
نمونه سوالات آزمون
Implementing Cisco IP Switched Networks - exam 300-115
Topic 1, Layer 2 Technologies
QUESTION NO: 21
A network engineer deployed a switch that operates the LAN base feature set and decides to use the SDM VLAN template. The SDM template is causing the CPU of the switch to spike during peak working hours. What is the root cause of this issue?
A. The VLAN receives additional frames from neighboring switches.
B. The SDM VLAN template causes the MAC address-table to overflow.
C. The VLAN template disables routing in hardware.
D. The switch needs to be rebooted before the SDM template takes effect.
Answer: C
Explanation:
SDM Template Notes:
Choosing the VLAN template will actually disable routing (number of entry for unicast or multicast route is zero) in hardware.
QUESTION NO: 22
An access switch has been configured with an EtherChannel port. After configuring SPAN to monitor this port, the network administrator notices that not all traffic is being replicated to the management server. What is a cause for this issue?
A. VLAN filters are required to ensure traffic mirrors effectively.
B. SPAN encapsulation replication must be enabled to capture EtherChannel destination traffic.
C. The port channel can be used as a SPAN source, but not a destination.
D. RSPAN must be used to capture EtherChannel bidirectional traffic.
Answer: C
Explanation:
A source port or EtherChannel is a port or EtherChannel monitored for traffic analysis. You can configure both Layer 2 and Layer 3 ports and EtherChannels as SPAN sources. SPAN canmonitor one or more source ports or EtherChannels in a single SPAN session. You can configure ports or EtherChannels in any VLAN as SPAN sources. Trunk ports or EtherChannels can be configured as sources and mixed with nontrunk sources. A port-channel interface (an EtherChannel) can be a SPAN source, but not a destination.
QUESTION NO: 23
Refer to the exhibit.
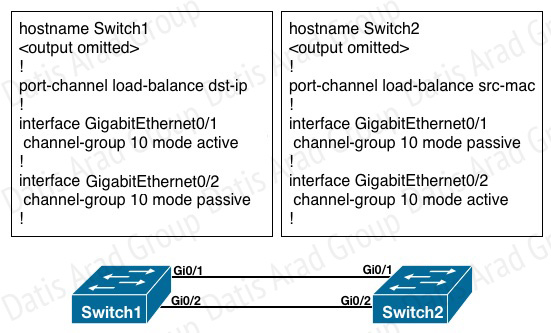 What is the result of the configuration?
What is the result of the configuration?
A. The EtherChannels would not form because the load-balancing method must match on the devices.
B. The EtherChannels would form and function properly even though the load-balancing and EtherChannel modes do not match.
C. The EtherChannels would form, but network loops would occur because the load-balancing methods do not match.
D. The EtherChannels would form and both devices would use the dst-ip load-balancing method because Switch1 is configured with EtherChannel mode active.
Answer: B
Explanation:
An etherchannel will form if one end is active and the other is passive.
QUESTION NO: 24
A network engineer tries to configure storm control on an EtherChannel bundle. What is the result of the configuration?
A. The storm control settings will appear on the EtherChannel, but not on the associated physical ports.
B. The configuration will be rejected because storm control is not supported for EtherChannel.
C. The storm control configuration will be accepted, but will only be present on the physical interfaces.
D. The settings will be applied to the EtherChannel bundle and all associated physical interfaces.
Answer: D
Explanation:
After you configure an EtherChannel, any configuration that you apply to the port-channel interface affects the EtherChannel; any configuration that you apply to the physical interfaces affects only the interface where you apply the configuration.
Storm Control is an exception to this rule. For example, you cannot configure Storm Control on some of the members of an EtherChannel; Storm Control must be configured on all or none of the ports. If you configure Storm Control on only some of the ports, those ports will be dropped from the EtherChannel interface (put in suspended state). Therefore, you should configure Storm Control at the EtherChannel Interface level, and not at the physical interface level.
QUESTION NO: 25
What is the function of NSF?
