نمونه سوالات آزمون
Implementing Cisco IP Switched Networks - exam 300-115
Topic 3, Infrastructure Services
QUESTION NO: 141
What is the maximum number of virtual MAC addresses that GLBP allows per group?
A. 2
B. 4
C. 6
D. 8
Answer: B
Explanation:
GLBP Virtual MAC Address Assignment
A GLBP group allows up to four virtual MAC addresses per group. The AVG is responsible for assigning the virtual MAC addresses to each member of the group. Other group members request a virtual MAC address after they discover the AVG through hello messages. Gateways are assigned the next MAC address in sequence. A virtual forwarder that is assigned a virtual MAC address by the AVG is known as a primary virtual forwarder. Other members of the GLBP group learn the virtual MAC addresses from hello messages. A virtual forwarder that has learned the virtual MAC address is referred to as a secondary virtual forwarder.
QUESTION NO: 142
Which gateway role is responsible for answering ARP requests for the virtual IP address in GLBP?
A. active virtual forwarder
B. active virtual router
C. active virtual gateway
D. designated router
Answer: C
Explanation:
GLBP Active Virtual Gateway
Members of a GLBP group elect one gateway to be the active virtual gateway (AVG) for that group. Other group members provide backup for the AVG in the event that the AVG becomes unavailable. The AVG assigns a virtual MAC address to each member of the GLBP group. Each gateway assumes responsibility for forwarding packets sent to the virtual MAC address assigned to it by the AVG. These gateways are known as active virtual forwarders (AVFs) for their virtual MAC address.
The AVG is responsible for answering Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) requests for the virtual IP address. Load sharing is achieved by the AVG replying to the ARP requests with different virtual MAC addresses.
QUESTION NO: 143
Which VRRP router is responsible for forwarding packets that are sent to the IP addresses of the virtual router?
A. virtual router master
B. virtual router backup
C. virtual router active
D. virtual router standby
Answer: A
Explanation:
VRRP Definitions
VRRP Router A router running the Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol. It may participate in one or more virtual routers.
Virtual Router An abstract object managed by VRRP that acts as a default router for hosts on a shared LAN. It consists of a Virtual Router Identifier and a set of associated IP address(es) across a common LAN. A VRRP Router may backup one or more virtual routers.
IP Address Owner The VRRP router that has the virtual router's IP address(es) as real interface address(es). This is the router that, when up, will respond to packets addressed to one of these IP addresses for ICMP pings, TCP connections, etc.
Primary IP Address An IP address selected from the set of real interface addresses. One possible selection algorithm is to always select the first address. VRRP advertisements are always sent using the primary IP address as the source of the IP packet.
Virtual Router Master The VRRP router that is assuming the responsibility of forwarding packets sent to the IP address(es) associated with the virtual router, and answering ARP requests for these IP addresses.Note that if the IP address owner is available, then it will always become the Master.
QUESTION NO: 144
Which command correctly configures standby tracking for group 1 using the default decrement priority value?
A. standby 1 track 100
B. standby 1 track 100 decrement 1
C. standby 1 track 100 decrement 5
D. standby 1 track 100 decrement 20
Answer: A
Explanation:
The default decrement value for HSRP standby tracking is 10. There is no need to explicitly state the value if the desired value is the default value.
QUESTION NO: 145
Which command configures an HSRP group to become a slave of another HSRP group?
A. standby slave
B. standby group track
C. standby follow
D. standby group backup
Answer: C
Explanation:
Perform this task to configure multiple HSRP client groups.
The “standby follow” command configures an HSRP group to become a slave of another HSRP group.
HSRP client groups follow the master HSRP with a slight, random delay so that all client groups do not change at the same time.
QUESTION NO: 146
Refer to the exhibit.
![]()
A. Unavailable GLBP active forwarder
B. Incorrect GLBP IP address
C. HSRP configured on same interface as GLBP
D. Layer 2 loop
Answer: D
Explanation:
Answer: D
Explanation:
This section provides information you can use to troubleshoot your configuration.
%GLBP-4-DUPADDR: Duplicate address
The error message indicates a possible layer2 loop and STP configuration issues. In order to resolve this issue, issue the show interface command to verify the MAC address of the interface. If the MAC address of the interface is the same as the one reported in the error message, then it indicates that this router is receiving its own hello packets sent. Verify the spanning-tree topology and check if there is any layer2 loop. If the interface MAC address is different from the one reported in the error message, then some other device with a MAC address reports this error message.
