نمونه سوالات آزمون CCIE Routing and Switching 400-101
QUESTION NO: 61
Refer to the exhibit.
 While troubleshooting high CPU utilization on one of your Cisco Catalyst switches, you find that the issue is due to excessive flooding that is caused by STP. What can you do to prevent this issue from happening again?
While troubleshooting high CPU utilization on one of your Cisco Catalyst switches, you find that the issue is due to excessive flooding that is caused by STP. What can you do to prevent this issue from happening again?
A. Disable STP completely on the switch.
B. Change the STP version to RSTP.
C. Configure PortFast on port-channel 1.
D. Configure UplinkFast on the switch.
E. Configure PortFast on interface Gi0/15.
Answer: E
Explanation:
Topology Changes (TC) should be a rare event in a well-configured network. When a link on a switch port goes up or down, there is eventually a TC, once the STP state of the port is changing to or from forwarding. When the port is flapping, this would cause repetitive TCs and flooding. Ports with the STP portfast feature enabled will not cause TCs when going to or from the forwarding state. The configuration of portfast on all end-device ports (such as printers, PCs, and servers) should limit TCs to a low amount and is highly recommended.
QUESTION NO: 62
Refer to the exhibit.
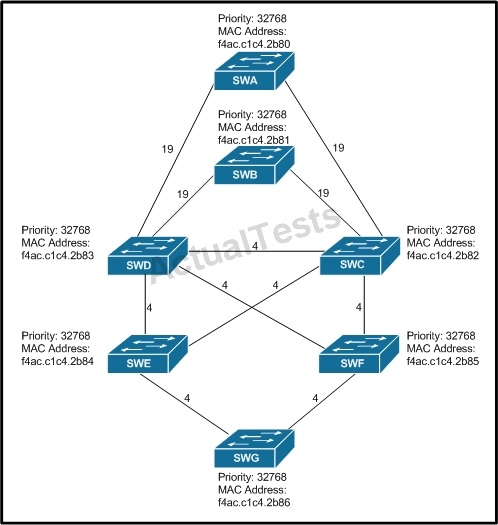
All switches have default bridge priorities, and originate BPDUs with MAC addresses as indicated. The numbers shown are STP link metrics. Which two ports are forwarding traffic after STP converges? (Choose two.)
A. The port connecting switch SWD with switch SWE B. The port connecting switch SWG with switch SWF C. The port connecting switch SWC with switch SWE D. The port connecting switch SWB with switch SWC
Answer: C,D
Explanation:
Here, we know SWB to SWC are forwarding because we already identified the blocking port. So for the last correct answer let’s consider what must be done to prevent a switch loop between SWC/SWD/SWE. SWE to SWD will be blocked because SWC has a lower MAC address so it wins the forwarding port. And to look at it further, you could try to further understand what would happen with ports on SWG. Would the ports on SWG try to go through SWE or SWF? SWE has the lower MAC address so the port from SWG to SWE would win the forwarding election.
Therefore, answer B could never be correct.
QUESTION NO: 63
Refer to the exhibit.
 Which three statements about the output are true? (Choose three.)
Which three statements about the output are true? (Choose three.)
A. An mrouter port can be learned by receiving a PIM hello packet from a multicast router.
B. This switch is configured as a multicast router.
C. Gi2/0/1 is a trunk link that connects to a multicast router.
D. An mrouter port is learned when a multicast data stream is received on that port from a multicast router.
E. This switch is not configured as a multicast router. It is configured only for IGMP snooping.
F. IGMP reports are received only on Gi2/0/1 and are never transmitted out Gi2/0/1 for VLANs 10 and 20.
Answer: A,B,C
Explanation:
In this example, the switch has been configured as a multicast router since IGMP snooping has been enabled. All mrouters can learn about other mrouters by receiving a PIM hello packet from another multicast router. Also, since two different VLANs are being used by the same port of gi 2/0/1, it must be a trunk link that connects to another multicast router.
