, which provides the synchronous framing and error detection functions of HDLC without windowing or retransmission.