Note: GLBP members communicate between each other through hello messages sent every 3 seconds to the multicast address 224.0.0.102 and User Datagram Protocol (UDP) port 3222 (source and destination). When configuring the multicast boundary command, permit the Multicast address by permit 224.0.0.0 15.255.255.255.
QUESTION NO: 147
Ferris Plastics, Inc. is a medium sized company, with an enterprise network (access, distribution and core switches) that provides LAN connectivity from user PCs to corporate servers. The distribution switches are configured to use HSRP to provide a high availability solution.
• DSW1 -primary device for VLAN 101 VLAN 102 and VLAN 105
• DSW2 - primary device for VLAN 103 and VLAN 104
• A failure of GigabitEthemet1/0/1 on primary device should cause the primary device to release its status as the primary device, unless GigabitEthernet1/0/1 on backup device has also failed.
Troubleshooting has identified several issues. Currently all interfaces are up. Using the running configurations and show commands, you have been asked to investigate and respond to the following question.
During routine maintenance, GigabitEthernet1/0/1 on DSW1 was shut down. All other interfaces were up. DSW2 became the active HSRP device for VLAN 101 as desired. However, after GigabitEthemet1/0/1 on DSW1 was reactivated, DSW1 did not become the active router for VLAN 101 as desired. What needs to be done to make the group for VLAN 101 function properly?
A. Enable preempt in the VLAN 101 HSRP group on DSW1.
B. Disable preempt in the VLAN 101 HSRP group on DSW2's.
C. In the VLAN 101 HSRP group on DSW1, decrease the priority value to avaluethatis less ' than the priority value configured in the VLAN 101 HSRP group on DSW2.
D. Decrease the decrement value in the track command for the VLAN 101 HSRP group on U DSWTs to a values less than the value in the track command for the VLAN 101 HSRP group on DSW2.
Answer: A
Explanation:
QUESTION NO: 148
Ferris Plastics, Inc. is a medium sized company, with an enterprise network (access, distribution and core switches) that provides LAN connectivity from user PCs to corporate servers. The distribution switches are configured to use HSRP to provide a high availability solution.
• DSW1 -primary device for VLAN 101 VLAN 102 and VLAN 105
• DSW2 - primary device for VLAN 103 and VLAN 104
• A failure of GigabitEthemet1/0/1 on primary device should cause the primary device to release its status as the primary device, unless GigabitEthernet1/0/1 on backup device has also failed. Troubleshooting has identified several issues. Currently all interfaces are up. Using the running configurations and show commands, you have been asked to investigate and respond to the following question.
During routine maintenance, it became necessary to shut down the GigabitEthernet1/0/1 interface on DSW1. All other interfaces were up. During this time, DSW1 remained the active device for the VLAN 102 HSRP group. You have determined that there is an issue with the decrement value in the track command for the VLAN 102 HSRP group. What needs to be done to make the group function properly?
A. The decrement value on DSW1 should be greaterthan 5 and less than 15. 0
B. The decrement value on DSW1 should be greaterthan 9 and less than 15.
C. The decrement value on DSW1 should be greaterthan 11 and less than 19.
D. The decrement value on DSWTs should be greaterthan 190 and less than 200.
E. The decrement value on DSWTs should be greaterthan 195 and less than 205.
Answer: C
Explanation:
Use "show run" command to show. The left Vlan102 is console1 of DS1. Priority value is 200, we should decrement value in the track command from 11 to 18. Because 200 – 11 = 189 < 190 (priority of Vlan102 on DS2).
QUESTION NO: 149
Ferris Plastics, Inc. is a medium sized company, with an enterprise network (access, distribution and core switches) that provides LAN connectivity from user PCs to corporate servers. The distribution switches are configured to use HSRP to provide a high availability solution.
• DSW1 -primary device for VLAN 101 VLAN 102 and VLAN 105
• DSW2 - primary device for VLAN 103 and VLAN 104
• A failure of GigabitEthemet1/0/1 on primary device should cause the primary device to release its status as the primary device, unless GigabitEthernet1/0/1 on backup device has also failed.
Troubleshooting has identified several issues. Currently all interfaces are up. Using the running configurations and show commands, you have been asked to investigate and respond to the following question.
