
نمونه سوالات آزمون
Implementing Cisco IP Switched Networks - exam 300-115
Topic 2, Infrastructure Security
QUESTION NO: 121
Which type of information does the DHCP snooping binding database contain?
A. untrusted hosts with leased IP addresses
B. trusted hosts with leased IP addresses
C. untrusted hosts with available IP addresses
D. trusted hosts with available IP addresses
Answer: A
Explanation:
DHCP snooping is a security feature that acts like a firewall between untrusted hosts and trusted DHCP servers. The DHCP snooping feature performs the following activities:
• Validates DHCP messages received from untrusted sources and filters out invalid messages.
• Rate-limits DHCP traffic from trusted and untrusted sources.
• Builds and maintains the DHCP snooping binding database, which contains information about untrusted hosts with leased IP addresses.
• Utilizes the DHCP snooping binding database to validate subsequent requests from untrusted hosts.
QUESTION NO: 122
Which switch feature determines validity based on IP-to-MAC address bindings that are stored in a trusted database?
A. Dynamic ARP Inspection
B. storm control
C. VTP pruning
D. DHCP snooping
Answer: A
Explanation:
Dynamic ARP inspection determines the validity of an ARP packet based on valid IP-to-MAC address bindings stored in a trusted database, the DHCP snooping binding database. This database is built by DHCP snooping if DHCP snooping is enabled on the VLANs and on the switch. If the ARP packet is received on a trusted interface, the switch forwards the packet without any checks. On untrusted interfaces, the switch forwards the packet only if it is valid.
QUESTION NO: 123
Which command is needed to enable DHCP snooping if a switchport is connected to a DHCP server?
A. ip dhcp snooping trust
B. ip dhcp snooping
C. ip dhcp trust
D. ip dhcp snooping information
Answer: A
Explanation:
When configuring DHCP snooping, follow these guidelines:
• DHCP snooping is not active until you enable the feature on at least one VLAN, and enable DHCP globally on the switch.
• Before globally enabling DHCP snooping on the switch, make sure that the devices acting as the DHCP server and the DHCP relay agent are configured and enabled.
• If a Layer 2 LAN port is connected to a DHCP server, configure the port as trusted by entering the “ip dhcp snooping trust” interface configuration command.
• If a Layer 2 LAN port is connected to a DHCP client, configure the port as untrusted by entering the no ip dhcp snooping trust interface configuration command.
QUESTION NO: 124
Which private VLAN access port belongs to the primary VLAN and can communicate with all interfaces, including the community and isolated host ports?
A. promiscuous port
B. isolated port
C. community port
D. trunk port
Answer: A
Explanation:
The types of private VLAN ports are as follows:
• Promiscuous — A promiscuous port belongs to the primary VLAN.The promiscuous port can communicate with all interfaces, including the community and isolated host ports, that belong to those secondary VLANs associated to the promiscuous port and associated with the primary VLAN. You can have several promiscuous ports in a primary VLAN. Each promiscuous port can have several secondary VLANs, or no secondary VLANs, associated to that port. You can associate a secondary VLAN to more than one promiscuous port, as long as the promiscuous port and secondary VLANs are within the same primary VLAN. You may want to do this for loadbalancing or redundancy purposes. You can also have secondary VLANs that are not associated to any promiscuous port.
• Isolated — An isolated port is a host port that belongs to an isolated secondary VLAN. This port has complete isolation from other ports within the same private VLAN domain, except that it can communicate with associated promiscuous ports. Private VLANs block all traffic to isolatedports except traffic from promiscuous ports. Traffic received from an isolated port is forwarded only to promiscuous ports. You can have more than one isolated port in a specified isolated VLAN. Each port is completely isolated from all other ports in the isolated VLAN.
• Community — A community port is a host port that belongs to a community secondary VLAN. Community ports communicate with other ports in the same community VLAN and with associated promiscuous ports. These interfaces are isolated from all other interfaces in other communities and from all isolated ports within the private VLAN domain.
QUESTION NO: 125
Which private VLAN can have only one VLAN and be a secondary VLAN that carries unidirectional traffic upstream from the hosts toward the promiscuous ports and the gateway?