A. forward traffic simultaneously using both supervisors
B. forward traffic based on Cisco Express Forwarding
C. provide automatic failover to back up supervisor in VSS mode
D. provide nonstop forwarding in the event of failure of one of the member supervisors
Answer: D
Explanation:
VSS is network system virtualization technology that pools multiple Cisco Catalyst 6500 Series Switches into one virtual switch, increasing operational efficiency, boosting nonstop communications, and scaling system bandwidth capacity to 1.4 Tbps. Switches would operate as a single logical virtual switch called a virtual switching system 1440 (VSS1440). VSS formed by two Cisco Catalyst 6500 Series Switches with the Virtual Switching Supervisor 720-10GE. In a VSS, the data plane and switch fabric with capacity of 720 Gbps of supervisor engine in each chassis are active at the same time on both chassis, combining for an active 1400-Gbps switching capacity per VSS. Only one of the virtual switch members has the active control plane. Both chassis are kept in sync with the inter-chassis Stateful Switchover (SSO) mechanism along with Nonstop Forwarding (NSF) to provide nonstop communication even in the event of failure of one of the member supervisor engines or chassis.
QUESTION NO: 26
After UDLD is implemented, a Network Administrator noticed that one port stops receiving UDLD packets. This port continues to reestablish until after eight failed retries. The port then transitions into the errdisable state. Which option describes what causes the port to go into the errdisable state?
A. Normal UDLD operations that prevent traffic loops.
B. UDLD port is configured in aggressive mode.
C. UDLD is enabled globally.
D. UDLD timers are inconsistent.
Answer: B
Explanation:
With UDLD aggressive mode enabled, when a port on a bidirectional link that has a UDLD neighbor relationship established stops receiving UDLD packets, UDLD tries to reestablish the connection with the neighbor. After eight failed retries, the port is disabled.
QUESTION NO: 27
After reviewing UDLD status on switch ports, an engineer notices that the." Which statement describes what this indicates about the status of the port?
A. The port is fully operational and no known issues are detected.
B. The bidirectional status of "unknown" indicates that the port will go into the disabled state because it stopped receiving UDLD packets from its neighbor.
C. UDLD moved into aggressive mode after inconsistent acknowledgements were detected.
D. The UDLD port is placed in the "unknown" state for 5 seconds until the next UDLD packet is received on the interface.
Answer: A
Explanation:
By default, UDLD is disabled on all interfaces. We can enable UDLD globally on the device, or individually on specific interfaces with the command udld port. This enables UDLD in normal mode.
It would be prohibitively difficult to coordinate the configuration of UDLD on both ends of a link at the same time, so when UDLD is first enabled and does not detect a neighbor the link state is considered unknown, which is not necessarily an error condition. The port will remain operational during this time. When UDLD is finally enabled on the other end, the status will transitionto bidirectional.
QUESTION NO: 28
Pilot testing of the new switching infrastructure finds that when the root port is lost, STP immediately replaces the root port with an alternative root port. Which spanning-tree technology is used to accomplish backup root port selection?
A. PVST+
B. PortFast
C. BackboneFast
D. UplinkFast
E. Loop Guard
F. UDLD
Answer: D
Explanation:
If a switch loses connectivity, it begins using the alternate paths as soon as the spanning tree selects a new root port. By enabling UplinkFast with the spanning-tree uplinkfast global configuration command, you can accelerate the choice of a new root port when a link or switch fails or when the spanning tree reconfigures itself. The root port transitions to the forwarding state immediately without going through the listening and learning states, as it would with the normal spanning-tree procedures.
UplinkFast provides fast convergence after a direct link failure and achieves load balancing between redundant Layer 2 links using uplink groups. An uplink group is a set of Layer 2 interfaces (per VLAN), only one of which is forwarding at any given time. Specifically, an uplink group consists of the root port (which is forwarding) and a set of blocked ports, except for selflooping ports. The uplink group provides an alternate path in case the currently forwarding link fails.
QUESTION NO: 29
A network engineer must adjust the STP interface attributes to influence root port selection. Which two elements are used to accomplish this? (Choose two.)
A. port-priority
B. cost
C. forward-timers
D. link type
E. root guard
Answer: A,B
Explanation:
Spanning tree forces redundant data paths into a standby (blocked) state. If a network segment in the spanning tree fails and a redundant path exists, the spanning-tree algorithm recalculates the spanning-tree topology and activates the standby path. Switches send and receive spanning-tree frames, called bridge protocol data units (BPDUs), at regular intervals. The switches do not forward these frames but use them to construct a loop-free path. BPDUs contain informationabout the sending switch and its ports, including switch and MAC addresses, switch priority, port priority, and path cost. Spanning tree uses this information to elect the root switch and root port for the switched network and the root port and designated port for each switched segment.