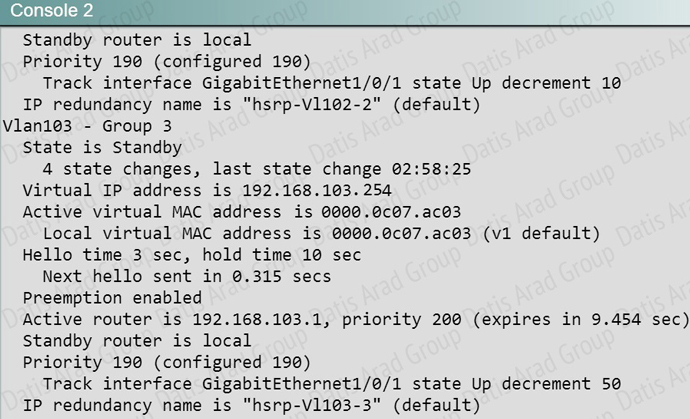
 All interfaces are active. DSW2 has not become the active device for the VLAN 103 HSRP group. As related to the VLAN 103 HSRP group, what can be done to make the group function properly?
All interfaces are active. DSW2 has not become the active device for the VLAN 103 HSRP group. As related to the VLAN 103 HSRP group, what can be done to make the group function properly?
A. On DSW1, disable preempt.
B. On DSW1, decrease the priority value to a value less than 190 and greater than 150.
C. On DSW2, increase the priority value to a value greater 200 and less than 250.
D. On DSW2, increase the decrement value in the track command to a value greater than 10 and less than 50.
Answer: C
Explanation:
From the output shown below of the HSRP status of DSW2, we see that the active router has a priority of 200, while the local priority is 190. We need to increase the priority of DSW2 to greater than 200, but it should be less than 250 so that if the gig 1/0/1 interface goes down, DSW1 will become active. DSW2 is configured to decrement the priority by 50 if this interface goes down, so the correct answer is to increase the priority to more than 200, but less than 250.
QUESTION NO: 150
Ferris Plastics, Inc. is a medium sized company, with an enterprise network (access, distribution and core switches) that provides LAN connectivity from user PCs to corporate servers. The distribution switches are configured to use HSRP to provide a high availability solution.
• DSW1 -primary device for VLAN 101 VLAN 102 and VLAN 105
• DSW2 - primary device for VLAN 103 and VLAN 104
• A failure of GigabitEthemet1/0/1 on primary device should cause the primary device to release its status as the primary device, unless GigabitEthernet1/0/1 on backup device has also failed.
Troubleshooting has identified several issues. Currently all interfaces are up. Using the running configurations and show commands, you have been asked to investigate and respond to the following question.
 During routine maintenance, it became necessary to shut down the GigabitEthernet1/0/1 interface on DSW1 and DSW2. All other interfaces were up. During this time, DSW1 became the active router for the VLAN 104HSRP group. As related to the VLAN 104HSRP group, what can to be done to make the group function properly?
During routine maintenance, it became necessary to shut down the GigabitEthernet1/0/1 interface on DSW1 and DSW2. All other interfaces were up. During this time, DSW1 became the active router for the VLAN 104HSRP group. As related to the VLAN 104HSRP group, what can to be done to make the group function properly?
A. On DSW1, disable preempt.
B. On DSW2 decrease the priority value to a value less than 150.
C. On DSW1, increase the decrement value in the track command to a value greater than 6.
D. On DSW1, decrease the decrement value in the track command to a value less than 1.
Answer: C
Explanation:
We should NOT disable preempt on DS1. By do that, you will make Vlan104’s HSRP group fail function. Example: if we are disable preempt on DS1. It can not become active device when G1/0/1 on DS2 fail. In this question, G0/1/0 on DS1 &DS2 is shutdown. Vlan104 (left):150 – 1 = 149. Vlan104 (right): 200 – 155 = 145. Result is priority 149 > 145 (Vlan104 on DS1 is active). If increase the decrement in the track value to a value greater than 6 (> or = 6). Vlan104 (left): 150 – 6 = 144. Result is priority 144 < 145 (vlan104 on DS2 is active).
QUESTION NO: 151
Ferris Plastics, Inc. is a medium sized company, with an enterprise network (access, distribution and core switches) that provides LAN connectivity from user PCs to corporate servers. The distribution switches are configured to use HSRP to provide a high availability solution.
• DSW1 -primary device for VLAN 101 VLAN 102 and VLAN 105
• DSW2 - primary device for VLAN 103 and VLAN 104
• A failure of GigabitEthemet1/0/1 on primary device should cause the primary device to release its status as the primary device, unless GigabitEthernet1/0/1 on backup device has also failed.