QUESTION NO: 64
Refer to the exhibit.

If a port is configured as shown and receives an untagged frame, of which VLAN will the untagged frame be a member?
A. VLAN 1
B. VLAN 2
C. VLAN 3
D. VLAN 4
Answer: B
Explanation:
When typing:
Switch(config-if)#switchport mode ?
access Set trunking mode to ACCESS unconditionally
dynamic Set trunking mode to dynamically negotiate access or trunk mode
trunk Set trunking mode to TRUNK unconditionally
and
Switch(config-if)#switchport mode dynamic ?
auto Set trunking mode dynamic negotiation parameter to AUTO
desirable Set trunking mode dynamic negotiation parameter to DESIRABLE So if we configure Fa0/1 as dynamic auto mode, it will not initiate any negotitation but waiting for the other end negotiate to be a trunk with DTP. If the other end does not ask it to become a trunk then it will become an access port. Therefore when using the “show interface fastEthernet0/1 switchport” command we will see two output lines “Administrative ModE. dynamic auto” and “ Operational ModE. static access“
NotE. To set this port to VLAN 2 as the output above just use one additional commanD. “switchport access vlan 2.
Now back to our question, from the output we see that Fa0/1 is operating as an access port on VLAN 2 so if it receive untagged frame it will suppose that frame is coming from VLAN 2.
QUESTION NO: 65
Refer to the exhibit.
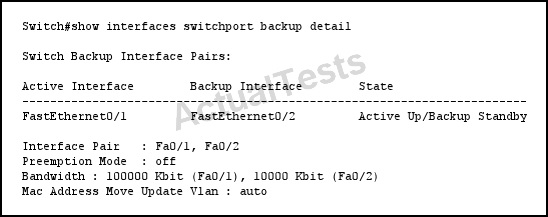 Which statement describes the effect on the network if FastEthernet0/1 goes down temporarily?
Which statement describes the effect on the network if FastEthernet0/1 goes down temporarily?
A. FastEthernet0/2 forwards traffic only until FastEthernet0/1 comes back up.
B. FastEthernet0/2 stops forwarding traffic until FastEthernet0/1 comes back up.
C. FastEthernet0/2 forwards traffic indefinitely.
D. FastEthernet0/1 goes into standby.
Answer: C
Explanation:
Use the switchport backup interface interface configuration command on a Layer 2 interface to configure Flex Links, a pair of interfaces that provide backup to each other. Use the no form of this command to remove the Flex Links configuration.
With Flex Links configured, one link acts as the primary interface and forwards traffic, while the other interface is in standby mode, ready to begin forwarding traffic if the primary link shuts down. The interface being configured is referred to as the active link; the specified interface is identified as the backup link. The feature provides an alternative to the Spanning Tree Protocol (STP), allowing users to turn off STP and still retain basic link redundancy.
QUESTION NO: 66
Refer to the exhibit.
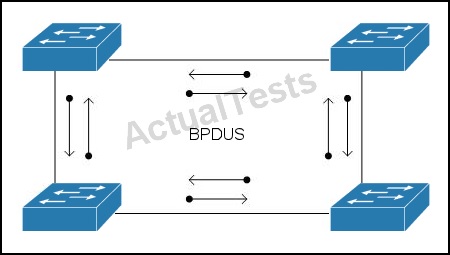 Which technology does the use of bi-directional BPDUs on all ports in the topology support?
Which technology does the use of bi-directional BPDUs on all ports in the topology support?