A. isolated VLAN
B. primary VLAN
C. community VLAN
D. promiscuous VLAN
Answer: A
Explanation:
Understanding Primary, Isolated, and Community Private VLANs
Primary VLANs and the two types of secondary VLANs (isolated and community) have these characteristics:
• Primary VLAN — The primary VLAN carries traffic from the promiscuous ports to the host ports, both isolated and community, and to other promiscuous ports.
• Isolated VLAN — An isolated VLAN is a secondary VLAN that carries unidirectional traffic upstream from the hosts toward the promiscuous ports.You can configure multiple isolated VLANs in a private VLAN domain; all the traffic remains isolated within each one. Each isolated VLAN can have several isolated ports, and the traffic from each isolated port also remains completely separate.
• Community VLAN — A community VLAN is a secondary VLAN that carries upstream traffic from the community ports to the promiscuous port and to other host ports in the same community. You can configure multiple community VLANs in a private VLAN domain. The ports within one community can communicate, but these ports cannot communicate with ports in any other community or isolated VLAN in the private VLAN.
QUESTION NO: 126
Which database is used to determine the validity of an ARP packet based on a valid IP-to-MAC address binding?
A. DHCP snooping database
B. dynamic ARP database
C. dynamic routing database
D. static ARP database
Answer: A
Explanation:
Information About Dynamic ARP Inspection
DAI is used to validate ARP requests and responses as follows:
• Intercepts all ARP requests and responses on untrusted ports.
• Verifies that a packet has a valid IP-to-MAC address binding before updating the ARP cache or forwarding the packet.
• Drops invalid ARP packets.
DAI can determine the validity of an ARP packet based on valid IP-to-MAC address bindings stored in a DHCP snooping binding database.This database is built by DHCP snooping when it is enabled on the VLANs and on the device. It may also contain static entries that you have created.
QUESTION NO: 127
When IP Source Guard with source IP filtering is enabled on an interface, which feature must be enabled on the access VLAN for that interface?
A. DHCP snooping
B. storm control
C. spanning-tree portfast
D. private VLAN
Answer: A
Explanation:
IP Source Guard Configuration Guidelines
• You can configure static IP bindings only on nonrouted ports. If you enter the ip source binding mac-address vlan vlan-id ip-address interface interface-id global configuration command on a routed interface, this error message appears:
Static IP source binding can only be configured on switch port.
• When IP source guard with source IP filtering is enabled on an interface, DHCP snooping must be enabled on the access VLAN for that interface.
• If you are enabling IP source guard on a trunk interface with multiple VLANs and DHCP snooping is enabled on all the VLANs, the source IP address filter is applied on all the VLANs.
• You can enable this feature when 802.1x port-based authentication is enabled.
QUESTION NO: 128
Which switch feature prevents traffic on a LAN from being overwhelmed by continuous multicast or broadcast traffic?
A. storm control
B. port security
C. VTP pruning
D. VLAN trunking
Answer: A
Explanation:
A traffic storm occurs when packets flood the LAN, which creates excessive traffic and degrades network performance. The traffic storm control feature prevents LAN ports from being disrupted by a broadcast, multicast, or unicast traffic storm on physical interfaces from either mistakes in network configurations or from users issuing a DoS attack.
QUESTION NO: 129
Which command would a network engineer apply to error-disable a switchport when a packetstorm is detected?
A. router(config-if)#storm-control action shutdown
B. router(config-if)#storm-control action trap
C. router(config-if)#storm-control action error
D. router(config-if)#storm-control action enable
Answer: A
Explanation:
Configuring the Traffic Storm Control Shutdown Mode
To configure the traffic storm control shutdown mode on an interface, perform this task:
Command
Purpose
Step 1
Router(config)#interface{{type1 slot/port} | {port-channel number}}
Selects an interface to configure.
Step 2
Router(config-if)#storm-control action shutdown
(Optional) Configures traffic storm control to error-disable ports when a traffic storm occurs.
• Enter the no storm-control action shutdown command to revert to the default action (drop).