Troubleshooting has identified several issues. Currently all interfaces are up. Using the running configurations and show commands, you have been asked to investigate and respond to the following question.
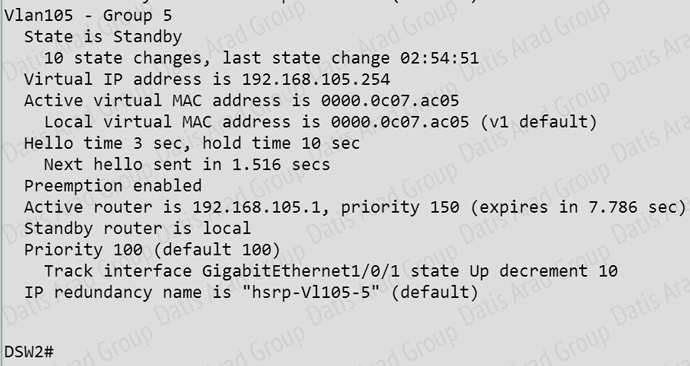
What is the priority value of the VLAN 105 HSRP group on DSW2?
A. 50
B. 100
C. 150
D. 200
Answer: B
Explanation:
Each (non-Root) bridge has exactly one Root Port, which represents the best path to the Root Bridge. In this case, fa0/21 has the lowest cost, so it will be the root port.
QUESTION NO: 152
Ferris Plastics, Inc. is a medium sized company, with an enterprise network (access, distribution and core switches) that provides LAN connectivity from user PCs to corporate servers. The distribution switches are configured to use HSRP to provide a high availability solution.
• DSW1 -primary device for VLAN 101 VLAN 102 and VLAN 105
• DSW2 - primary device for VLAN 103 and VLAN 104
• A failure of GigabitEthemet1/0/1 on primary device should cause the primary device to release its status as the primary device, unless GigabitEthernet1/0/1 on backup device has also failed.
Troubleshooting has identified several issues. Currently all interfaces are up. Using the running configurations and show commands, you have been asked to investigate and respond to the following question.
If GigabitEthemet1/0/1 on DSW2 is shutdown, what will be the resulting priority value of the VLAN 105 HSRP group on router DSW2?
A. 90
B. 100
C. 150
D. 200
Answer: A
Explanation:
As seen below, the current priority for VLAN 105 is 100, and the tracking feature for Gig 1/0/0 is enabled which will decrement the priority by 10 if this interface goes down for a priority value of 90.
QUESTION NO: 153
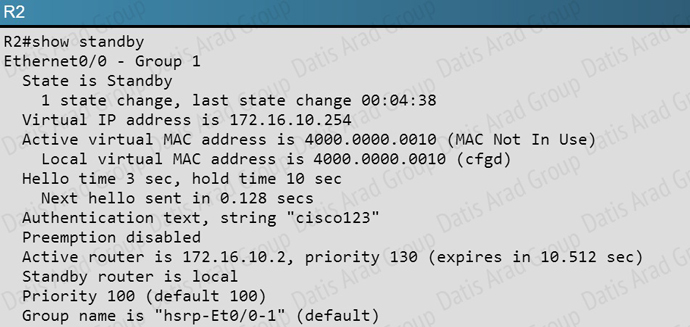
Your customer has asked you to come in and verify the operation of routers R1 and R2 which are configured to use HSRP. They have questions about how these two devices will perform in the event of a device failure.
What percentage of the outgoing traffic from the 172.16.10.0/24 subnet is being forwarded through R1?
A. R1-0%
B. R1-50 %, R2-50%
C. R2-100%
D. R1-100%
Answer: D
Explanation:
Based on the following output, we see that R1 is the active standby router for the Ethernet 0/0 link, so all outgoing traffic will be forwarded to R1.
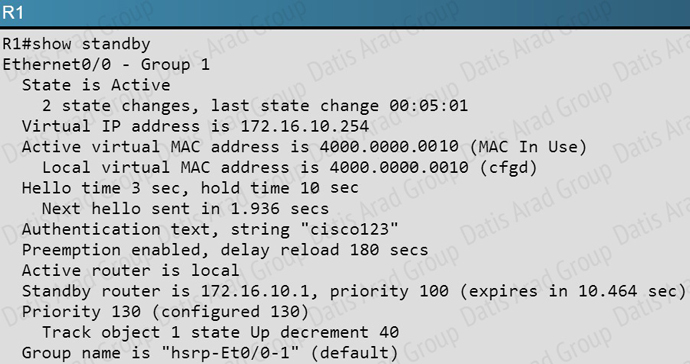
QUESTION NO: 154
Your customer has asked you to come in and verify the operation of routers R1 and R2 which are configured to use HSRP. They have questions about how these two devices will perform in the event of a device failure.