A. RSTP
B. MST
C. Bridge Assurance
D. Loop Guard
E. Root Guard
F. UDLD
Answer: C
Explanation:
Spanning Tree Bridge Assurance
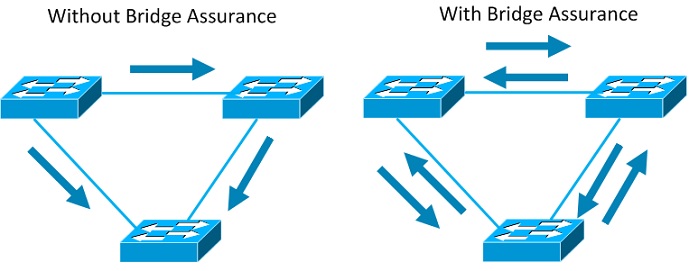
Bridge Assurance (BA) can help protect against bridging loops where a port becomesdesignated because it has stopped receiving BPDUs. This is similar to the functionof loop guard.
QUESTION NO: 67
Which three statements are true about PPP CHAP authentication? (Choose three.)
A. PPP encapsulation must be enabled globally.
B. The LCP phase must be complete and in closed state.
C. The hostname used by a router for CHAP authentication cannot be changed.
D. PPP encapsulation must be enabled on the interface.
E. The LCP phase must be complete and in open state.
F. By default, the router uses its hostname to identify itself to the peer.
Answer: D,E,F
Explanation:
Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP) authentication issues are one of the most common causes for dialup link failures. This document provides some troubleshooting procedures for PPP authentication issues.
QUESTION NO: 68
Which two statements are true about an EPL? (Choose two.)
A. It is a point-to-point Ethernet connection between a pair of NNIs.
B. It allows for service multiplexing.
C. It has a high degree of transparency.
D. The EPL service is also referred to as E-line.
Answer: C,D
Explanation:
Ethernet private line (EPL) and Ethernet virtual private line (EVPL) are carrier Ethernet data services defined by the Metro Ethernet Forum. EPL provides a point-to-point Ethernet virtual connection (EVC) between a pair of dedicated user–network interfaces (UNIs), with a high degree of transparency. EVPL provides a point-to-point or point-to-multipoint connection between a pair of UNIs.
QUESTION NO: 69
Which two statements describe characteristics of HDLC on Cisco routers? (Choose two.)
A. It supports multiple Layer 3 protocols.
B. It supports multiplexing.
C. It supports only synchronous interfaces.
D. It supports authentication.
Answer: A,C
Explanation:
Cisco High-Level Data Link Controller (HDLC) is the Cisco proprietary protocol for sending data over synchronous serial links using HDLC. Cisco HDLC also provides a simple control protocol called Serial Line Address Resolution Protocol (SLARP) to maintain serial link keepalives. Cisco HDLC is the default for data encapsulation at Layer 2 (data link) of the Open System Interconnection (OSI) stack for efficient packet delineation and error control.
The absence of a protocol type field in the HDLC header posed a problem for links that carried traffic from more than one Layer 3 protocol. Cisco, therefore, added an extra Type field to the HDLC header, creating a Cisco-specific version of HDLC. Cisco routers can support multiple network layer protocols on the same HDLC link. For example an HDLC link between two Cisco routers can forward both IPv4 and IPv6 packets because the Type field can identify which type of packet is carried inside each HDLC frame.
QUESTION NO: 70
Which mechanism can be used on Layer 2 switches so that only multicast packets with downstream receivers are sent on the multicast router-connected ports?
A. IGMP snooping
B. Router Guard
C. PIM snooping
D. multicast filtering
Answer: C
Explanation:
Ideally, the Layer 2 device should forward the multicast transmission only out ports to which receivers are connected and also out any ports that are connected to downstream multicast routers. This configuration requires a Layer 2 device to be able to determine the ports on which multicast routers and receivers for each separate (S,G) or (*,G) multicast group are located. To facilitate intelligent forwarding of multicast traffic on the LAN, Cisco Catalyst switches support two mechanisms.
QUESTION NO: 71
Which technology can be used to prevent flooding of IPv6 multicast traffic on a switch?
A. IGMP snooping
B. IGMP filtering
C. MLD snooping
D. MLD filtering
Answer: C
Explanation:
MLD snooping allows the switch to examine MLD packets and make forwarding decisions based on their content.