• Use the error disable detection and recovery feature, or the shutdown and no shutdown
commands to reenable ports.
QUESTION NO: 130
A network engineer configures port security and 802.1x on the same interface. Which option describes what this configuration allows?
A. It allows port security to secure the MAC address that 802.1x authenticates.
B. It allows port security tosecure the IP address that 802.1x authenticates.
C. It allows 802.1x to secure the MAC address that port security authenticates.
D. It allows 802.1x to secure the IP address that port security authenticates.
Answer: A
Explanation:
802.1X and Port Security
You can configure port security and 802.1X on the same interfaces. Port security secures the MAC addresses that 802.1X authenticates. 802.1X processes packets before port securityprocesses them, so when you enable both on an interface, 802.1X is already preventing inbound traffic on the interface from unknown MAC addresses.
QUESTION NO: 131
Which feature describes MAC addresses that are dynamically learned or manually configured, stored in the address table, and added to the running configuration?
A. sticky
B. dynamic
C. static
D. secure
Answer: A
Explanation:
With port security, you can configure MAC addresses to be sticky. These can be dynamically learned or manually configured, stored in the address table, and added to the running configuration. If these addresses are saved in the configuration file, the interface does not need to dynamically relearn them when the switch restarts. Although sticky secure addresses can be manually configured, it is not recommended.
QUESTION NO: 132
On which interface can port security be configured?
A. static trunk ports
B. destination port for SPAN
C. EtherChannel port group
D. dynamic access point
Answer: A
Explanation:
Port Security and Port Types
You can configure port security only on Layer 2 interfaces. Details about port security and different types of interfaces or ports are as follows:
• Access ports—You can configure port security on interfaces that you have configured as Layer 2 access ports. On an access port, port security applies only to the access VLAN.
• Trunk ports—You can configure port security on interfaces that you have configured as Layer 2 trunk ports. VLAN maximums are not useful for access ports. The device allows VLAN maximums only for VLANs associated with the trunk port.
• SPAN ports—You can configure port security on SPAN source ports but not on SPAN destination ports.
• Ethernet Port Channels—Port security is not supported on Ethernet port channels.
QUESTION NO: 133
When you configure private VLANs on a switch, which port type connects the switch to the gateway router?
A. promiscuous
B. community
C. isolated
D. trunked
Answer: A
Explanation:
There are mainly two types of ports in a Private VLAN: Promiscuous port (P-Port) and Host port. Host port further divides in two types – Isolated port (I-Port) and Community port (C-port).
QUESTION NO: 134
When you configure a private VLAN, which type of port must you configure the gateway router port as?
A. promiscuous port
B. isolated port
C. community port
D. access port
Answer: A
Explanation:
There are mainly two types of ports in a Private VLAN: Promiscuous port (P-Port) and Host port. Host port further divides in two types – Isolated port (I-Port) and Community port (C-port).
QUESTION NO: 135 Labrator
SWITCH.com is an IT company that has an existing enterprise network comprised of two layer 2 only switches; DSW1 and ASW1. The topology diagram indicates their layer 2 mapping. VLAN 20 is a new VLAN that will be used to provide the shipping personnel access to the server. Corporate polices do not allow layer 3 functionality to be enabled on the switches. For security reasons, it is necessary to restrict access to VLAN 20 in the following manner:
• Users connecting to VLAN 20 via portfO/1 on ASW1 must be authenticated before they are given access to the network. Authentication is to be done via a Radius server:
• Radius server host: 172.120.40.46
• Radius key: rad123
• Authentication should be implemented as close to the host as possible.
• Devices on VLAN 20 are restricted to the subnet of 172.120.40.0/24.
• Packets from devices in the subnet of 172.120.40.0/24 should be allowed on VLAN 20.
• Packets from devices in any other address range should be dropped on VLAN 20.
• Filtering should be implemented as close to the serverfarm as possible.
The Radius server and application servers will be installed at a future date. You have been tasked with implementing the above access control as a pre-condition to installing the servers. You must use the available IOS switch features.