Refer to the exhibit. If router R1 interface Etherne0/0 goes down and recovers, which of the statement regarding HSRP priority is true?
A. The interface will have the priority decremented by 40 for HSRP group 1.
B. The interface will have the priority decremented by 60 for HSRP group 1
C. The interface will have its current priority incremented by 40 for HSRP group 1
D. The interface will have its current priority incremented by 60 for HSRP group 1
E. The interface will default to the a priority of 100 for HSRP group 1
Answer: C
Explanation:
Here is the HSRP configuration seen on R1:
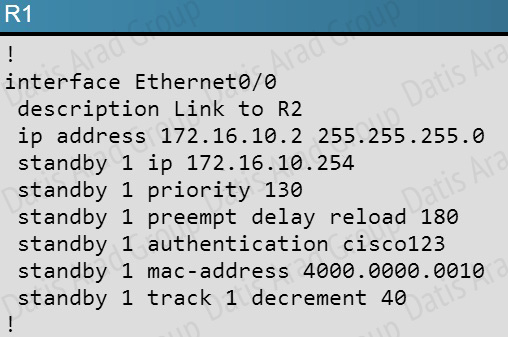
Here, when the Ethernet 0/0 interface goes down, the standby 1 track decrement command will lower the priority from 130 to 90. However, when it comes back up, it will then increment it by 40 back to 130 for HSRP group 1.
QUESTION NO: 155
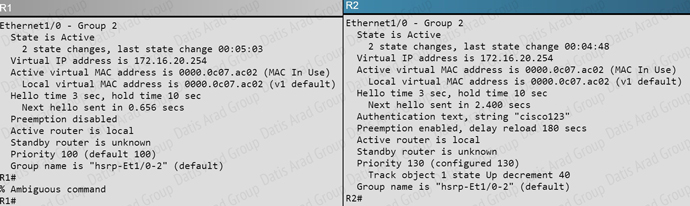
Your customer has asked you to come in and verify the operation of routers R1 and R2 which are configured to use HSRP. They have questions about how these two devices will perform in the event of a device failure.
What issue is causing Router R1 and R2 to both be displayed as the HSRP active router for group 2?
A. The HSRP group number mismatch
B. The HSRP group authentication is misconfigured
C. The HSRP Hello packets are blocked
D. The HSRP timers mismatch
E. The HSRP group priorities are different
Answer: B
Explanation:
Based on the configuration output, we see that authentication is configured on R2, but not on R1:
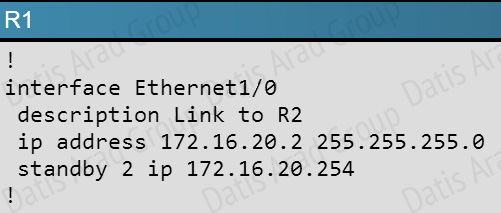
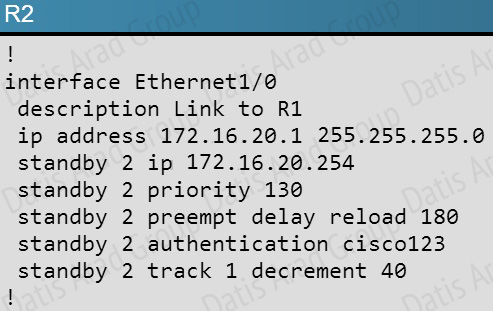
This can be further verified by issuing the “show standby” command on each router.
QUESTION NO: 156
Your customer has asked you to come in and verify the operation of routers R1 and R2 which are configured to use HSRP. They have questions about how these two devices will perform in the event of a device failure.