You can configure the switch to use MLD snooping in subnets that receive MLD queries from either MLD or the MLD snooping querier. MLD snooping constrains IPv6 multicast traffic at Layer 2 by configuring Layer 2 LAN ports dynamically to forward IPv6 multicast traffic only to those ports that want to receive it.
QUESTION NO: 72
Refer to the exhibit.
 Which VLANs are permitted to send frames out port FastEthernet0/1?
Which VLANs are permitted to send frames out port FastEthernet0/1?
A. 100 - 200
B. 4 - 100
C. 1 and 4 - 100
D. 3 and 4 - 100
Answer: D
Explanation:
Traffic on the native vlan does not get tagged as it crosses a trunk, so there is no dot1q tag in the first place to be filtered. And you don’t need to allow the native vlan. But if we force to tag the native vlan (with the “switchport trunk native vlan tag” command) then if the native vlan is not in the “allowed vlan” list it will be dropped.
QUESTION NO: 73
Which option is the default maximum age of the MAC address table?
A. 300 seconds
B. 500 seconds
C. 1200 seconds
D. 3600 seconds
Answer: A
QUESTION NO: 74
Refer to the exhibit.
 Which two statements about the output are true? (Choose two.)
Which two statements about the output are true? (Choose two.)
A. 802.1D spanning tree is being used.
B. Setting the priority of this switch to 0 for VLAN 1 would cause it to become the new root.
C. The hello, max-age, and forward delay timers are not set to their default values.
D. Spanning-tree PortFast is enabled on GigabitEthernet1/1.
Answer: A,B
Explanation:
802.1D is the standard for Spanning tree, which is being used here. For priority, The priority order starts from 0 (yes, 0 is valid) and then increases in 4096.
0, 4096, 8192, 12288, …. Etc.
The lower the number, the higher the priority. Here we see that the current root has a priority of 8192, so configuring this with a priority of 0 will make it the new root.
QUESTION NO: 75
Which statement is true about Fast Link Pulses in Ethernet?
A. They are used during collision detection.
B. They are used only if the media type is optical.
C. They are part of UniDirectional Link Detection.
D. They are used during autonegotiation.
Answer: D
Explanation:
To make sure that your connection is operating properly, IEEE 802.3 Ethernet employs normal link pulses (NLPs), which are used for verifying link integrity in a 10BaseT system. This signaling gives you the link indication when you attach to the hub and is performed between two directly connected link interfaces (hub-to-station or station-to-station). NLPs are helpful in determining that a link has been established between devices, but they are not a good indicator that your cabling is free of problems.
An extension of NLPs is fast link pulses. These do not perform link tests, but instead are employed in the autonegotiation process to advertise a device's capabilities.
QUESTION NO: 76
Which statement is true regarding UDLD and STP timers?
A. The UDLD message timer should be two times the STP forward delay to prevent loops.
B. UDLD and STP are unrelated features, and there is no relation between the timers.
C. The timers need to be synced by using the spanning-tree udld-sync command.
D. The timers should be set in such a way that UDLD is detected before the STP forward delay expires.
Answer: D
Explanation:
UDLD is designed to be a helper for STP. Therefore, UDLD should be able to detect an unidirectional link before STP would unblock the port due to missed BPDUs. Thus, when you configure UDLD timers, make sure your values are set so that unidirectional link is detected before “STP MaxAge + 2xForwardDelay” expires.
QUESTION NO: 77
Which switching technology can be used to solve reliability problems in a switched network?