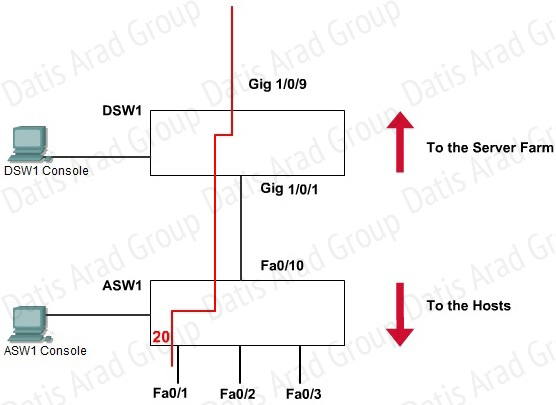
Answer:
Step1: Console to ASW1 from PC console 1
ASW1(config)#aaa new-model
ASW1(config)#radius-server host 172.120.39.46 key rad123
ASW1(config)#aaa authentication dot1x default group radius
ASW1(config)#dot1x system-auth-control
ASW1(config)#inter fastEthernet 0/1
ASW1(config-if)#switchport mode access
ASW1(config-if)#dot1x port-control auto
ASW1(config-if)#exit
ASW1#copy run start
Step2: Console to DSW1 from PC console 2
DSW1(config)#ip access-list standard 10
DSW1(config-ext-nacl)#permit 172.120.40.0 0.0.0.255
DSW1(config-ext-nacl)#exit
DSW1(config)#vlan access-map PASS 10
DSW1(config-access-map)#match ip address 10
DSW1(config-access-map)#action forward
DSW1(config-access-map)#exit
DSW1(config)#vlan access-map PASS 20
DSW1(config-access-map)#action drop
DSW1(config-access-map)#exit
DSW1(config)#vlan filter PASS vlan-list 20
DSW1#copy run start
Topic 3, Infrastructure Services
QUESTION NO: 136
Which configuration command ties the router hot standby priority to the availability of its interfaces?
A. standby group
B. standby priority
C. backup interface
D. standby track
Answer: D
Explanation:
The standby track interface configuration command ties the router hot standby priority to the availability of its interfaces and is useful for tracking interfaces that are not configured for HSRP. When a tracked interface fails, the hot standby priority on the device on which tracking has been configured decreases by 10. If an interface is not tracked, its state changes do not affect the hot standby priority of the configured device. For each interface configured for hot standby, you can configure a separate list of interfaces to be tracked.
QUESTION NO: 137
What is the default HSRP priority?
A. 50
B. 100
C. 120
D. 1024
Answer: B
Explanation:
QUESTION NO: 138
Which option is a benefit of using VSS?
A. reduces cost
B. simplifies configuration
C. provides two independent supervisors with two different control planes
D. removes the need for a First Hop Redundancy Protocol
Answer: D
Explanation:
First Hop Redundancy Protocols (FHRPs) such as VRRP and HSRP were designed to allow for a highly available first IP route hop for host systems. FHRPs allow two (or more) distinct routers to share a common IP address providing a redundant Layer-3 default gateway for end nodes. The VSS system creates a single logical router at Layer 3. This VSS routing instance fulfills this first-hop role without the need for a dedicated protocol. The VSS IP route is highly available due to MEC and the resiliency of the VSS system. VSS eliminates the need for FHRP at the aggregation layer of the data center.
QUESTION NO: 139
Which First Hop Redundancy Protocol is an IEEE Standard?
A. GLBP
B. HSRP
C. VRRP
D. OSPF
Answer: C
QUESTION NO: 140
What is the default amount by which the hot standby priority for the router is decremented or incremented when the interface goes down or comes back up?
A. 1
B. 5
C. 10
D. 15
Answer: C
The standby track interface configuration command ties the router hot standby priority to the availability of its interfaces and is useful for tracking interfaces that are not configured for HSRP. When a tracked interface fails, the hot standby priority on the device on which tracking has been configured decreases by 10. If an interface is not tracked, its state changes do not affect the hot standby priority of the configured device. For each interface configured for hot standby, you can configure a separate list of interfaces to be tracked.