When two ports on a switch are part of a loop, the spanning-tree port priority and path cost settings control which port is put in the forwarding state and which is put in the blocking state. The spanning-tree port priority value represents the location of a port in the network topology and how well it is located to pass traffic. The path cost value represents the media speed.
QUESTION NO: 30
A network engineer must set the load balance method on an existing port channel. Which action must be done to apply a new load balancing method?
A. Configure the new load balancing method using port-channel load-balance.
B. Adjust the switch SDM back to "default".
C. Ensure that IP CEF is enabled globally to support all load balancing methods.
D. Upgrade the PFC to support the latest load balancing methods.
Answer: A
Explanation:
EtherChannel balances the traffic load across the links in a channel through the reduction of part of the binary pattern that the addresses in the frame form to a numerical value that selects one of the links in the channel. EtherChannel load balancing can use MAC addresses or IP addresses, source or destination addresses, or both source and destination addresses. The mode applies to all EtherChannels that are configured on the switch. You configure the load balancing and forwarding method with use of the port-channel load-balance {dst-ip | dst-mac | src-dst-ip | srcdst- mac | src-ip | src-mac} global configuration command.
QUESTION NO: 31
Refer to the exhibit.
 A network engineer investigates a recent network failure and notices that one of the interfaces on the switch is still down. What is causing the line protocol on this interface to be shown as down?
A network engineer investigates a recent network failure and notices that one of the interfaces on the switch is still down. What is causing the line protocol on this interface to be shown as down?
A. There is a layer 1 physical issue.
B. There is a speed mismatch on the interface.
C. The interface is configured as the target of the SPAN session.
D. The interface is configured as the source of the SPAN session.
E. There is a duplex mismatch on the interface.
Answer: C
Explanation:
With the SAPN destination port, the state of the destination port is up/down by design. The interface shows the port in this state in order to make it evident that the port is currently not usable as a production port. This is the normal operational state for SPAN destinations.
QUESTION NO: 32
While doing network discovery using Cisco Discovery Protocol, it is found that rapid error tracking is not currently enabled. Which option must be enabled to allow for enhanced reporting mechanisms using Cisco Discovery Protocol?
A. Cisco Discovery Protocol version 2
B. Cisco IOS Embedded Event Manager
C. logging buffered
D. Cisco Discovery Protocol source interface
E. Cisco Discovery Protocol logging options
Answer: A
Explanation:
• CDP Version 1 — This is the first version of CDP which was used for the discovery of Cisco devices in the network. This version is mainly used for backward compatibility.
• CDP Version 2 — This is the most recent version of CDP which has enhanced features such as rapid reporting mechanism, which is used to track down errors and minimize costly downtime. It allows you to track instances even if the native VLAN ID or port duplex states do not match between connecting devices. This is the default version on all switches.
QUESTION NO: 33
Which technique allows specific VLANs to be strictly permitted by the administrator?
A. VTP pruning
B. transparent bridging
C. trunkallowed VLANs
D. VLAN access-list
E. L2P tunneling
Answer: C
Explanation:
By default, a trunk port sends traffic to and receives traffic from all VLANs. All VLAN IDs, 1 to 4094, are allowed on each trunk. However, you can remove VLANs from the allowed list, preventing traffic from those VLANs from passing over the trunk. To restrict the traffic a trunk carries, use the “switchport trunk allowed vlan remove vlan-list” interface configuration command to remove specific VLANs from the allowed list.
QUESTION NO: 34
For security reasons, the IT manager has prohibited users from dynamically establishing trunks with their associated upstream switch. Which two actions can prevent interface trunking? (Choose two.)
A. Configure trunk and access interfaces manually.
B. Disable DTP on a per interface basis.
C. Apply BPDU guard and BPDU filter.
D. Enable switchport block on access ports.
Answer: A,B
Explanation:
The Dynamic Trunking Protocol (DTP) is used to negotiate forming a trunk between two Cisco devices. DTP causes increased traffic, and is enabled by default, but may be disabled. To disable DTP, configure “switchport nonegotiate.” This prevents the interface from generating DTP frames. You can use this command only when the interface switchport mode is access or trunk. You must manually configure the neighboring interface as a trunk interface to establish a trunk link, otherwise the link will be a non-trunking link.