A. fragment-free mode
B. cut-through mode
C. check mode
D. store-and-forward mode
Answer: D
Explanation:
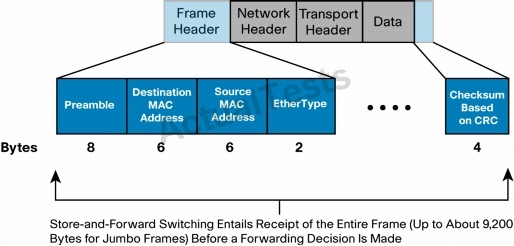
Characteristics of Store-and-Forward Ethernet Switching
This section provides an overview of the functions and features of store-and-forward Ethernet switches.
Error Checking
Figure 1 shows a store-and-forward switch receiving an Ethernet frame in its entirety. At the end of that frame, the switch will compare the last field of the datagram against its own frame-checksequence (FCS) calculations, to help ensure that the packet is free of physical and data-link errors. The switch then performs the forwarding process.
Whereas a store-and-forward switch solves reliability issues by dropping invalid packets, cutthrough devices forward them because they do not get a chance to evaluate the FCS before transmitting the packet.
Figure 1. Ethernet Frame Entering a Store-and-Forward Bridge or Switch (from Left to Right)
QUESTION NO: 78
Refer to the exhibit.
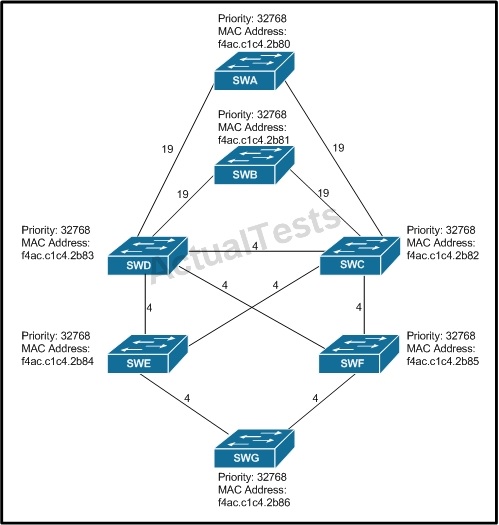 All switches have default bridge priorities, and originate BPDUs with MAC addresses as indicated. The numbers shown are STP link metrics. Which two ports are in blocking state after STP converges? (Choose two.)
All switches have default bridge priorities, and originate BPDUs with MAC addresses as indicated. The numbers shown are STP link metrics. Which two ports are in blocking state after STP converges? (Choose two.)
A. the port on switch SWD that connects to switch SWE B. the port on switch SWF that connects to switch SWG C. the port on switch SWD that connects to switch SWC D. the port on switch SWB that connects to switch SWD
Answer: C,D
Explanation:
This is a scenario that wants you to demonstrate understanding of the Root switch and Root port election process. So, it’s best to start with where the root switch will be and work down from there. It’s setup nicely because the lowest MAC address switch starts at the top and then the lower priority/higher mac addresses move down the architecture. SWA wins the root election and of course all ports in SWA are forwarding. SWB introduces the possibility for a switching loop so it’s important to understand which ports will be put into the blocking state. Since SWD is a higher MAC address it will end up with a blocked port connected to SWB to prevent a loop: and this is one of the correct answers. To prevent the possibility of another potential switching loop, SWD again ends up with the higher MAC address so blocking the link between D and C prevents a B/C/D switching loop.
QUESTION NO: 79
Which statement is true about IGMP?
A. Multicast sources send IGMP messages to their first-hop router, which then generates a PIM join message that is then sent to the RP.
B. Multicast receivers send IGMP messages to their first-hop router, which then forwards the IGMP messages to the RP.
C. IGMP messages are encapsulated in PIM register messages and sent to the RP.
D. Multicast receivers send IGMP messages to signal their interest to receive traffic for specific multicast groups.
Answer: D
Explanation:
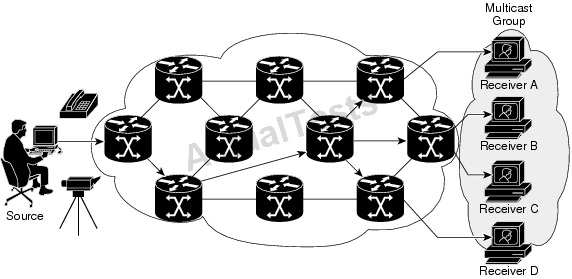
In the example shown above, the receivers (the designated multicast group) are interested in receiving the video data stream from the source. The receivers indicate their interest by sending an Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP) host report to the routers in the network. The routers are then responsible for delivering the data from the source to the receivers. Reference.