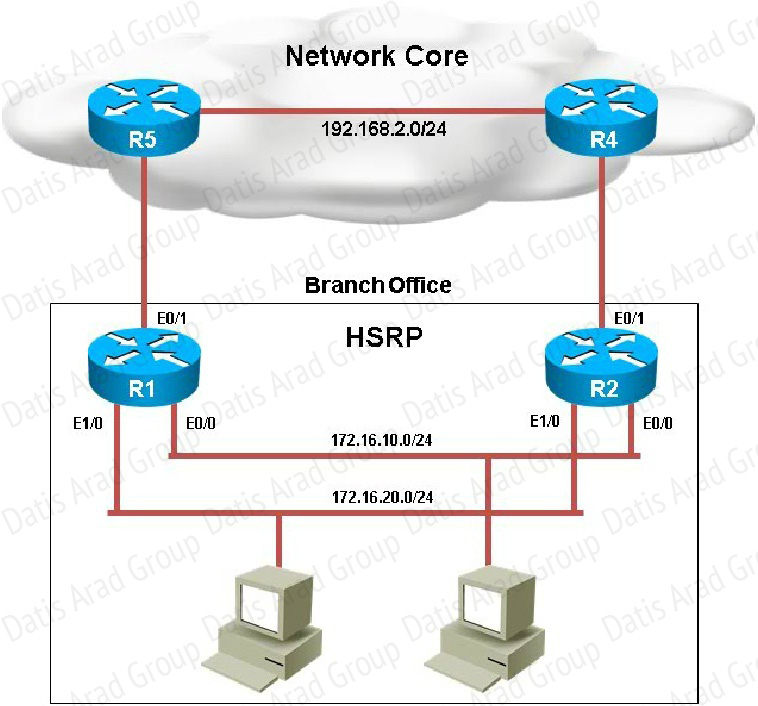 What is the virtual mac-address of HSRP group 1?
What is the virtual mac-address of HSRP group 1?
A. 0000.0c07.ac02
B. 4000.0000.0010
C. 0000.0c07.ac01
D. 4000.0000.ac01
E. 4000.0000.ac02
F. 0000.0c07.0010
Answer: B
Explanation:
Issuing the “show standby” command on either router shows us that the virtual MAC used by HSRP group 1 is 4000.0000.0010.
QUESTION NO: 157
DHCP snooping and IP Source Guard have been configured on a switch that connects to several client workstations. The IP address of one of the workstations does not match any entries found in the DHCP binding database. Which statement describes the outcome of this scenario?
A. Packets from the workstation will be rate limited according to the default values set on the switch.
B. The interface that is connected to the workstation in question will be put into the errdisabled state.
C. Traffic will pass accordingly after the new IP address is populated into the binding database.
D. The packets originating from the workstation are assumed to be spoofed and will be discarded.
Answer: D
Explanation:
The IP source binding table has bindings that are learned by DHCP snooping or are manually configured (static IP source bindings). An entry in this table has an IP address, its associated MAC address, and its associated VLAN number. The switch uses the IP source binding table only wIen IP source guard is enabled.
You can configure IP source guard with source IP address filtering, or with source IP and MAC address filtering. When IP source guard is enabled with this option, IP traffic is filtered based on the source IP address. The switch forwards IP traffic when the source IP address matches an entry in the DHCP snooping binding database or a binding in the IP source binding table. When IP source guard is enabled with this option, IP traffic is filtered based on the source IP and MAC addresses. The switch forwards traffic only when the source IP and MAC addresses match an entry in the IP source binding table. If there is no match, the packets are assumed to be spoofed and will be discarded.
QUESTION NO: 158
Refer to the exhibit.

When troubleshooting a network problem, a network analyzer is connected to Port f0/1 of a LAN switch. Which command can prevent BPDU transmission on this port?
A. spanning-tree portfast bpduguard enable
B. spanning-tree bpduguard default
C. spanning-tree portfast bpdufilter default
D. no spanning-tree link-type shared
Answer: C
QUESTION NO: 159
Which four LACP components are used to determine which hot-standby links become active after an interface failure within an EtherChannel bundle? (Choose four.)
A. LACP system priority
B. LACP port priority
C. interface MAC address
D. system ID
E. port number
F. hot-standby link identification number
G. interface bandwidth
Answer: A,B,D,E
QUESTION NO: 160
RSPAN has been configured on a Cisco Catalyst switch; however, traffic is not being replicated to the remote switch. Which type of misconfiguration is a cause?
A. The RSPAN designated VLAN is missing the remote span command.
B. The local and remote RSPAN switches are configured using different session IDs.
C. The local RSPAN switch is replicating only Rx traffic to the remote switch.
D. The local switch is overloaded with the amount of sourced traffic that must be replicated to the remote switch.
Answer: A