QUESTION NO: 35
Which two protocols can be automatically negotiated between switches for trunking? (Choose two.)
A. PPP
B. DTP
C. ISL
D. HDLC
E. DLCI
F. DOT1Q
Answer: C,F
Explanation:
Switches such as the Catalyst 3550 that are capable of either 802.1Q or ISL trunking encapsulation, the switchport trunk encapsulation [dot1q | isl | negotiate] interface command must be used prior to the switchport mode trunk command.
QUESTION NO: 36
A network is running VTPv2. After verifying all VTP settings, the network engineer notices that the new switch is not receiving the list of VLANs from the server. Which action resolves this problem?
A. Reload the new switch.
B. Restart the VTP process on the new switch.
C. Reload the VTP server.
D. Verify connected trunk ports.
Answer: D
Explanation:
VTP should never need to have the switch reloaded or the VTP process to restart in order for it to work. The first thing that should be done is to verify that the trunk ports are connected and up.
QUESTION NO: 37
After configuring new data VLANs 1020 through 1030 on the VTP server, a network engineer notices that none of the VTP clients are receiving the updates. What is the problem?
A. The VTP server must be reloaded.
B. The VTP version number must be set to version 3.
C. After each update to the VTP server, it takes up to 4 hours propagate.
D. VTP must be stopped and restarted on the server.
E. Another switch in the domain has a higher revision number than the server.
Answer: B
Explanation:
VTP version 3 supports these features that are not supported in version 1 or version 2:
• Enhanced authentication—You can configure the authentication as hidden or secret. When hidden, the secret key from the password string is saved in the VLAN database file, but it does not appear in plain text in the configuration. Instead, the key associated with the password is saved in hexadecimal format in the running configuration. You must reenter the password if you enter a takeover command in the domain. When you enter the secret keyword, you can directly configure the password secret key.
• Support for extended range VLAN (VLANs 1006 to 4094) database propagation. VTP versions 1 and 2 propagate only VLANs 1 to 1005. If extended VLANs are configured, you cannot convert from VTP version 3 to version 1 or 2.
QUESTION NO: 38
A network engineer is extending a LAN segment between two geographically separated data centers. Which enhancement to a spanning-tree design prevents unnecessary traffic from crossing the extended LAN segment?
A. Modify the spanning-tree priorities to dictate the traffic flow.
B. Create a Layer 3 transit VLAN to segment the traffic between the sites.
C. Use VTP pruning on the trunk interfaces.
D. Configure manual trunk pruning between the two locations.
Answer: C
Explanation:
Pruning unnecessary VLANs from the trunk can be performed with one of two methods:
• Manual pruning of the unnecessary VLAN on the trunk—This is the best method, and it avoids the use of the spanning tree. Instead, the method runs the pruned VLAN on trunks.
• VTP pruning—Avoid this method if the goal is to reduce the number of STP instances. VTPpruned VLANs on a trunk are still part of the spanning tree. Therefore, VTP-pruned VLANs do not reduce the number of spanning tree port instances.
Since the question asked for the choice that is an enhancement to the STP design, VTP pruning is the best choice.
QUESTION NO: 39
The network manager has requested that several new VLANs (VLAN 10, 20, and 30) are allowed to traverse the switch trunk interface. After the command switchport trunk allowed vlan 10,20,30 is issued, all other existing VLANs no longer pass traffic over the trunk. What is the root cause of the problem?
A. The command effectively removed all other working VLANs and replaced them with the new VLANs.
B. VTP pruning removed all unused VLANs.
C. ISL was unable to encapsulate more than the already permitted VLANs across the trunk.
D. Allowing additional VLANs across the trunk introduced a loop in the network.
Answer: A
Explanation:
The “switchport trunk allowed vlan” command will only allow the specified VLANs, and overwrite any others that were previously defined. You would also need to explicitly allow the other working VLANs to this configuration command, or use the “issue the switchport trunkallowed vlan add vlanlist” command instead to add these 3 VLANS to the other defined allowed VLANs.
QUESTION NO: 40
When you design a switched network using VTPv2, how many VLANs can be used to carry user traffic?
A. 1000
B. 1001
C. 1024
D. 2048
E. 4095
F. 4096
Answer: B
Explanation:
VTP versions 1 and 2 Supports normal VLAN numbers (1-1001). Only VTP version 3 supports extended VLANs (1-4095).