QUESTION NO: 80
Which two statements are true about RSTP? (Choose two.)
A. By default, RTSP uses a separate TCN BPDU when interoperating with 802.1D switches.
B. By default, RTSP does not use a separate TCN BPDU when interoperating with 802.1D switches.
C. If a designated port receives an inferior BPDU, it immediately triggers a reconfiguration.
D. By default, RTSP uses the topology change TC flag.
E. If a port receives a superior BPDU, it immediately replies with its own information, and no reconfiguration is triggered.
Answer: B,D
Explanation:
The RSTP does not have a separate topology change notification (TCN) BPDU. It uses the topology change (TC) flag to show the topology changes.
QUESTION NO: 81
Refer to the exhibit.
 Which two statements are true about the displayed STP state? (Choose two.)
Which two statements are true about the displayed STP state? (Choose two.)
A. The STP version configured on the switch is IEEE 802.1w.
B. Port-channel 1 is flapping and the last flap occurred 1 minute and 17 seconds ago.
C. The switch does not have PortFast configured on Gi0/15.
D. BPDUs with the TCN bit set are transmitted over port channel 1.
Answer: C,D
Explanation:
A port enabled with portfast will not send topology changes when a port goes up or down, but here we see that 296 TCN’s were sent so we know that Gi 0/15 does not have portfast enabled. TCN’s are sent using BPDU’s over the root port, which we see is port channel 1.
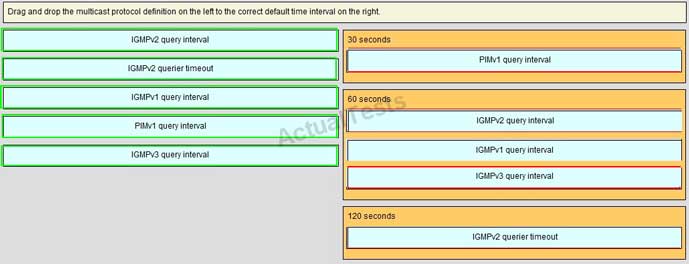
QUESTION NO: 82 Drag & Drop
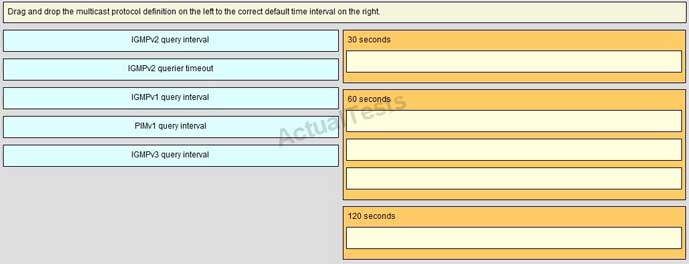
Answer:
QUESTION NO: 83
When you migrate a network from PVST+ to rapid-PVST+, which two features become inactive?(Choose two.)
A. Root guard
B. Loop guard
C. UplinkFast
D. UDLD
E. BackboneFast
F. Bridge Assurance
Answer: C,E
QUESTION NO: 84
Which statement is true about MLD?
A. MLD v1 gives hosts the ability to receive multicast packets from specific source addresses.
B. All MLD messages are sent with a link-local IPv6 source address of FF02::D.
C. The multicast address field is cleared to zero when sending an MLD report message.
D. MLD is used by IPv6 routers to discover multicast listeners on a directly attached link.
Answer: D
Explanation:
IPv6 Multicast Listener Discovery (MLD) is used by IPv6 devices to discover multicast listeners (nodes that want to receive multicast packets destined for specific multicast addresses) on directly attached links. There are two versions of MLD. MLD version 1 is based on version 2 of the IGMP for IPv4, and MLD version 2 is based on version 3 of the IGMP for IPv4. IPv6 multicast for Cisco software uses both MLD version 2 and MLD version 1.
QUESTION NO: 85
Which statement is true about LLDP?
A. LLDP provides VTP support.
B. LLDP does not use a multicast address to communicate.
C. LLDP can indicate only the duplex setting of a link, and not the speed capabilities.
D. LLDP does not support native VLAN indication.
Answer: D
QUESTION NO: 86
Which statement is true when using a VLAN ID from the extended VLAN range (1006–4094)?
A. VLANs in the extended VLAN range can be used with VTPv2 in either client or server mode.
B. VLANs in the extended VLAN range can only be used as private VLANs.
C. STP is disabled by default on extended-range VLANs.
D. VLANs in the extended VLAN range cannot be pruned.
Answer: D
Explanation:
Enabling VTP pruning on a VTP server enables pruning for the entire management domain. Making VLANs pruning-eligible or pruning-ineligible affects pruning eligibility for those VLANs on that device only (not on all switches in the VTP domain). VTP pruning takes effect several seconds after you enable it. VTP pruning does not prune traffic from VLANs that are pruning-ineligible. VLAN 1 and VLANs 1002 to 1005 are always pruning-ineligible; traffic from these VLANs cannot be pruned. Extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs higher than 1005) are also pruning-ineligible.
QUESTION NO: 87
Which statement is true about trunking?
A. Cisco switches that run PVST+ do not transmit BPDUs on nonnative VLANs when using a dot1q trunk.
B. When removing VLAN 1 from a trunk, management traffic such as CDP is no longer passed in that VLAN.
C. DTP only supports autonegotiation on 802.1q and does not support autonegotiation for ISL.
D. DTP is a point-to-point protocol.
Answer: D
Explanation:
Ethernet trunk interfaces support different trunking modes. You can set an interface as trunking or nontrunking or to negotiate trunking with the neighboring interface. To autonegotiate trunking, the interfaces must be in the same VTP domain. Trunk negotiation is managed by the Dynamic Trunking Protocol (DTP), which is a Point-to-Point Protocol. However, some internetworking devices might forward DTP frames improperly, which could cause misconfigurations.
QUESTION NO: 88
Which three statements are true about an EtherChannel? (Choose three.)
A. PAGP and LACP can be configured on the same switch if the switch is not in the same EtherChannel.
B. EtherChannel ports in suspended state can receive BPDUs but cannot send them.
C. An EtherChannel forms between trunks that are using different native VLANs.
D. LACP can operate in both half duplex and full duplex, if the duplex setting is the same on both ends.
E. Ports with different spanning-tree path costs can form an EtherChannel.
Answer: A,B,E
Explanation:
QUESTION NO: 89
Which technology can be affected when switches are used that do not support jumbo frames?
A. 802.1x
B. BFD
C. OSPFv3
D. 802.1q
Answer: D
Explanation:
The 802.1Q tag is 4 bytes. Therefore, the resulting Ethernet frame can be as large as 1522 bytes. If jumbo frames are not supported, then typically the MTU on an Ethernet link needs to be lowered to 1496 to support this extra 802.1Q tag.
QUESTION NO: 90
Which statement describes the native VLAN concept in an ISL trunk?
A. It is the VLAN ID that is assigned to untagged packets.
B. It is the VLAN with highest priority.
C. It is the default VLAN for a trunk.
D. There is no native VLAN concept in an ISL trunk.
Answer: D
Explanation:
ISL has no native VLAN concept because it places the entire ethernet frame in the payload of an ISL frame. Native VLANs is an 802.1Q specific concept